المُلخص التنفيذي
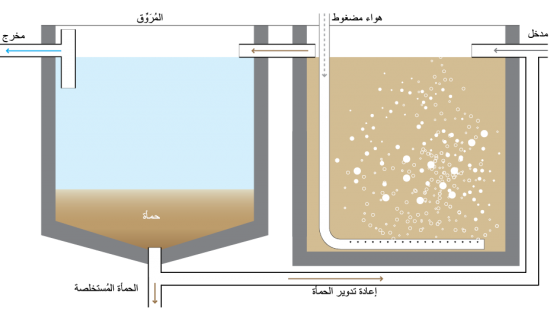
عملية الحمأة المُنشطة Activated Sludge تُشير إلى وحدة مُعالجة تتكون من مُفاعل مُتعدد الغُرَف، والذي يتَستخدم الكائنات الحيَّة الدقيقة المُركزة لتحلل المواد العضوية، ولإزالة المُغذيات من مياه الصرف؛ وذلك من أجل إنتاج تدفقات سائلة خارجة عالية الجودة. وللحفاظ على الظروف الهوائية، ولإبقاء الحمأة النشطة مُعلّقة، فإن إمدادت الأكسجين المُستمرة والمنتظمة مطلوبة.
يُمكن استخدام العديد من التجهيزات المختلفة لعملية الحمأة المُنشطة لضمان مزج وتهوية مياه الصرف جيدًا في حَوْض التهوية، ويُمكن القيام بعمليتي التهوية والمزج عن طريق ضخ الهواء أو الأكسجين إلى الخزَّان، أو باستخدام أجهزة التهوية السطحية. تُؤكسد الكائنات الحية الدقيقة الكربون العضوي الموجود في مياه الصرف، مما يؤدي إلى إنتاج خلايا جديدة، وثاني أكسيد الكربون والماء. على الرغم من أن البكتريا الهوائية هي الكائنات الحية الأكثر تواجدًا داخل المُفاعل، فإن البكتريا الاختيارية Facultative Bacterial -بالإضافة إلى بعض الكائنات الحية الأكبر- ممكن أن تتواجد. التكوين الفعلي لمحتوى المُفاعل يعتمد على التصميم، والبيئة، وخصائص مياه الصرف.
الندف (تكتلات من جزيئات الحمأة النشطة) التي تكونت في حَوْض التهوية، يُمكن إزالتها في المُرَوِّق الثانوي، وذلك عن طريق الترسيب الطبيعى المُعتمد على الجاذبية الأرضية. يتم إعادة تدوير جزء من هذه الحمأة من المُرَوّقات إلى المُفاعل مرة أخرى. يُمكن تصريف التدفقات السائلة الخارجة أو مُعالجتها في مُنشأة مُعالجة ثلاثية إذا لزم الأمر لاستخدامها فيما بعد.
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
| النفايات السائلة، المياه السوداء،المياه البُنّية، المياه الرمادية. |
الحمأة، النفايات السائلة |
المُلاءَمَة
اعتبارات التصميم
الجوانب الصحية/ القبول
بسبب متطلبات المساحة ومشاكل الروائح، تقع مرافق المُعالجة المركزية على أطراف المناطق ذات الكثافة السكانية العالية. على الرغم من أن جودة التدفقات السائلة الخارجة المُنتجة تكون عالية، فإنها لا تزال تشكل خطرًا على الصحة، وينبغي ألا يتم التعامل معها مباشرة. في الحمأة الزائدة يكون هناك انخفاض كبير لمسببات الأمراض، ولكن لا يتم القضاء عليها نهائيًّا.
التشغيل والصيانة
برنامج المسار الوظيفي للعاملين بقطاع مياه الشرب والصرف الصحي
كراس استرشادى عن ادارة المخلفات السائلة للانشطة الخدمية محطات الصرف الصحى ووحدات المعالجة فى المؤسسات الصحية
المعالجة البيولوجية لمياة الصرف الصحى فى محطات المعالجة
المعالجة البيولوجية لمياه الصرف الصحى المبادئ وأعمال النمذجة والتصميم
Language: Arabic
Managing the other side of the Water Cycle - Making Wastewater an Asset
Schematic view of an activated WWTP using the Sequencing Batch Reactor
Activated Sludge Process
Small and Decentralized Wastewater Management Systems
Decentralised wastewater management presents a comprehensive approach to the design of both conventional and innovative systems for the treatment and disposal of wastewater or the reuse of treaded effluent. Smaller treatment plants, which are the concern of most new engineers, are the primary focus of this book.
