Sanitation
- Hardware
- Software
- Sections
- Important Considerations
- Use and/or Disposal
- Sanitation Systems
- User Interface
- Collection and Storage / Treatment
- Conveyance
- (Semi-)centralised Treatment
Important Considerations
Sanitation in Prolonged Encampments
Use and/or Disposal
Urine Fertilisation (Large-scale)
Separately collected and hygienised urine is a concentrated source of nutrients which can be applied as a liquid fertilizer in agriculture to replace…
Fill and Cover / Arborloo
To decommission a pit, it can simply be filled with soil and covered. Although there is no received benefit, the full pit poses no immediate health…
Leach Field
A leach field, or drainage field, is a network of perforated pipes that are laid in underground gravel-filled trenches to dissipate the effluent from…
Soak Pit
A soak pit, also known as a soakaway or leach pit, is a covered, porous-walled chamber that allows water to slowly soak into the ground. Pre-settled…
Fish Pond (Aquaculture)
Fish can be grown in ponds that receive effluent or sludge where they can feed on algae and other organisms that grow in the nutrient-rich water. The…
Application of Dehydrated Faeces
When faeces are stored in the absence of moisture (i.e., urine), they [8251-dehydrate] into a crumbly, white-beige coarse, flaky material or powder.…
Application of Pit Humus and Compost
Compost is the soil-like substance resulting from the controlled aerobic degradation of organics. Pit humus is the term used to describe the material…
Floating Plant Pond
A floating plant pond is a modified maturation pond with floating (macrophyte) plants. Plants such as water hyacinths or duckweed float on the…
Irrigation
To reduce dependence on freshwater and maintain a constant source of water for irrigation throughout the year, wastewater of varying quality can be…
Water Disposal / Groundwater Recharge
Treated effluent and/or stormwater can be directly discharged into receiving water bodies (such as rivers, lakes, etc.) or into the ground to…
Surface Disposal and Storage
Surface disposal refers to the stockpiling of sludge, faeces or other materials that cannot be used elsewhere. Once the material has been taken to a…
Biogas Combustion
In principal, biogas can be used like other fuel gas. When produced in household-level [8221-biogas reactors], it is most suitable for cooking.…
Application of Sludge
Depending on the treatment type and quality, digested or stabilized sludge can be applied to public or private lands for landscaping or agriculture.
Sanitation Systems
System 1: Single Pit System
System 2: Waterless Pit System without Sludge Production
System 3: Pour Flush Pit System without Sludge Production
System 4: Waterless System with Urine Diversion
System 5: Biogas System
System 6: Blackwater Treatment System with Infiltration
System 7: Blackwater Treatment System with Effluent Transport
System 8: Blackwater Transport to (Semi-) Centralized Treatment System
User Interface
Urine-Diverting Dry Toilet (UDDT)
A urine-diverting dry toilet (UDDT) is a toilet that operates without water and has a divider so that the user, with little effort, can divert the…
Pour flush Toilet
A pour flush toilet is like a regular cistern flush toilet except that the water is poured in by the user, instead of coming from the cistern above.…
Cistern Flush Toilet
The cistern flush toilet is usually made of porcelain and is a mass-produced, factory-made user interface. The flush toilet consists of a water tank…
Urinal
An urinal is used only for collecting urine. Urinals are generally for men, although models for women have also been developed. Most urinals use…
Dry Toilet
A dry toilet is a toilet that operates without flushwater. The dry toilet may be a raised pedestal on which the user can sit, or a squat pan over…
Collection and Storage / Treatment
Anaerobic Filter
An anaerobic filter is a fixed-bed biological reactor with one or more filtration chambers in series. As wastewater flows through the filter,…
Anaerobic Baffled Reactor (ABR)
An anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR) is an improved [8217-septic tank] with a series of baffles under which the wastewater is forced to flow. The…
Septic Tank
A septic tank is a watertight chamber made of concrete, fibreglass, PVC or plastic, through which blackwater and greywater flows for primary…
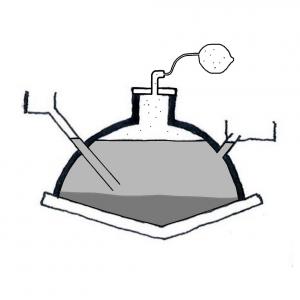
Anaerobic Digestion (Small-scale)
A small-scale biogas reactor or anaerobic digester is an anaerobic treatment technology that produces (a) a digested slurry (digestate) that can be…
Biogas Reactor
A biogas reactor or anaerobic digester is an anaerobic treatment technology that produces (a) a digested slurry (digestate) that can be used as a…
Double Ventilated Improved Pit (VIP)
The double VIP has almost the same design as the single VIP with the added advantage of a second pit that allows it to be used continuously and…
Dehydration and Storage
