المُلخص التنفيذي
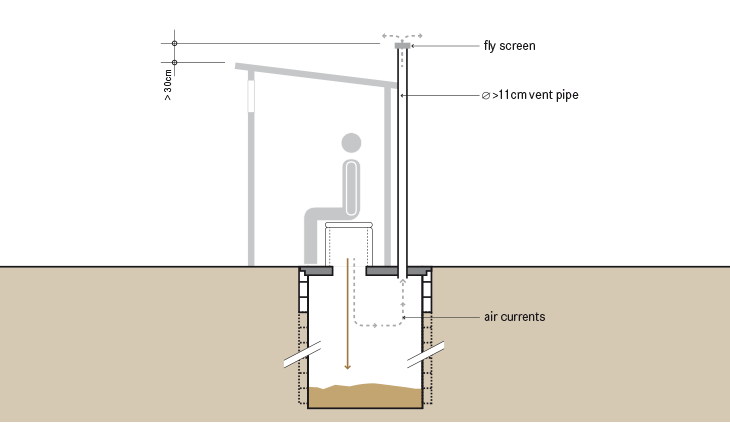
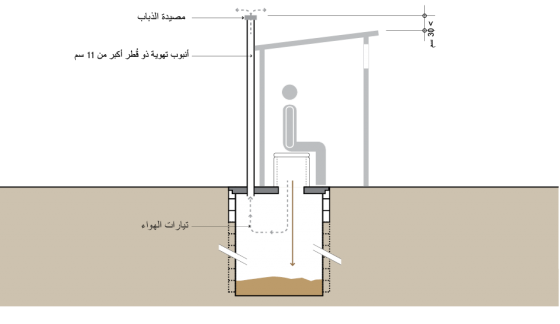
تُعتبر الحُفرة الواحدة المُطورة المُهواة Single Ventilated Improved Pit (VIP) تطويرًا لتقنية الحُفرة الواحدة وذلك بسبب تدفق الهواء المستمر عبر أنبوب التهوية لطرد الروائح، كما يعمل الأنبوب أيضًا كمصيدة للذباب لأنه يخرج ناحية الضوء.
وبالرغم من بساطة هذه التقنية، فإنها تكون خالية تمامًا من الروائح إذا صُممت جيدًا، وتعتبر أكثر جذبًا للاستخدام من بعض التقنيات الأخرى التي تعتمد على توافر المياه.
ينجذب الذباب المتواجد بالحُفرة إلى الضوء في الجزء العلوي من أنبوب التهوية. وعندما يتجه نحو الضوء محاولًا الخروج يتم احتباسه بمصيدة الذباب ويموت. كما تسمح التهوية أيضًا بخروج الروائح من الحُفرة مما يقلل من جذب الذباب.
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
| فضلات الجسم، المياه السوداء، البراز، مياه تنظيف الشرج، مواد التطهير الجافة |
الحمأة |
المُلاءَمَة
تكون عمليات المُعالجة في الحُفرة الواحدة المُطورة المُهواة )الهوائية، اللاهوائية، التجفيف، التسميد، أو غيره( محدودة، ولذلك فإن معدل تخفيض مُسببات الأمراض والتحلّل العضوي غير كبير، ولكن بما أن فضلات الجسم يتم احتواؤها، فذلك يحد من انتقال مُسببات الأمراض للمستخدمين. وتُعد هذه التقنية متطورة بشكلٍ ملحوظ عن الحُفر الواحدة التقليدية أو التغوط في العراء.
وتكون الحُفرة الواحدة المُطورة المُهواة مناسبة للمناطق الريفية وشبه الحضرية، على عكس المناطق المُكتظة بالسكان، حيث يكون من الصعب تفريغها و/أو لا توجد مساحة كافية للترشيح. كما أنها مناسبة في حالة نُدرَة المياه، وحيث يكون منسوب المياه الجوفية مُنخفضًا. وينبغي أن تتواجد في منطقة جيدة التهوية لضمان التهوية الفعالة. كما أنها غير مناسبة في حالة التربة الصخرية أو المدكوكة )التي يصعب حَفرها(، أو للأماكن التي تتكرر بها الفيضانات.