CRITES, R. TCHOBANOGLOUS, G. (1998): Small and Decentralized Wastewater Management Systems. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies IncGuide to Instrumentation in Wastewater
Mechanisms involved in Biological Phosphorus removal
Possibilities and Limits of Wastewater-fed Aquaculture
At the University of Applied Sciences Waedenswil, Switzerland, wastewater-fed aquaculture is a research focus since 1993. This paper summarises some of the results and insights gained since then.
JUNGE-BERBEROVIC, R. University of Applied Sciences Waedenswil. (2001): Possibilities and Limits of Wastewater-fed Aquaculture. Waedenswil: University of Applied Sciences Waedenswil URL [Accessed: 19.02.2010]Appropriate Technology for Municipal Sewerage/Excreta Management in Developing Countries, Thailand Case Study
Assessment of the appropriateness of activated sludge for Thailand.
LUDWIG, H. F. ; MOHIT, K. (2000): Appropriate Technology for Municipal Sewerage/Excreta Management in Developing Countries, Thailand Case Study. المُدخلات: The Environmentalist: Volume 20 , 215-219. URL [Accessed: 19.08.2014]Nutrients in urine: energetic aspects of removal and recovery
The analysis of different removal and recovery techniques for nutrients in urine shows that in many cases recovery is energetically more efficient than removal and new production from natural resources.
MAURER, M. ; SCHWEGLER, T. ; SCHWEGLER, P. ; LARSEN, T.A. (2003): Nutrients in urine: energetic aspects of removal and recovery. المُدخلات: Water Science and Technology 8: Volume 1 , 37-46.Community-Based Technologies for Domestic Wastewater Treatment and Reuse- options for urban agriculture
The report suggests that emerging trends in low-cost, decentralised naturally-based infrastructure and urban wastewater management which promote the recovery and reuse of wastewater resources are increasingly relevant. Technologies for these sanitation options are presented. The concept of managing urban wastewater flows at a decentralised or "intermediate" level, based on micro watersheds, is explored. Effluent treatment standards that are currently accepted in order to protect public health and safety are reviewed.
ROSE, D.G. (1999): Community-Based Technologies for Domestic Wastewater Treatment and Reuse- options for urban agriculture. (= Cities Feeding People (CFP) Report Series. , 27 ). Ottawa: International Development Research Center Canada (IDRC) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2018]Informed Choice Catalogue
This informed choice catalogue for community based wastewater treatment technologies helps to identify suitable sanitation options and facilitates the assessment of different sanitation system components with regard to stakeholder preferences. A powerful tool for technical bottom-up planning giving overall information about technical options at a "glance".
SANIMAS (2005): Informed Choice Catalogue. pdf presentation. BORDA and USAID URL [Accessed: 29.05.2019]Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions Volume 2
Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions gives a state-of-the-art presentation of the science and technology of biological wastewater treatment, particularly domestic sewage. The book covers the main treatment processes used worldwide with wastewater treatment in warm climate regions given a particular emphasis where simple, affordable and sustainable solutions are required. The 55 chapters are divided into 7 parts over two volumes: Volume One (also available in the SSWM library): Introduction to wastewater characteristics, treatment and disposal; Basic principles of wastewater treatment; Stabilisation ponds; Anaerobic reactors; Volume Two: Activated sludge; Aerobic biofilm reactors; Sludge treatment and disposal.
SPERLING, M. von LEMOS CHERNICHARO, C.A. de (2005): Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions Volume 2. London: International Water Association (IWA) Publishing URL [Accessed: 26.05.2019]Wastewater Engineering, Treatment and Reuse
Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFCompendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., LUETHI, C., MOREL, A., ZURBRUEGG, C. and SCHERTENLEIB, R. (2008): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (EAWAG) and Water Supply and Sanitation Collaborative Council (WSSCC) URL [Accessed: 15.02.2010] PDFSequencing Batch Reactors
Technical factsheet on the design, application, performance and operation of sequencing batch reactors (SBRs), a type of activated sludge wastewater treatment plants. English, Spanish
U.S. EPA (1999): Sequencing Batch Reactors. (= Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet, EPA 832-F-99-073 ). United States Environment Protection Agency (U.S. EPA)Oxidation Ditches
Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems Manual
Rather old design manual for onsite wastewater treatment options. However, valuable information on established systems such as septic tanks, sand filters, aerobic treatment units (suspended growth and fixed film), disinfection, nutrient removal as well as wastewater segregation and recycling are given. Additional information is given on disposal methods and appurtenances.