Dehydration by adding dry organic material and long-term storage at high ambient temperature is the simplest treatment in order to transform faeces…
Dehydration Vaults
Dehydration vaults are used to collect, store and dry (dehydrate) faeces. Faeces will only dehydrate when the vaults are well ventilated, watertight…
Twin Pits for Pour Flush
This technology consists of two alternating pits connected to a pour flush toilet. The blackwater (and in some cases greywater) is collected in the…
Urine Storage Tank / Container
When urine cannot be used immediately or transported using a conveyance technology (i.e. [8287-jerrycans]) it can be stored onsite in containers or…
Single Ventilated Improved Pit (VIP)
The single VIP is a ventilated improved pit. It is an improvement over the [8237-single pit] because continuous airflow through the ventilation pipe…
Conveyance
Human-powered Emptying and Transport
Human-powered emptying and transport refers to the different ways in which people can manually empty and/or transport sludge and solid products…
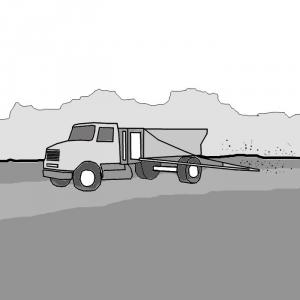
Motorised Emptying and Transport
Motorized emptying and transport refers to a vehicle equipped with a motorized pump and a storage tank for emptying and transporting faecal sludge…
Conventional Gravity Sewer
Conventional gravity sewers are large networks of underground pipes that convey blackwater, greywater and, in many cases, stormwater from individual…
Simplified Sewer
A simplified sewer describes a sewerage network that is constructed using smaller diameter pipes laid at a shallower depth and at a flatter gradient…
Transfer Station (Underground Holding Tank)
Transfer stations or underground holding tanks act as intermediate dumping points for faecal sludge when it cannot be easily transported to a (Semi…
Solids-free Sewer
A solids-free sewer is a network of small-diameter pipes that transports pre-treated and solids-free wastewater (such as septic tank effluent). It…
Jerrycan / Tank
Jerrycans are light, plastic containers that are readily available and can be easily carried by one person. When sealed, they can be used to safely…
(Semi-)centralised Treatment
Aerated Pond
An aerated pond is a large, mixed aerobic reactor. Mechanical aerators provide oxygen and keep the aerobic organisms suspended and mixed with water…
Waste Stabilization Ponds (WSP)
Waste Stabilization Ponds (WSPs) are large, man-made water bodies. The ponds can be used individually, or linked in a series for improved treatment.…
Anaerobic Filter
An anaerobic filter is a fixed-bed biological reactor with one or more filtration chambers in series. As wastewater flows through the filter,…
Anaerobic Baffled Reactor (ABR)
An anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR) is an improved [8217-septic tank] with a series of baffles under which the wastewater is forced to flow. The…
Trickling Filter
A trickling filter, is a fixed-bed, biological reactor that operates under (mostly) aerobic conditions. Pre-settled wastewater is continuously ‘…
Anaerobic Digestion (Large-Scale)
Large-scale anaerobic biogas digesters are reactors used for the conversion of the organic fraction of large volumes of slurries and sludge into…
Settler
A settler is a primary treatment technology for wastewater; it is designed to remove suspended solids by sedimentation. It may also be referred to as…
Unplanted Drying Beds
An unplanted drying bed is a simple, permeable bed that, when loaded with sludge, collects percolated leachate and allows the sludge to dry by…
Imhoff Tank
The Imhoff tank is a primary treatment technology for raw wastewater, designed for solid-liquid separation and digestion of the settled sludge. It…
Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland
A horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlandis a large gravel and sand-filled basin that is planted with wetland vegetation. As wastewater flows…
Vertical Flow Constructed Wetland
A vertical flow constructed wetland is a planted filter bed that is drained at the bottom. Wastewater is poured or dosed onto the surface from above…
Sedimentation/ Thickening Ponds
Sedimentation or thickening ponds are settling ponds that allow sludge to thicken and dewater. The effluent is removed and treated, while the…
Co-Composting
Co-composting is the controlled aerobic degradation of organics, using more than one feedstock (faecal sludge and organic solid waste). Faecal sludge…
Pre-Treatment Technologies
Pre-treatment is the preliminary removal of wastewater or sludge constituents, such as oil, grease, and various solids (e.g., sand, fibres and trash…
Disinfection and Tertiary Filtration
Depending on the end-use of the effluent or national standards for discharge in water bodies, a post-treatment step may be required to remove…
Planted Drying Beds
A planted drying bed is similar to an [8223-Unplanted Drying Bed], but has the added benefit of transpiration and enhanced sludge treatment due to…