المُلخص التنفيذي
أحواض التجفيف غير المزروعة Unplanted Drying Beds هي أحواض بسيطة ذات قاع مساميّ. عندما تمتلئ الأحواض بالحمأة، فإنَّها تجمّع السوائل المُترشحة، وتسمح للحمأة بأن تجف عن طريق التبخر. يتم التخلص من حوالي 50% إلى 80% من حجم الحمأة عن طريق ارتشاح السوائل أو تبخرها، ومع ذلك فإنّ الحمأة ليست مُثبّتة (مهضومة جيدًا) أو مُطهّرة على نحوٍ فَعَّال.
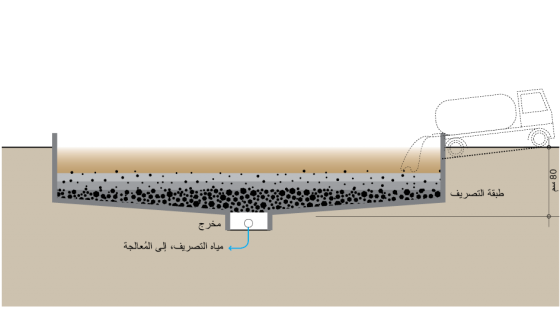
يتم بسط قاع أحواض التجفيف بأنابيب مُثقبة لتصريف السوائل المرتشحة من الحوض، وتُوجد فوق الأنابيب طبقات من الحصى والرمال التي تدعم الحمأة، وتسمح للسائل بالارتشاح والتجمع في أنابيب التصريف. ولا ينبغي تطبيقها عندما تكون الحمأة سميكة للغاية (الحد الأقصى هو 20 سنتيمترًا)، وإلا فلن تجف الحمأة بشكل فعَّال. يجب أن يكون مُحتوى الرطوبة النهائي بعد 10 إلى 15 يومًا من التجفيف ما يقرب من 60%. عندما يتم تجفيف الحمأة، فإنَّه يجب أن يتم فصلها عن طبقة الرمال، ويتم نقلها لمزيد من عمليات المُعالجة، أو الاستخدام، أو التخلص النهائي. ويجب أن يتم التعامل مع السوائل المرتشحة -التي تُجمَعُ في أنابيب التصريف- بشكل صحيح، وهذا يتوقف على المكان الذي يتم تصريفها إليه.
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
| الحمأة |
التدفقات السائلة الخارجة , الحمأة |
المُلاءَمَة
تجفيف الحمأه هي طريقة فعَّالة لخفض حجمها، وذلك مهم للغاية عند نقلها إلى مكان آخر لمزيد من عمليات المُعالجة، أو الاستخدام، أو التخلص النهائي. هذه التقنية ليست فعالة في تثبيت جزيئات المواد العضوية أو تخفيض مسببات الأمراض. قد تتطلب الحمأة المجففة مزيدًا من التخزين أو المُعالجة )على سبيل المثال؛ إعداد السماد مع إضافة المواد العضوية (.
تناسب أحواض التجفيف غير المزروعة -بشكل أكبر- المُجتمعات الصغيرة إلى المتوسطة، ذات كثافةٍ سكانيةٍ قد تصل إلى 100 ألف نسمة، ولكن توجد أحواض أخرى أكبر، حيث تكون مُناسبة للتجمعات الحضرية الكبيرة. أحواض التجفيف غير المزروعة تُناسب المناطق الريفية وشبه الحضرية حيث تتوفر المساحة بثمن قليل، وتقع بعيدًا عن المنازل ومناطق الأعمال.
إذا تم تصميمها من أجل خدمة المناطق الحضرية؛ فإن أحواض التجفيف غير المزروعة يجب أن تُنشَأ عند أطراف المدينة، ولكن يجب أن تكون أيضًا في المتناول الاقتصادي للعاملين على التفريغ والنقل بواسطة المحركات. هذا الخيار مُنخفض التكلفة ويمكن انشاؤه في معظم المناخات الحارة والمُعتدلة. الأمطار الغزيرة قد تمنع الحمأة من الجفاف بشكل صحيح.
