Executive Summary
Vacuum toilets are flush toilets that use suction for the removal of faeces and urine resulting in a minimal requirement of water (0.5 to 1.5 litres). Vacuum toilets provide the same level of comfort as traditional flush toilets and they help saving costs due to the minimised amount of flush water. Due to the fact that the effluent has a high organic matter content, vacuum toilets are specifically adapted for the use in combination with separate greywater and blackwater treatment; or aerobic digestion treatment for biogas production. Vacuum toilet systems are applicable both in large and small buildings, trains, ships and airplanes.
| In | Out |
|---|---|
(Freshwater), Blackwater, Faecal Sludge, Greywater, Brownwater, Urine or Yellowwater, Faeces, Excreta, Energy |
Blackwater, Faecal Sludge |
Introduction
The use of vacuum toilets provides a similar level of comfort as traditional flush toilets, but they use much less water due to air sucked into the toilet when flushing, thereby producing a vacuum. This results in a minimal requirement of water (0.5 to 1.5 litres) for the transport of faeces and urine (WHO 2006; ROEVAC 2011). The system is completely closed. Is there a leak, the negative pressure in the pipes reduces the risk of raw sewage spill (see also vacuum sewers) (WHO 2006). Vacuum toilets can be installed in single households, hotels, or whole communities and are also adapted for train, ships or airplanes. Due to the fact that the effluent has a high organic matter content, vacuum toilets are specifically adapted for the use in combination with separate greywater and blackwater treatment; or aerobic digestion treatment for biogas production. To minimise the water consumption of a vacuum toilet even more, urine diversion bowls can be applied (learn more about it: urine diversion components).
Basic Design Principles
Basically, there are two different designs for a vacuum toilet system: The constant vacuum system (CVS) and the vacuum on demand (VOD) system. Which one will be applied depends on specific framework conditions.
Constant Vacuum System (CVS)
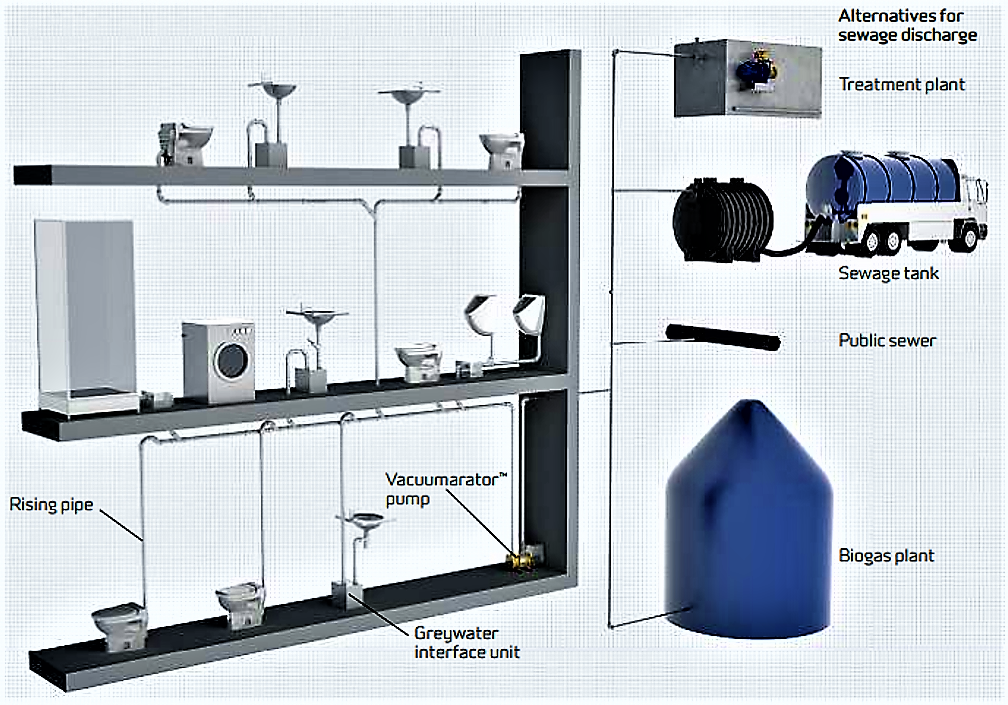
This is the better solution for larger buildings. Virtually, it is possible to add an unlimited number of toilets and the system can be expanded later on. If there is a permanent vacuum, the risk of a leakage is very low (JETSGROUP 2011). However, energy requirement are generally high in order to maintain the vacuum constantly. It depends on the manufacturer, but normally a constant vacuum system functions as follows (adapted from ROEVAC 2011):
Step 1: The user pushes the push-button, the interface valve is opened and the wastewater is evacuated. Air, which also helps to transport the waste, is also sucked into the system. At the same time, the clean water valve is opened and rinsing water is sprayed into the bowl.