U.S.EPA (1980): Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems Manual. (= EPA 625/1-80 , 12 ). United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water Office of Research and DevelopmentA Directory of Environmentally Sound Technologies for the Integrated Management of Solid, Liquid and Hazardous Waste for SIDS in the Caribbean Region
This directory is part of UNEP collaboration with SIDS on the implementation of the Waste Management chapter of the Barbados Programme of Action. It focuses primarily on proven sound environmental technologies for solid, liquid and hazardous waste management plus those currently successfully being used in SIDS within the Caribbean Region.
UNEP (2004): A Directory of Environmentally Sound Technologies for the Integrated Management of Solid, Liquid and Hazardous Waste for SIDS in the Caribbean Region. Nairobi: United Nations Environment Programme Global Programme of Action (UNEP-GPA)) and Caribbean Environmental Health Institute (CEHI) URL [Accessed: 04.08.2023] PDFEnvironmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment for the implementation of the UNEP/GPA "Guidelines on Municipal Wastewater Management"
Technical information on environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment.
UNEP ; MURDOCH UNIVERSITY (2004): Environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment for the implementation of the UNEP/GPA "Guidelines on Municipal Wastewater Management". The Hague: United Nations Environment Programme Global Programme of Action (UNEP/GPA), Coordination OfficeSewage treatment in a deep shaft activated sludge system
Ecological Sanitation - revised and enlarged edition
This book is one of the most fundamental and important books that defined the concept of ecological sanitation. The first version came out in 1998 - this version presents the findings of over ten years of research and development in ecological sanitation supported by SIDA (Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency).
WINBLAD, U. SIMPSON-HERBERT, M. (2004): Ecological Sanitation - revised and enlarged edition. (pdf presentation). Sweden: Stockholm Environment Institute URL [Accessed: 04.08.2010]Belebtschlammverfahren
Language: Spanish
Ecological Sanitation - revised and enlarged edition
This book is one of the most fundamental and important books that defined the concept of ecological sanitation. The first version came out in 1998 - this version presents the findings of over ten years of research and development in ecological sanitation supported by SIDA (Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency).
WINBLAD, U. SIMPSON-HERBERT, M. (2004): Ecological Sanitation - revised and enlarged edition. (pdf presentation). Sweden: Stockholm Environment Institute URL [Accessed: 04.08.2010]Philippines Sanitation Source Book and Decision Aid
This Sanitation Sourcebook distils some of the core concepts of sanitation in a user-friendly format so that the book can serve as a practical reference to sanitation professionals and investment decision-makers, particularly the local governments. The annexe contains a practical collection of factsheets on selected sanitation system options.
WSP (2007): Philippines Sanitation Source Book and Decision Aid. pdf presentation. Washington: Water and Sanitation Program (WSP). URL [Accessed: 01.06.2019]Technology Options for Urban Sanitation in India. A Guide to Decision-Making
These guidance notes are designed to provide state governments and urban local bodies with additional information on available technologies on sanitation. The notes also aid in making an informed choice and explain the suitability of approaches.
WSP (2008): Technology Options for Urban Sanitation in India. A Guide to Decision-Making. pdf presentation. New Delhi: Water and Sanitation Program (WSP) URL [Accessed: 03.06.2019]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFSmall and Decentralized Wastewater Management Systems
Decentralised wastewater management presents a comprehensive approach to the design of both conventional and innovative systems for the treatment and disposal of wastewater or the reuse of treaded effluent. Smaller treatment plants, which are the concern of most new engineers, are the primary focus of this book.
CRITES, R. TCHOBANOGLOUS, G. (1998): Small and Decentralized Wastewater Management Systems. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies IncSOS - Management of Sludges from On-Site Sanitation. Co-treatment of Faecal Sludge and Wastewater in Tropical Climates
This article provides operational and design guidance for the co-treatment of faecal sludge in waste stabilisation ponds and in activated sludge sewage treatment plants. Problems which may arise when highly concentrated faecal sludge is not properly included in the design of the co-treatment system are also discussed.
HEINSS, U. STRAUSS, M. (1999): SOS - Management of Sludges from On-Site Sanitation. Co-treatment of Faecal Sludge and Wastewater in Tropical Climates. Duebendorf and Accra: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG) URL [Accessed: 21.04.2010]Sustainable Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater contains organic matter and the three main nutrients for plant production: nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Nitrogen fertilizer is energy consuming to produce and phosphorus is a limited mineral resource. Scandinavia is pioneering sustainable solutions to wastewater treatment. Source separation (blackwater/greywater) systems produce almost zero emissions and open up exiting urban applications of sanitation options in order to close the loop.