اعتبارات التصميم
تتم تغطية أنابيب الصرف بحوالي 3-5 طبقات مُتدرجة من الحصى والرمال؛ الطبقة السفليّة يجب أن تكون من الحصى الخشن، أما الطبقة العليا فمن الرمال الناعمة )0.1 إلى 0.5 ملليمتر هو حجم الحبيبات الفعَّال( يجب أن يتراوح سمك طبقة الرمال في الأعلى ما بين 250 إلى 300 ملليمتر؛ لأن بعض الرمال سيتم فقدانها في كل مرة يتم فيها إزالة الحمأة.
لتحسين عمليتيّ التجفيف والارتشاح، فإنه يُمكن استخدام الحمأة بالتناوب بين حوضين أو أكثر. ويجب أن يكون المدخل مُجهّزًا بمنصةٍ لتوزيع السائل المُتدفق بالرش؛ وذلك لمنع انجراف طبقة الرمال، وللسماح بعملية توزيعٍ جيدةٍ للحمأة.
يجب أن تؤخذ بعين الاعتبار الصيانة المستقبلية في تصميم أحواض التجفيف غير المزروعة، لأن ضمان وصول الناس والشاحنات لضخ الحمأة وإزالة الحمأة المجففة أمر ضروري.
إذا تم إنشاء المَرفق في المناخات الرطبة فيجب تغطية السقف والحرص الشديد على منع تدفق مياه الجريان السطحي إلى المرفق.
الجوانب الصحية / القبول
تُعتبر الحمأة الداخلة المُخفَّفة مُسببة للأمراض؛ لذلك يجب تزويد العاملين بوسائل الحماية المُناسبة )الأحذية الطويلة، والقفازات، والملابس الواقية( تكون الحمأة المجففة والتدفقات السائلة الخارجة غير معقمة وتتطلب مزيدًا من عمليات المُعالجة أو التخزين، وذلك اعتمادًا على الاستخدام النهائي المطلوب.
قد تسبب أحواض التجفيف إزعاجًا لسكان المناطق المجاورة؛ نتيجة للروائح الكريهة ووجود الذباب. وبالتالي فإنها يجب أن تتواجد بعيدًا بما فيه الكفاية عن المناطق السكنية.
التشغيل والصيانة
تتطلب طاقمًا مُدربًا لأعمال التشغيل والصيانة؛ لضمان عملها بشكل فعَّال.
يُمكن إزالة الحمأة الجافة بعد حوالي 10-15 أيام، ولكن يعتمد ذلك على الظروف المناخية. ولأنَّ بعض الرمال يتم فقدها مع كل عملية إزالة للحمأة، فإن الطبقة العُليا يجب أن يتم استبدالها عندما تُصبح رقيقة. ويجب الحفاظ على نظافة منطقة التفريغ، كما يجب تنظيف مصارف التدفقات السائلة الخارجة بانتظام.
التلوث : المخاطر والحلول
Small and Decentralized Wastewater Management Systems
Decentralised wastewater management presents a comprehensive approach to the design of both conventional and innovative systems for the treatment and disposal of wastewater or the reuse of treaded effluent. Smaller treatment plants, which are the concern of most new engineers, are the primary focus of this book.
CRITES, R. TCHOBANOGLOUS, G. (1998): Small and Decentralized Wastewater Management Systems. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies IncHousehold Water Treatment and Safe Storage (HWTS). Lecture Notes
Lecture notes on the technical and non-technical aspects of sanitation household-level drinking water treatment and safe storage (HWTS) in developing countries.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage (HWTS). Lecture Notes. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 3 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 08.04.2010]Faecal Sludge Management. Pdf Presentation
A presentation about faecal sludge management in developing countries.