Step 2: The vacuum valve is closed but the water valve remains open. A small amount of fresh water is sprayed into the bowl.
Step 3: The water valve is closed, a small volume of clean water is retained in the bowl and the toilet is ready for use again.
The collected blackwater can be discharged in different ways (JETSGROUP 2011):
- Semi-centralised treatment plant (e.g. free surface, horizontal or vertical constructed wetland)
- Biogas production (e.g. biogas settler)
- Sewage tank (which is emptied by a vacuum truck periodically)
- Public sewer system (e.g. conventional- or separate sewer)
Vacuum toilets systems are very favourable for source separation. In this case, greywater is collected in “greywater interface units” and is soaked away as soon as it is filled up.
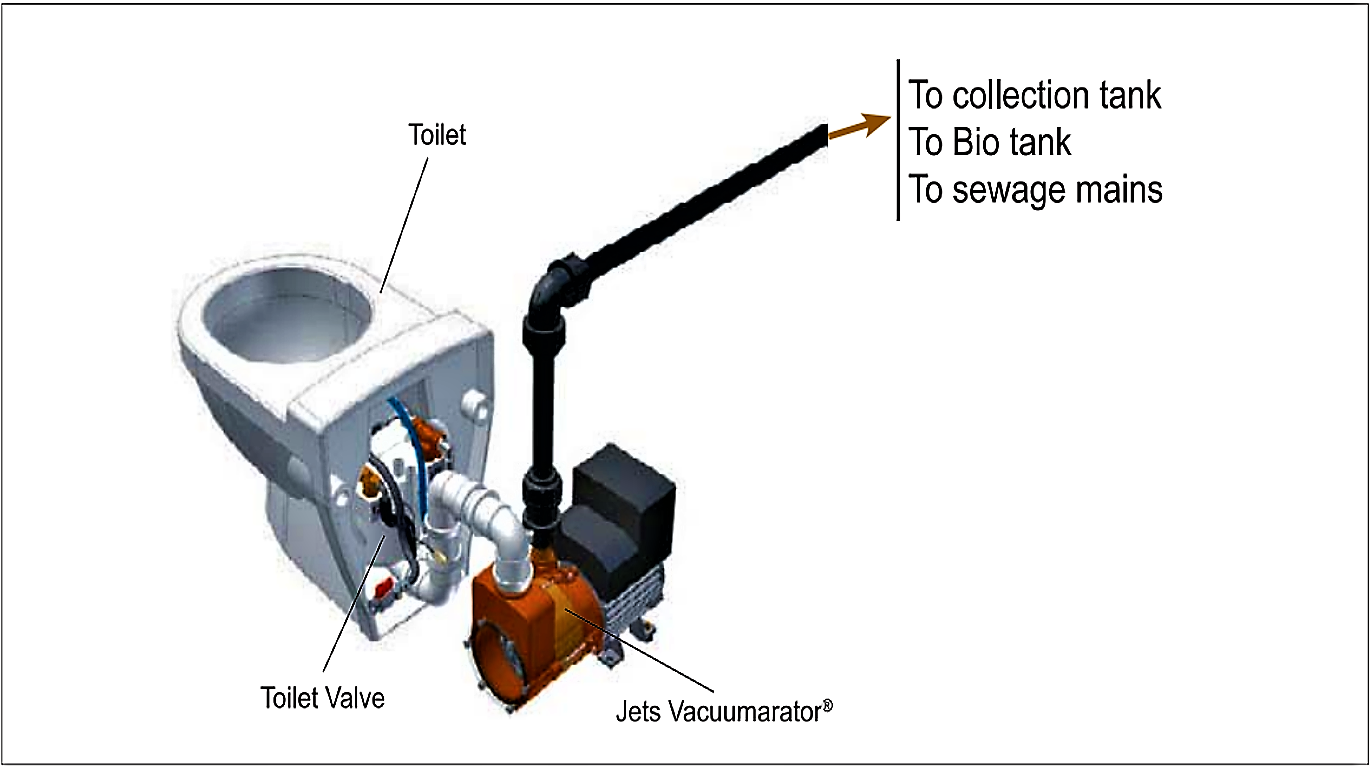
Vacuum On Demand (VOD)
(adapted from JETSGROUP 2005)
Vacuum on demand systems produce a vacuum only at the moment the toilet needs to be flushed. The system also uses air together with water for transport of sewage, as opposed to conventional