اعتبارات التصميم
ينبغي ألا يقل القطر الداخلي لأنبوب التهوية عن 110 ملليمتر يمتد إلى أكثر من 300 ملليمتر فوق أعلى نقطة من البنية الفوقية للمِرحاض )الحمَّام) يخلق مرور الرياح أعلى أنبوب التهوية ضغطًا ساحباً للهواء من داخلها وذلك يُحفز دورة الهواء في الحُفرة. يتم سحب الهواء عبر واجهة المستخدم إلى الحُفرة، ويتحرك صعودًا داخل أنبوب التهوية خارجاً إلى الجو. وينبغى مراعاة عدم إعاقة الأشياء مثل الأشجار أو المنازل لتيار الهواء. تكون التهوية أفضل في المناطق التي بها رياح، أما في حالة التهوية الضعيفة، فيمكن تحسين فاعليتها بطلاء الأنابيب باللون الأسود، فإن الفارق الحراري بين الحُفرة )الباردة( وأنبوب التهوية )الدافئ( يخلق تيارًا هوائيًا صاعدًا يسحب الهواء والروائح ويُخرجها من الحُفرة. ولاختبار فعالية التهوية، يمكن وضع سيجارة مشتعلة فوق فتحة واجهة المستخدم، حيث يتم سحب الدخان إلى الأسفل داخل الحُفرة ومن ثم إلى فتحة التهوية ولا يتبقى منه شيء في الحمَّام.
يجب أن تكون فتحات الشبكة السلكية لمصيدة الذباب كبيرة بما فيه الكفاية لمنع انسدادها بالتراب وللسماح بسريان الهواء بحُرِّية. أثبتت شبكات الألومنيوم السلكية ذات فتحات الثقوب بين 1.2 إلى 1.5 ملليمتر أنها الأكثر فعالية. لا يقل عمق الحُفرة - في العادة - عن 3 أمتار وقطرها من 1 إلى 1.5 متر، ويتوقف ذلك على عدد المستخدمين. ويمكن أن تستمر الحُفر العميقة لمدة تصل إلى 20 سنة أو أكثر.
بينما تتسرب السوائل من الحُفرة وتنتقل عبر التربة المسامية غير المُشبَّعة، فإن الجراثيم المسببة للأمراض تُمتص على سطح حبيبات التربة، وبهذه الطريقة يمكن إزالة مُسببات الأمراض قبل أن تصل إلى المياه الجوفية. وتختلف درجة الإزالة حسب نوع التربة، والمسافة المقطوعة، والرطوبة وعوامل بيئية أخرى، ولذلك فإنه من الصعب تقدير المسافة الضرورية بين الحُفرة ومصدر المياه، ولكن يُنصح أن تكون المسافة الأفقية بينهما حوالي 30 مترًا على الأقل للحد من التعرض للتلوث الميكروبي.
وعندما لا يكون من الممكن حَفر حُفرة عميقة، أو عندما يكون مستوى المياه الجوفية عاليًا جدًا، فإن بناء حُفرة مرتفعة يمكن أن يكون بديلًا مُجديًا، حيث يمكن تمديد الحُفرة غير العميقة عن طريق بناء حلقات أو كُتل خرسانية بشكل رأسي فوقها، ويمكن بناء الحُفرة المُرتفعة في مكان تحدث فيه فيضانات أو سيول مُتكررة؛ للحفاظ على المياه من التدفُّق إلى الحُفرة أثناء الأمطار الغزيرة.
يمكن تطوير وتحسين مستوى المِرحاض ذي الحُفرة الواحدة المُطورة المُهواة ليصبح مِرحاض ذو الحُفرة المزدوجة المُطورة المُهواة حيث إنها تحتوي على حُفرة إضافية، ولذلك عندما تكون واحدة منهما قيد الاستخدام، يمكن تصريف وتخمر وتحلل محتويات الحُفرة الممتلئة.
وإذا تم استخدام واجهة المُستخدم الفاصلة للبول، فسيتم تجميع البُراز فقط في الحُفرة وبذلك يقل الرشح.
الجوانب الصحية / القبول
تُعتبر الحُفرة الواحدة المُطورة المُهواة من خيارات الصرف الصحي المقبولة بشكل جيد، والنظيفة والمريحة. ومع ذلك فتوجد بعض المخاوف الصحية:.
• السوائل المرتشحة قد تُسبب تلوث المياه الجوفية.
• قد تكون الحُفر عُرضة للهدم و/أو الطفح أثناء الفيضانات.
• المخاطر الصحية من الذباب لا يتم تجنبها بشكل كامل بالتهوية فقط.