EAWAG ; SANDEC (2008): Faecal Sludge Management. Pdf Presentation. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 5 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (Eawag), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (Sandec) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2012]Urban Compost: A Socio-economic and Agronomic Evaluation in Kumasi, Ghana
Use of Reed Beds for Faecal Sludge Dewatering
This study project tested reed beds for their ability to treat septage.
HEINSS, U. KOOTAATEP, T. (1998): Use of Reed Beds for Faecal Sludge Dewatering. A Synopsis of Reviewed Literature and Interim Results of Pilot Investigations with Septage Treatment in Bangkok, Thailand. Duebendorf and Bangkok: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (Eawag), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (Sandec) and Asian Institute of Technology (AIT)Solids Separation and Pond Systems for the Treatment of Faecal Sludges in the Tropics
The report sets out to provide guidelines for the preliminary design of faecal sludge treatment schemes comprising solids-liquid separation and stabilisation ponds. The document is based on the results of collaborative field research conducted by the Ghana Water Research Institute and SANDEC on full and pilot-scale faecal sludge (FS) treatment plants located in Accra, Ghana.
HEINSS, U. LARMIE, S.A. STRAUSS, M. (1998): Solids Separation and Pond Systems for the Treatment of Faecal Sludges in the Tropics . Lessons Learnt and Recommendations for Preliminary Design . (= SANDEC Report , 5 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 12.04.2010]Arcata's Wastewater Treatment Plant & The Arcata Marsh and Wildlife Sanctuary
Faecal Sludge Treatment
This document reviews current practices of faecal sludge management and treatment.
MONTANGERO, A. STRAUSS, M. (2004): Faecal Sludge Treatment. Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 10.06.2019]DEWATS
Exhaustive report on technological, operational and economic aspects of decentralised waste water treatment systems. Spreadsheet examples support the reader in designing and planning waste water treatment systems components.
SASSE, L. BORDA (1998): DEWATS. Decentralised Wastewater Treatment in Developing Countries. Bremen: Bremen Overseas Research and Development Association (BORDA) URL [Accessed: 03.06.2019]Faecal Sludge Management
This is the first book to compile the current state of knowledge on faecal sludge management. It addresses the organization of the entire faecal sludge management service chain, from the collection and transport of sludge, to the current state of knowledge of treatment options, and the final end use or disposal of treated sludge. It presents an integrated approach that brings together technology, management, and planning, based on Sandec’s 20 years of experience in the field. It also discusses important factors to consider when evaluating and upscaling new treatment technology options. The book is designed for undergraduate and graduate students, engineers, and practitioners in the field who have some basic knowledge of environmental and/or wastewater engineering.
STRANDE, L. ; RONTELTAP, M. ; BRDJANOVIC, D. (2014): Faecal Sludge Management. Systems Approach for Implementation and Operation. London: IWA Publishing URL [Accessed: 16.07.2014]Treatment of sludges from on-site sanitation — Low-cost options
Published in 1997, this article gives an overview on current literature-based knowledge regarding faecal sludge treatment along with results and conclusions from field research.
STRAUSS, M. ; LARMIE, S.A. ; HEINSS, U. (1997): Treatment of sludges from on-site sanitation — Low-cost options. المُدخلات: Water Science and Technology: Volume 6 , 129-136. URL [Accessed: 23.06.2010]FS Management – Review of Practices, Problems and Initiatives
A study on management and institutional aspects regarding the challenges and possible improvements in managing faecal sludge.
STRAUSS, M. MONTANGERO, A. (2002): FS Management – Review of Practices, Problems and Initiatives. London and Duebendorf: DFID Project R8056, Capacity Building for Effective Decentralised Wastewater Management, Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 28.05.2019]Wastewater Engineering, Treatment and Reuse
Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFCompendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., LUETHI, C., MOREL, A., ZURBRUEGG, C. and SCHERTENLEIB, R. (2008): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (EAWAG) and Water Supply and Sanitation Collaborative Council (WSSCC) URL [Accessed: 15.02.2010] PDFCompendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFSludge Treatment and Disposal
Sludge Treatment and Disposal is the sixth volume in the series Biological Wastewater Treatment. The book covers in a clear and informative way the sludge characteristics, production, treatment (thickening, dewatering, stabilisation, pathogens removal) and disposal (land application for agricultural purposes, sanitary landfills, landfarming and other methods). Environmental and public health issues are also fully described.