JENSSEN, P.D. VRAALE, L. LINDHOLM, O. SENG, L. (2007): Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. المُدخلات: SENG, L. (2007): Proceedings of the International Conference on Natural Resources and Environmental Management and Environmental Safety and Health. Norway: .Nutrients in urine: energetic aspects of removal and recovery
The analysis of different removal and recovery techniques for nutrients in urine shows that in many cases recovery is energetically more efficient than removal and new production from natural resources.
MAURER, M. ; SCHWEGLER, T. ; SCHWEGLER, P. ; LARSEN, T.A. (2003): Nutrients in urine: energetic aspects of removal and recovery. المُدخلات: Water Science and Technology 8: Volume 1 , 37-46.Water Pollution Control - A Guide to the Use of Water Quality Management Principles
This document is rather old, but its publication was a milestone as it demonstrates WSSCCs capacity to bring together water and sanitation professionals from industrialised and developing countries to formulate practical guidance on a key issue of the day. Mainly regulatory, financial and technical aspects are discussed and illustrated with an extensive collection of case studies from the developing world.
HELMER, R. ; HESPANHOL, I. (1997): Water Pollution Control - A Guide to the Use of Water Quality Management Principles. World Health Organization (WHO), Water Supply and Sanitation Collaborative Council (WSSCC) and United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) URL [Accessed: 21.04.2010]Philippines Sanitation Source Book and Decision Aid
This Sanitation Sourcebook distils some of the core concepts of sanitation in a user-friendly format so that the book can serve as a practical reference to sanitation professionals and investment decision-makers, particularly the local governments. The annexe contains a practical collection of factsheets on selected sanitation system options.
WSP (2007): Philippines Sanitation Source Book and Decision Aid. pdf presentation. Washington: Water and Sanitation Program (WSP). URL [Accessed: 01.06.2019]Technology Options for Urban Sanitation in India. A Guide to Decision-Making
These guidance notes are designed to provide state governments and urban local bodies with additional information on available technologies on sanitation. The notes also aid in making an informed choice and explain the suitability of approaches.
WSP (2008): Technology Options for Urban Sanitation in India. A Guide to Decision-Making. pdf presentation. New Delhi: Water and Sanitation Program (WSP) URL [Accessed: 03.06.2019]Basic Principles of Wastewater Treatment
Basic Principles of Wastewater Treatment is the second volume in the series Biological Wastewater Treatment, and focusses on the unit operations and processes associated with biological wastewater treatment. The major topics covered are: microbiology and ecology of wastewater treatment, reaction kinetics and reactor hydraulics, conversion of organic and inorganic matter, sedimentation, aeration.
SPERLING, M. von (2007): Basic Principles of Wastewater Treatment. (= Biological Wastewater Treatment Series , 2 ). London: International Water Association (IWA) Publishing URL [Accessed: 26.05.2019]Activated Sludge and Aerobic Biofilm Reactors
Activated Sludge and Aerobic Biofilm Reactors is the fifth volume in the series Biological Wastewater Treatment. The first part of the book is devoted to the activated sludge process, covering the removal of organic matter, nitrogen and phosphorus. A detailed analysis of the biological reactor (aeration tank) and the final sedimentation tanks is provided. The second part of the book covers aerobic biofilm reactors, especially trickling filters, rotating biological contractors and submerged aerated biofilters. For all the systems, the book presents in a clear and informative way the main concepts, working principles, expected removal efficiencies, design criteria, design examples, construction aspects and operational guidelines.
SPERLING, M. von (2007): Activated Sludge and Aerobic Biofilm Reactors. (= Biological Wastewater Treatment Series , 5 ). London: International Water Association (IWA) Publishing URL [Accessed: 03.06.2019]Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions Volume 2
Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions gives a state-of-the-art presentation of the science and technology of biological wastewater treatment, particularly domestic sewage. The book covers the main treatment processes used worldwide with wastewater treatment in warm climate regions given a particular emphasis where simple, affordable and sustainable solutions are required. The 55 chapters are divided into 7 parts over two volumes: Volume One (also available in the SSWM library): Introduction to wastewater characteristics, treatment and disposal; Basic principles of wastewater treatment; Stabilisation ponds; Anaerobic reactors; Volume Two: Activated sludge; Aerobic biofilm reactors; Sludge treatment and disposal.
SPERLING, M. von LEMOS CHERNICHARO, C.A. de (2005): Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions Volume 2. London: International Water Association (IWA) Publishing URL [Accessed: 26.05.2019]Wastewater Engineering, Treatment and Reuse
Box 4.2: Forest irrigation in Kaageroed
Case study from Sweden, describing forest irrigation as a final treatment step and reuse option for activated sludge effluents.
