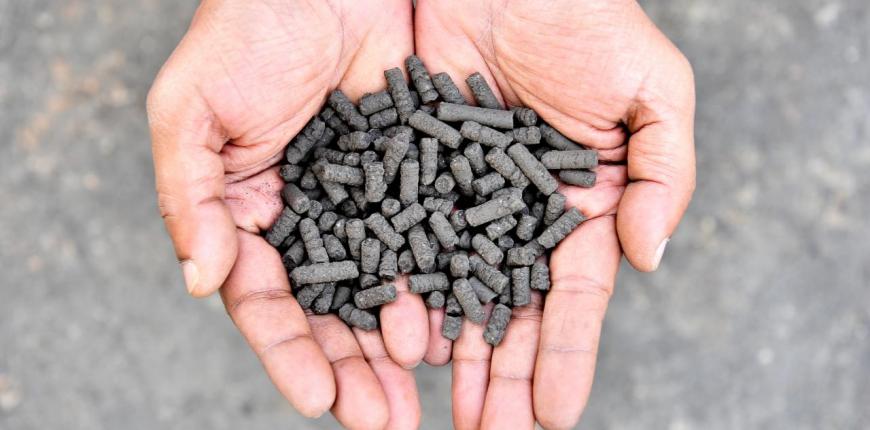


"Resources Recovery and Reuse (RRR) Entrepreneurship" Online Course
Perspectives are different frameworks from which to explore the knowledge around sustainable sanitation and water management. Perspectives are like filters: they compile and structure the information that relate to a given focus theme, region or context. This allows you to quickly navigate to the content of your particular interest while promoting the holistic understanding of sustainable sanitation and water management.


The Online Course "Resources, Recovery and Reuse (RRR) Entrepreneurship" is for entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs interested in business opportunities in the waste and sanitation sectors.
Humans generate millions of tons of waste every day. This waste is rich in water, nutrients, energy, and organic compounds. Yet waste is often not managed in a way that permits to derive value from its reuse. At the same time millions of farmers struggle with depleted soils and lack of water. Resource recovery and reuse (RRR) can create livelihoods, enhance food security, support green economies, reduce waste and contribute to cost recovery in the sanitation chain.
By following this course, you will get sector specific insights and hands-on knowledge and thus have more confidence on starting-up a RRR business and experience less frustration in going through the start-up process. Each week contains a video lecture, practical worksheets as well as further readings and useful weblinks.
 Duration
Duration6 Modules comprising 20 weeks of video lectures
 Time investment
Time investment Recommended 8 hours/week or at your own pace
 Target group
Target groupEntrepreneurs or intrapreneurs with technical RRR prototype
 Requirements
RequirementsBackground in engineering, water and sanitation management or agriculture recommended
 Contents
ContentsBusiness opportunities and environment, business model, planning operations and finances, planning and financing the launch
| This course was developed by researchers at the International Water Management Institute (IWMI) and business development experts at cewas – coaching entrepreneurs in water and sanitation. Course business models were also supported by the CGIAR Research Program on Water, Land and Ecosystems (WLE). Funded by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ). |
This module introduces the importance of market-based RRR solutions. At the end of this module you have identified key challenges in your local sanitation and waste management system and a RRR-related business idea.
This module introduces the importance of market-based RRR solutions. At the end of this module you have identified key challenges in your local sanitation and waste management system and a RRR-related business idea.

This module sheds light on the importance of studying the business environment and its components like waste supply, market demand, competition and the institutional framework. At the end of this module you have gained insights to evaluating the potential of your business idea.

This module shows how a business idea can be turned into a business model while putting a specific focus on understanding the customer and designing products that meet their needs. At the end of this module you will have developed a business model and positioned your offer in the market.

This module focusses on planning the operations of a RRR related business. During this part RRR technologies will be introduced for different waste streams and tools for planning the production process. At the end of this module you will have blueprinted your production process and the required technology and production inputs.

This module covers key aspects of financial planning and analysis. At the end of this module you will have forecasted your profits, cash flows, required investment and evaluated the financial viability of your business model.

This module enables you to set objectives and plan activities for the launch of your RRR business and identify potential financing sources. At the end of this module you will have developed an action plan for launch and identified appropriate financing sources.