flush toilets, which use water only. The VOD toilet evacuates air from the drainpipes automatically upon activation of the activator button. A valve opens in the toilet, and the difference in air pressure that results causes the sewage to be flushed.Due to lower energy requirement, small VOD systems can be solar powered.
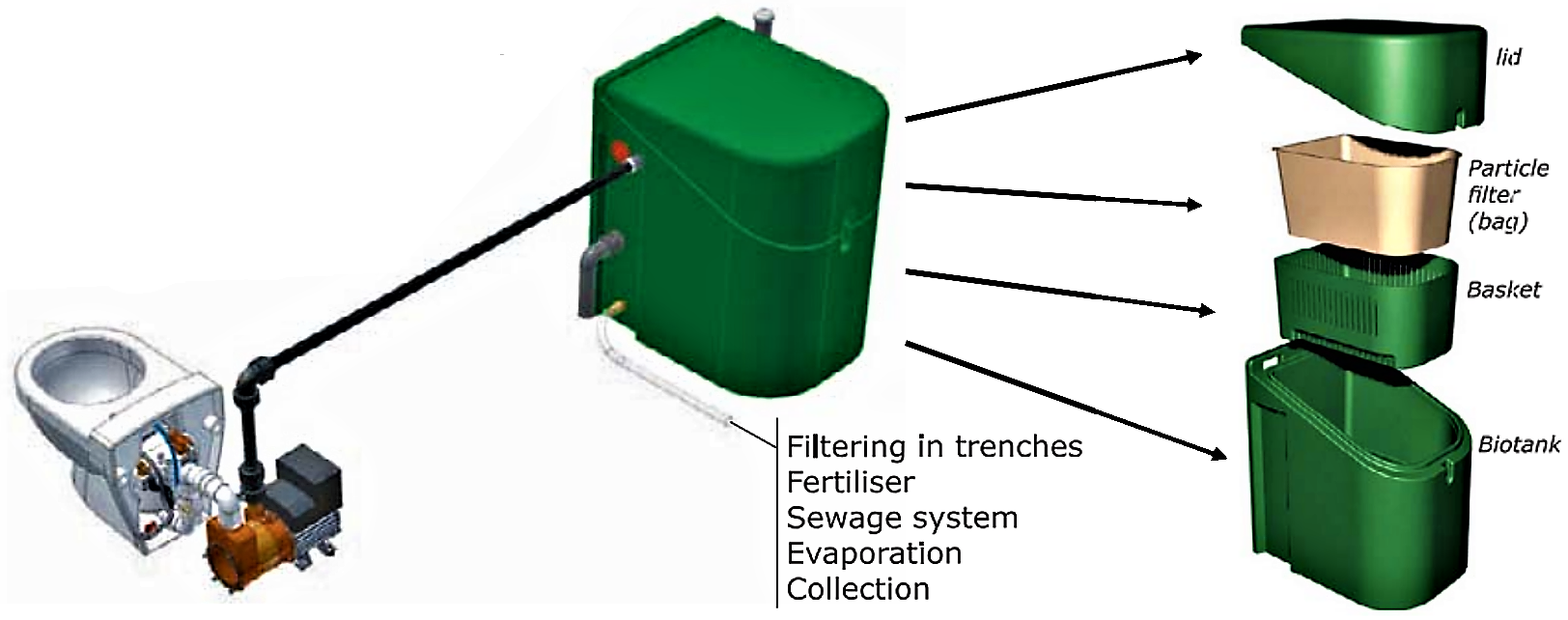
At the end of the vacuum pipes, “biotanks” can be made available to compost the already shredded waste on-site. Flushed sewage is pumped through a particle filter into the composting tank. As soon as it is full, it can be emptied and put aside for further composting (see also small-scale or large-scale co-composting. The liquid, which is collected at the bottom of the tank, can be infiltrated or used as fertiliser (see also leach field, soak pit, fertigation) (JETSGROUP 2005). Depending on the local standards and restrictions a secondary treatment may be required before discharge or reuse (see also non-planted filters; vertical, horizontal or free surface-flow constructed wetlands.