BODIK, I. RIDDERSTOLPE, P. (2008): Box 4.2: Forest irrigation in Kaageroed. المُدخلات: BODIK, I. ; RIDDERSTOLPE, P. (2008): Sustainable sanitation in Central and Eastern Europe - addressing the needs of small and medium-size settlements. Stockholm: 68 . URL [Accessed: 21.04.2010]Opportunities in Fecal Sludge Management for Cities in Developing Countries: Experiences from the Philippines
In July 2012, a team from RTI International deployed to the Philippines to evaluate four FSM programs with the goal of reporting on best practices and lessons learned. The four cases—Dumaguete City, San Fernando City, Maynilad Water for the west zone of metro Manila, and Manila Water from the east zone of metro Manila—were chosen to highlight their different approaches to implementing FSM.
ROBBINS, D. STRANDE, L. DOCZI, J. (2012): Opportunities in Fecal Sludge Management for Cities in Developing Countries: Experiences from the Philippines. North Carolina: RTI International URL [Accessed: 10.06.2019]Anaerobic Digestion of Blackwater and Kitchen Refuse
Thesis assessing the anaerobic treatment of blackwater (toilet wastewater) from vacuum toilets without and with kitchen refuse and its potential for reuse and resources management sanitation concepts.
WENDLAND, C. (2008): Anaerobic Digestion of Blackwater and Kitchen Refuse. (PhD Thesis). (= Hamburger Berichte zur Siedlungswasserwirtschaft ). Hamburg: Institut fuer Abwasserwirtschaft und Gewaesserschutz (AWW), Technische Universitaet Hamburg-Hamburg (TUHH) URL [Accessed: 11.03.2010]Design Manual - Onsite Wastewater Treatment and Disposal Systems
Rather old design manual for onsite wastewater treatment options. However, valuable information on established systems such as septic tanks, sandfilters, aerobic treatment units (suspendend growth and fixed film), disinfection, nutrient removal as well as wastewater segregation and recycling are given. Additional information is given on disposal methods and appurtenances.
U.S. EPA (1980): Design Manual - Onsite Wastewater Treatment and Disposal Systems. (= EPA 625/1-80-0 ). United States Environmental Protection Agency and Office of Water Office of Research and Development URL [Accessed: 27.05.2019]4.2.1 Activated sludge treatment
Oxidation Ditches
Sequencing Batch Reactors
Technical factsheet on the design, application, performance and operation of sequencing batch reactors (SBRs), a type of activated sludge wastewater treatment plants. English, Spanish
U.S. EPA (1999): Sequencing Batch Reactors. (= Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet, EPA 832-F-99-073 ). United States Environment Protection Agency (U.S. EPA)Course ENV149: Wastewater Treatment Plant Operation: Lesson 10: Secondary Treatment
The Mountain Empire Community College ‘Water and Wastewater Distance Learning Course’ makes available all its documentation on the web. This section describes secondary treatment systems, including trickling filters, rotating biological contactors, activated sludge, operation and control, stabilization ponds, aerated lagoons and intermittent sand filters.
MECC (n.y): Course ENV149: Wastewater Treatment Plant Operation: Lesson 10: Secondary Treatment. (= Mountain Empire Community College. Water and Wastewater Distance Learning ). Big Stone Gap: Mountain Empire Community College (MECC) URL [Accessed: 18.03.2010]Sustainable Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater contains organic matter and the three main nutrients for plant production: nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Nitrogen fertilizer is energy consuming to produce and phosphorus is a limited mineral resource. Scandinavia is pioneering sustainable solutions to wastewater treatment. Source separation (blackwater/greywater) systems produce almost zero emissions and open up exiting urban applications of sanitation options in order to close the loop.
JENSSEN, P.D. VRAALE, L. LINDHOLM, O. SENG, L. (2007): Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. المُدخلات: SENG, L. (2007): Proceedings of the International Conference on Natural Resources and Environmental Management and Environmental Safety and Health. Norway: .ecosan - A Possible Approach to Sustainable Sanitation And Food Security
This master thesis illustrates the history of conventional wastewater treatment and the shift in paradigm towards recycling-oriented systems.
NEUPANE, K. (2004): ecosan - A Possible Approach to Sustainable Sanitation And Food Security. (= Master Thesis ). University of Applied Science Nordostniedersachenhttp://en.wikipedia.org
General Wikipedia article on activated sludge systems.
http://web.deu.edu.tr/atiksu/ana52/ani406.html
Different material on activated sludge wastewater treatment systems available on the Tropak Hompage hosted by the Turkish Dokuz Eylul University in Izmir.
http://www.ademe.fr/partenaires/Boues/Pages/f14.htm
This page explains in a very short and comprehensive way how activated sludge processes are applied for municipal wastewater treatment in France.