ANDREOLI, C.V. ; SPERLING, M. von ; FERNANDES, F. (2007): Sludge Treatment and Disposal. (= Biological Wastewater Treatment Series , 6 ). London: International Water Association (IWA) Publishing URL [Accessed: 27.05.2019]Small and Decentralized Wastewater Management Systems
Decentralised wastewater management presents a comprehensive approach to the design of both conventional and innovative systems for the treatment and disposal of wastewater or the reuse of treaded effluent. Smaller treatment plants, which are the concern of most new engineers, are the primary focus of this book.
CRITES, R. TCHOBANOGLOUS, G. (1998): Small and Decentralized Wastewater Management Systems. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies IncFaecal Sludge Treatment
This document reviews current practices of faecal sludge management and treatment.
MONTANGERO, A. STRAUSS, M. (2004): Faecal Sludge Treatment. Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 10.06.2019]Full-Chain Sanitation Services That Last
This paper sets out a framework for the delivery of non-sewered sanitation services that last, are accessible to all and are at scale. The framework is based on IRC International Water and Sanitation’s (IRC) experience and lessons learnt from its engagement in non-sewered sanitation service at scale.
VERHAGEN, J. CARRASCO, M. (2013): Full-Chain Sanitation Services That Last. Non-Sewered Sanitation Services. The Hague: International Water and Sanitation Center (IRC) URL [Accessed: 03.06.2019]Solids Separation and Pond Systems for the Treatment of Faecal Sludges in the Tropics
The report sets out to provide guidelines for the preliminary design of faecal sludge treatment schemes comprising solids-liquid separation and stabilisation ponds. The document is based on the results of collaborative field research conducted by the Ghana Water Research Institute and SANDEC on full and pilot-scale faecal sludge (FS) treatment plants located in Accra, Ghana.
HEINSS, U. LARMIE, S.A. STRAUSS, M. (1998): Solids Separation and Pond Systems for the Treatment of Faecal Sludges in the Tropics . Lessons Learnt and Recommendations for Preliminary Design . (= SANDEC Report , 5 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 12.04.2010]Use of Reed Beds for Faecal Sludge Dewatering
This study project tested reed beds for their ability to treat septage.
HEINSS, U. KOOTAATEP, T. (1998): Use of Reed Beds for Faecal Sludge Dewatering. A Synopsis of Reviewed Literature and Interim Results of Pilot Investigations with Septage Treatment in Bangkok, Thailand. Duebendorf and Bangkok: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (Eawag), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (Sandec) and Asian Institute of Technology (AIT)SOS - Management of Sludges from On-Site Sanitation. Characteristics of Faecal Sludges and their Solids-Liquid Separation
This document gives an overview on the characteristics of different sludges as well as monitoring results and recommendations for design of solid-liquid separation. It is based on a field report.
HEINSS, U. LARMIE, S.A. STRAUSS, M. (1999): SOS - Management of Sludges from On-Site Sanitation. Characteristics of Faecal Sludges and their Solids-Liquid Separation. Duebendorf and Accra: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG)SOS - Management of Sludges from On-Site Sanitation. Co-treatment of Faecal Sludge and Wastewater in Tropical Climates
This article provides operational and design guidance for the co-treatment of faecal sludge in waste stabilisation ponds and in activated sludge sewage treatment plants. Problems which may arise when highly concentrated faecal sludge is not properly included in the design of the co-treatment system are also discussed.