Costs Considerations
As it is a high-tech system, it is expensive. But in comparison with a common flush-toilet system, it can be slightly cheaper, because piping costs are lower (the dimensions are smaller, 50 to 75 mm) and a on-site treatment system can be more easily installed. Also the installation can be cheaper because piping is independent from the building structure. Vacuum lines may be installed vertically into the suspended ceiling as waste can be lifted.
Operation and Maintenance
The in-house installations require little maintenance and are easy to clean. The suction effect increases hygiene and reduces odour (HEEB et al. 2007). If a composting tank is used, it has to be emptied and cleaned periodically to avoid an overflow. If there are any problems with the technical components, such as valves or pipes, the manufacturer has to be contacted.
Health Aspects
A vacuum toilet system guarantees a high level of comfort and hygiene. As long as the toilet is kept clean, there are absolutely no hazards. When composting such products, special care should be taken as the associated health risk is higher than for common kitchen waste.
At a Glance
| Working Principle | Vacuum toilets are flush toilets that use a negative pressure (vacuum) to suck faeces away. |
| Capacity/Adequacy | A vacuum toilet system is designed for small cottage, large buildings and even trains, ships and planes. |
| Performance | If it is designed and constructed correctly performance is very reliable. |
| Costs | Costs are lower in comparison with a common flush-system |
| Self-help Compatibility | Low. Requires Installations through professionals. However, through the fact that pipes are much more flexible than conventional sewage pipes, and can be laid at a more shallow depth, reparations are easier than with other systems. |
| O&M | In-house installations are easy to clan and require little maintenance. Technical components should be maintained by professionals only. |
| Reliability | Very reliable. |
| Main strength | Saving significant quantities of water (only 0.5 to 1 litre required per flush) and allows a large flexibility for on-site treatment (independent of large sewer collection systems). |
| Main weakness | High costs and it needs expert design |
Vacuum technology for sanitary installations is an advanced technique in both economic and ecologic aspects. Its application is flexible and independent from a (natural) slope. New buildings as well as the sanitation of old buildings or the reconstruction of existing buildings are all appropriate fields of application. Vacuum sanitation systems are preferably used in buildings where the wastewater flow is high or varies greatly (hotels, restaurants, motorway services areas, airports, railway stations etc.), in bigger building complexes and in commercial and industrial halls, where the sanitary installations are often located at remote distances (adapted from ROEVAC 2011). Vacuum toilets are also a convenient solution for decentralised wastewater treatment. Effluents, such as urine and faeces can be treated by a biogas settler or a biotank with a following small scale composting attachment.
Sustainable Wastewater Management in Urban Areas
A document about sustainable wastewater management in urban areas.