This module introduces the importance of market-based RRR solutions. At the end of this module you have identified key challenges in your local sanitation and waste management system and a RRR-related business idea.
This module sheds light on the importance of studying the business environment and its components like waste supply, market demand, competition and the institutional framework. At the end of this module you have gained insights to evaluating the potential of your business idea.
This module shows how a business idea can be turned into a business model while putting a specific focus on understanding the customer and designing products that meet their needs. At the end of this module you will have developed a business model and positioned your offer in the market.
This module focusses on planning the operations of a RRR related business. During this part RRR technologies will be introduced for different waste streams and tools for planning the production process. At the end of this module you will have blueprinted your production process and the required technology and production inputs.
This module covers key aspects of financial planning and analysis. At the end of this module you will have forecasted your profits, cash flows, required investment and evaluated the financial viability of your business model.
This module enables you to set objectives and plan activities for the launch of your RRR business and identify potential financing sources. At the end of this module you will have developed an action plan for launch and identified appropriate financing sources.
This AGUASAN publication illustrates how the water and nutrient cycles can be used as a tool for creating a common understanding of a water and sanitation system and aligning it with SDG 6.
BROGAN, J., ERLMANN, T., MUELLER, K. and SOROKOVSKYI, V. (2017): SDG 6 along the water and nutrient cycles. Using the water and nutrient cycles as a tool for creating a common understanding of a water and sanitation system - including workshop material. Bern (Switzerland): AGUASAN and Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) URL [Accessed: 26.03.2019] PDF"3 billion people worldwide live in cities without sewers or wastewater treatment plant infrastructure. This forces them to dump their waste into open waters, contaminating the drinking water for others downstream. Imagine if we could harness nutrients in wastewater instead of harming human and environmental health. Christoph Lüthi sees a renewable, locally produced and growing resource where others see only human waste. Watch his talk to learn why shit matters! "
"Steve Jobs shares his amazingly different approach to marketing and how he used it to build Apple into one of the largest companies in the world".
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFVolume I of the Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater focuses on policy, regulation and institutional arrangements. Accordingly, its intended readership is made up of policy-makers and those with regulatory responsibilities. It provides guidance on policy formulation, harmonisation and mainstreaming, on regulatory mechanisms and on establishing institutional links between the various interested sectors and parties. It also presents a synthesis of the key issues from Volumes II, III, and IV and the index for all four volumes as well as a glossary of terms used in all four volumes is presented in Annex 1.
WHO (2006): Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume I. Policy and Regulatory Aspects. Geneva: World Health Organisation URL [Accessed: 10.04.2019]Volume II of the Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater, excreta and greywater provides information on the assessment and management of risks associated with microbial hazards and toxic chemicals. It explains requirements to promote the safe use of wastewater in agriculture, including minimum procedures and specific health-based targets, and how those requirements are intended to be used. It also describes the approaches used in deriving the guidelines, including health-based targets, and includes a substantive revision of approaches to ensuring microbial safety.
WHO (2006): Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume II. Wastewater Use in Agriculture. Geneva: World Health Organisation URL [Accessed: 05.06.2019] PDFVolume III of the Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater deals with wastewater and excreta use in aquaculture and describes the present state of knowledge regarding the impact of wastewater-fed aquaculture on the health of producers, product consumers and local communities. It assesses the associated health risks and provides an integrated preventive management framework.
WHO (2006): Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume III. Wastewater and Excreta Use in Aquaculture. Geneva: World Health Organisation URL [Accessed: 08.05.2019]Volume IV of the Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater recognizes the reuse potential of wastewater and excreta (including urine) in agriculture and describes the present state of knowledge as regards potential health risks associated with the reuse as well as measures to manage these health risks following a multi-barrier approach.
WHO (2006): Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume IV. Excreta and Greywater Use in Agriculture. Geneva: World Health Organisation (WHO) URL [Accessed: 09.05.2019] PDF
You want to stay up to date about water entrepreneurship?
Subscribe here to the new Sanitation and Water Entrepreneurship Pact (SWEP) newsletter!

We'd love to know what you think of the new website – please send us your feedback.
Provide Feedback