HEINSS, U. STRAUSS, M. (1999): SOS - Management of Sludges from On-Site Sanitation. Co-treatment of Faecal Sludge and Wastewater in Tropical Climates. Duebendorf and Accra: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG) URL [Accessed: 21.04.2010]Fecal Sludge Management in Developing Countries - A Planning Manual
This manual is a first approach to provide guidance on strategic planning of faecal sludge management. The study took place in the City of Nam Dinh, in Vietnam. The main principles for strategic sanitation planning have been adopted from the guide “Strategic Planning for Municipal Planning” from GHK Research and Training Ltd.
KLINGEL, F. MONTANGERO, A. KONE, M. STRAUSS, M. (2002): Fecal Sludge Management in Developing Countries - A Planning Manual. (= First Edition ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute for Environmental Science (EAWAG) URL [Accessed: 08.06.2019]Faecal Sludge Treatment
This document reviews current practices of faecal sludge management and treatment.
MONTANGERO, A. STRAUSS, M. (2004): Faecal Sludge Treatment. Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 10.06.2019]How to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation
The purpose of this guide is to assist local contracting authorities and their partners in identifying those sanitation technologies best suited to the different contexts that exist within their town. The first part of the guide contains a planning process and a set of criteria to be completed; these assist you in characterizing each area of intervention so that you are then in a position to identify the most appropriate technical solutions. The second part of the guide consists of technical factsheets which give a practical overview of the technical and economic characteristics, the operating principle and the pros and cons of the 29 sanitation technology options most commonly used in sub-Saharan Africa.
MONVOIS, J. GABERT, J. FRENOUX, C. GUILLAUME, M. (2010): How to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation. (= Six Methodological Guides for a Water and Sanitation Services' Development Strategy , 4 ). Cotonou and Paris: Partenariat pour le Développement Municipal (PDM) and Programme Solidarité Eau (pS-Eau) URL [Accessed: 19.10.2011]Faecal Sludge Management
This is the first book to compile the current state of knowledge on faecal sludge management. It addresses the organization of the entire faecal sludge management service chain, from the collection and transport of sludge, to the current state of knowledge of treatment options, and the final end use or disposal of treated sludge. It presents an integrated approach that brings together technology, management, and planning, based on Sandec’s 20 years of experience in the field. It also discusses important factors to consider when evaluating and upscaling new treatment technology options. The book is designed for undergraduate and graduate students, engineers, and practitioners in the field who have some basic knowledge of environmental and/or wastewater engineering.
STRANDE, L. ; RONTELTAP, M. ; BRDJANOVIC, D. (2014): Faecal Sludge Management. Systems Approach for Implementation and Operation. London: IWA Publishing URL [Accessed: 16.07.2014]Co-composting of Faecal Sludge and Municipal Organic Waste
The document gives an overview on the combined composting of (faecal) sludges and organic solid waste based on a pilot project in Kumasi, Ghana. Results of the investigation should help the city’s waste management department to develop its biosolids management strategy and enable the project team to develop guidelines for planners and engineers on the option of co-composting.
STRAUSS, M. DRESCHER, S. ZURBRUEGG, C. MONTANGERO, A. OLUFUNKE, C. DRECHSEL, P. (2003): Co-composting of Faecal Sludge and Municipal Organic Waste. Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) and International Water Management Institute (IWMI) URL [Accessed: 05.06.2019]Treatment of sludges from on-site sanitation — Low-cost options
Published in 1997, this article gives an overview on current literature-based knowledge regarding faecal sludge treatment along with results and conclusions from field research.
STRAUSS, M. ; LARMIE, S.A. ; HEINSS, U. (1997): Treatment of sludges from on-site sanitation — Low-cost options. المُدخلات: Water Science and Technology: Volume 6 , 129-136. URL [Accessed: 23.06.2010]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFWhat Happens When the Pit is Full?
This seminar report helps people responsible for the sustainable operation of on-site sanitation systems. It shows new developments in the field and contains a lot of detailed information about Faecal Sludge Management (FSM).