JENSSEN, P.D. GREATOREX, J.M. WARNER, W. S. (2004): Sustainable Wastewater Management in Urban Areas. (= Kapitel 4. Kurs WH33, Konzeptionen dezentralisierter Abwasserreinigung und Stoffstrommanagement ). Hannover: University of HannoverGuidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume IV. Excreta and Greywater Use in Agriculture
Volume IV of the Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater recognizes the reuse potential of wastewater and excreta (including urine) in agriculture and describes the present state of knowledge as regards potential health risks associated with the reuse as well as measures to manage these health risks following a multi-barrier approach.
WHO (2006): Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume IV. Excreta and Greywater Use in Agriculture. Geneva: World Health Organisation (WHO) URL [Accessed: 09.05.2019] PDFInstruction Manual VOD
This manual includes explanations, installation tips and technical information about VOD vacuum toilets.
JETSGROUP (2005): Instruction Manual VOD. Hareid: Jets AS URL [Accessed: 13.05.2019]Jets Sanitary Systems - A Smarter, Greentech Solution for any Building
This PDF presentation explains the vacuum system for large buildings and includes a collection of case studies.
JETSGROUP (2009): Jets Sanitary Systems - A Smarter, Greentech Solution for any Building. (= PDF presentation ). Hareid: Jets AS. [Accessed: 07.03.2011] PDFAnnex: Overview of Conventional Wastewater Treatment Systems
Sustainable Wastewater Management in Urban Areas
A document about sustainable wastewater management in urban areas.
JENSSEN, P.D. GREATOREX, J.M. WARNER, W. S. (2004): Sustainable Wastewater Management in Urban Areas. (= Kapitel 4. Kurs WH33, Konzeptionen dezentralisierter Abwasserreinigung und Stoffstrommanagement ). Hannover: University of HannoverInstruction Manual VOD
This manual includes explanations, installation tips and technical information about VOD vacuum toilets.
JETSGROUP (2005): Instruction Manual VOD. Hareid: Jets AS URL [Accessed: 13.05.2019]Jets Sanitary Systems - A Smarter, Greentech Solution for any Building
This PDF presentation explains the vacuum system for large buildings and includes a collection of case studies.
JETSGROUP (2009): Jets Sanitary Systems - A Smarter, Greentech Solution for any Building. (= PDF presentation ). Hareid: Jets AS. [Accessed: 07.03.2011] PDFAnnex: Overview of Conventional Wastewater Treatment Systems
How to Manage Public Toilets and Showers
The purpose of this decision-making aid is to provide practical advice and recommendations for managing toilet blocks situated in public places. It is primarily aimed at local decision-makers in developing countries and at their partners (project planners and managers).
TOUBKISS, J. (2010): How to Manage Public Toilets and Showers. (= Six Methodological Guides for a Water and Sanitation Services' Development Strategy , 5 ). Cotonou and Paris: Partenariat pour le Développement Municipal (PDM) and Programme Solidarité Eau (pS-Eau) URL [Accessed: 19.10.2011]Urine Diversion Vacuum Sanitation System
Case study about an alternative sanitation system for urban buildings. A vacuum urine-diverting sewerage system is used to reduce potable water consumption and to reduce wastewater production.
GERMER, J. SuSanA (2009): Urine Diversion Vacuum Sanitation System. Beijing, China: Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) URL [Accessed: 13.05.2019]Vacuum Technology Systems
This website of Aqseptence Group contains all kinds of information about vacuum toilets and vacuum sewer systems. The systems are explained with animations and short articles.
Sustainable Vacuum Solutions
Jetsgroup produces sanitary vacuum systems in the sectors land & transport as well as ships and offshore. Downloads, case studies, animations and information about its products are available.
A Better Toilet For A Cleaner World
The sanitation technology paradigm is under review, as past approaches are not sufficient or affordable to close the sanitation coverage gap. In 2011, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) launched the bold Reinvent the Toilet Challenge (RTTC) program to promote the development of radically new innovations to address the sanitation challenge on a large-scale. The RTTC is premised on the fact that ground-breaking improvements are required in toilet design and fecal sludge management to close the urban sanitation gap. The RTTC is focused on reinventing the flush toilet, a break-through public health invention that has not changed substantially since the first flush toilet patent was issued in 1775.