WINSA (2011): What Happens When the Pit is Full?. Developments in On-Site Faecal Sludge Management (FSM). Durban: Water Information Network South Afrika (WINSA) URL [Accessed: 06.10.2011]Technology Transfer – Forage Plants Used in Faecal Sludge Dewatering Beds in Sub-Saharan Africa
In collaboration with the Asian Institute of Technology (AIT), Bangkok, Eawag has previously demonstrated that constructed wetlands, especially in Thailand, offer a viable solution for the treatment of faecal sludge. However, since the characteristics of sludge vary widely from one region to another, appropriate indigenous plants had to be identified so as to ensure successful operation of these facilities.
KONE, D. ; KENGE, I. (2008): Technology Transfer – Forage Plants Used in Faecal Sludge Dewatering Beds in Sub-Saharan Africa. المُدخلات: Sandec News: Volume 9Low-cost Options for Treating Faecal Sludges (FS) in Developing Countries - Challenges and Performance
This article analyses and discusses the performances of low-cost technology for treating faecal sludges in developing countries. It shows that where septic tanks are the predominant type of on-site sanitation installations, septage is the only or predominant type of faecal sludge generated. It also shows that constructed wetlands, settling tanks/ponds, or unplanted drying beds might prove suitable as a pre-treatment.
KONE, D. STRAUSS, M. (2004): Low-cost Options for Treating Faecal Sludges (FS) in Developing Countries - Challenges and Performance. Duebendorf: Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC), Swiss Federal Institute for Environmental Science (EAWAG) URL [Accessed: 23.06.2010]Improvement of Sanitation at Kanawat Health Center Uganda
This study reports the improvement of the sanitation systems of a rural public health centre in Kanawat, Uganda. Excreta from UDDTs and composting pit latrines are treated together in sludge drying beds. Greywater is treated in a sludge drying bed and a constructed wetland and finally reused for irrigation.
MUELLEGGER, E. SCHLICK, J. WERNER, C. (2009): Improvement of Sanitation at Kanawat Health Center Uganda. (= SuSanA - Case Studies ). Eschborn: Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) URL [Accessed: 22.05.2012]Co-composting faecal sludge & organic solid waste, Kumasi, Ghana
This project aimed to gain scientific knowledge on the technical, socio-economical and operational aspects of co-composting (organic solid waste and faecal material). Dried faecal sludge (drying bed) is co-composted with the organic fraction of solid waste. The final product is used as compost for urban and periurban agriculture.
OLUFUNKE, C. DOULAYE, K. (2009): Co-composting faecal sludge & organic solid waste, Kumasi, Ghana. (= SuSanA - Case Studies ). Eschborn: Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) URL [Accessed: 22.05.2012]Chapter 3. Pilot Project "Navsarjan Vocational Training Institute Dalit Shakti Kendra"
The main aim of the project was to avoid manual scavenging of excreta and to improve the sanitation situation at the Navsarjan Vocational Training Institute. The technical solution proposed was source separation (grey-/blackwater) and reuse. Greywater is separately treated and reused in the garden while the urine and faeces (blackwater) are directly introduced into a biogas plant. Digested sludge is dried on basic drying beds and used as compost for the garden. UDDT were also installed. The concept was implemented and evaluated for its social and cultural acceptability, sustainable and hygienic safety.
WAFLER, M. (2006): Chapter 3. Pilot Project "Navsarjan Vocational Training Institute Dalit Shakti Kendra". المُدخلات: WAFLER, M. ; HEEB, J. ; (2006): Report on Case Studies of ecosan Pilot Projects in India. Eschborn: . URL [Accessed: 26.04.2010]Decentralized Wastewater Mgmt at Adarsh College, Badalapur, Maharashtra, India
This case study reports the development of an ecologically sound sanitation concept at Adarsh Bidyaprasarak Sanstha's College of Arts & Commerce. It comprises separate urine collection and a DEWATS system for the treatment of black- and greywater consisting of biogas settler, an anaerobic baffled reactor, and anaerobic filter, a horizontal flow wetland and a polishing pond.
ZIMMERMANN, N. WAFLER, M. (2009): Decentralized Wastewater Mgmt at Adarsh College, Badalapur, Maharashtra, India. (= SuSanA - Case Studies ). Eschborn: Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) URL [Accessed: 22.05.2012]Faecal Sludge Management. Lecture Notes
This module pays special attention to the haulage, treatment and reuse or disposal of faecal sludge. It covers both technical and non-technical (socio-cultural, economic, political etc.) aspects and provides practical information on design, financing and planning of faecal sludge treatment plants.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Faecal Sludge Management. Lecture Notes. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 5 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2012]Faecal Sludge Management. Pdf Presentation
A presentation about faecal sludge management in developing countries.
EAWAG ; SANDEC (2008): Faecal Sludge Management. Pdf Presentation. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 5 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (Eawag), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (Sandec) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2012]Faecal Sludge Treatment
This document reviews current practices of faecal sludge management and treatment.
MONTANGERO, A. STRAUSS, M. (2004): Faecal Sludge Treatment. Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 10.06.2019]DEWATS
Exhaustive report on technological, operational and economic aspects of decentralised waste water treatment systems. Spreadsheet examples support the reader in designing and planning waste water treatment systems components.
SASSE, L. BORDA (1998): DEWATS. Decentralised Wastewater Treatment in Developing Countries. Bremen: Bremen Overseas Research and Development Association (BORDA) URL [Accessed: 03.06.2019]FS Management – Review of Practices, Problems and Initiatives
A study on management and institutional aspects regarding the challenges and possible improvements in managing faecal sludge.
STRAUSS, M. MONTANGERO, A. (2002): FS Management – Review of Practices, Problems and Initiatives. London and Duebendorf: DFID Project R8056, Capacity Building for Effective Decentralised Wastewater Management, Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 28.05.2019]Informed Choice Catalogue
This informed choice catalogue for community based wastewater treatment technologies helps to identify suitable sanitation options and facilitates the assessment of different sanitation system components with regard to stakeholder preferences. A powerful tool for technical bottom-up planning giving overall information about technical options at a "glance".
SANIMAS (2005): Informed Choice Catalogue. pdf presentation. BORDA and USAID URL [Accessed: 29.05.2019]Environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment for the implementation of the UNEP/GPA "Guidelines on Municipal Wastewater Management"
Technical information on environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment.
UNEP ; MURDOCH UNIVERSITY (2004): Environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment for the implementation of the UNEP/GPA "Guidelines on Municipal Wastewater Management". The Hague: United Nations Environment Programme Global Programme of Action (UNEP/GPA), Coordination OfficeUrban Excreta Management - Situation, Challenges, and Promising Solutions
The objective of this paper is to render planners, decision makers, and consultants aware that faecal sludge management (FSM) should form an integral part of the urban development planning process. For this, three illustrative cases are presented, based on which an array of measures or tools, as well as institutional/regulatory, financial/economic, and technical aspects are discussed.
STRAUSS, M. ; BARREIRO, W.C. ; STEINER, M. ; MENSAH, A. ; JEULAND, M. ; BOLOMEY, S. ; MONTANGERO, A. ; KONE, D. (2003): Urban Excreta Management - Situation, Challenges, and Promising Solutions. المُدخلات: IWA Asia-Pacific Regional Conference Bangkok, Thailand: URL [Accessed: 23.06.2010]http://www.eawag.ch/
The department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) at the Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG) is a centre of excellence in the domain of faecal sludge treatment and management and many helpful publications can be downloaded.
http://www.unep.or.jp/
Link to the online version of the “International Source Book On Environmentally Sound Technologies for Wastewater and Stormwater Management” from the United Nations Environmental Programme. This section is about drying beds.