التشغيل والصيانة
للحفاظ على الحُفرة الواحدة المُطورة المُهواة من الذباب والروائح، فإن ذلك يتطلب التنظيف المستمر والصيانة بشكلٍ منتظم، ويجب إزالة الذباب الميت، وشبكات العنكبوت، والغبار وغيرها من العوالق عن شبكة التهوية لضمان التدفق الجيد للهواء.
حلول تقنيات وممارسات افضل للصرف الصحى دليل الاحياء الهاشمية فى نواكشوط -موريتانيا
المياه ،الصرف الصحي النظافة الصحية وظروف الإقامة في السجون
التلوث : المخاطر والحلول
بناء الحمامات وطرق تحسينها وصيانتها
الصرف الصحي الموقعي والمركزي - للمدن والتجمعات السكانية الصغيرة
Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Lecture Notes
Lecture notes on technical and non-technical aspects of sanitation systems in developing countries.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Lecture Notes . (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 4 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC)Ventilated Improved Latrine Construction in the Slum Areas of Kampala, Uganda
The Urban Affordable Clean Toilets (U-ACT) project aims at overcoming the constraints to private sanitation investment in poor urban areas. Field research was conducted in 40 randomly selected low-income areas of Uganda’s capital Kampala where people rely on on-site sanitation. The sanitation situation in these urban slum zones is characterised by a high number of users per toilet, and full or overflowing latrines that are not regularly emptied. This factsheet provides information on the construction and cost details of ventilated improved pit (VIP) latrines.
LUETHI, C. NIWAGABA, B.C. GUENTHER, I. HORST, A. MULONGO, P. GRUETER, R. (2013): Ventilated Improved Latrine Construction in the Slum Areas of Kampala, Uganda. Technical Factsheet. Zuerich: Nachdiplomstudium fuer Entwicklungslaender (NADEL) Eidgenoessische Technische Hochschule (ETH) URL [Accessed: 10.10.2013]The design of Ventilated Improved Pit Latrines
The purpose of this paper is to discuss general design criteria for VIP latrines and to review recent developments in VIP latrine design.
MARA, D.D. (1984): The design of Ventilated Improved Pit Latrines. UNDP Interregional Project. (= United Nations Development Programme Interregional Project , 47 ). Washington: The World Bank URL [Accessed: 11.10.2013]Low-cost Urban Sanitation
This book covers the public health, technical, socioeconomic, sociocultural and institutional aspects of sanitation in towns and cities of developing countries. The text features excreta-related diseases and the use of sanitation to reduce their transmission. The sanitation technologies covered in detail are VIP latrines, pour-flush toilets, septic tanks, settled sewerage and simplified sewerage, with additional chapters on sullage disposal, pit emptying, and sewage treatment and reuse. Sociocultural constraints on sanitation systems and their socioeconomic costing are described, together with hygiene education, which is essential in order to achieve maximum benefits to health. The text also explains how to choose the most appropriate sanitation option for a given low-income community. Finally, institutional aspects are reviewed, including effective sanitation programme planning, monitoring and evaluation.
MARA, D. (1996): Low-cost Urban Sanitation. United Kingdom: WileyEcological Toilets
This book describes how to construct Arborloo toilets and how it can be upgraded to VIPs at a later stage.
MORGAN, P. EcoSanRes (2009): Ecological Toilets. (pdf presentation). Stockholm: Stockholm Environment Institute URL [Accessed: 09.05.2019]The Upgradeable Blair VIP
This manual provides detailed design and construction information on the Blair VIP toilet.
MORGAN, P.P. (2011): The Upgradeable Blair VIP . Manual for upgradeable BVIP model with spiral superstructure and tubular vent. Stockholm: Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI) URL [Accessed: 31.01.2014]Ventilated Improved Pit Latrines: Vent Pipe Design Guidelines
This technical note sets out preliminary guidelines for the design and construction of vent pipes for ventilated improved pit (VIP) latrines.
RYAN, B.A. MARA, D.D. (1983): Ventilated Improved Pit Latrines: Vent Pipe Design Guidelines. (= UNDP Interregional Project INT/81/047 ). Washington: The World Bank, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) URL [Accessed: 31.01.2014]Informed Choice Catalogue
This informed choice catalogue for community based wastewater treatment technologies helps to identify suitable sanitation options and facilitates the assessment of different sanitation system components with regard to stakeholder preferences. A powerful tool for technical bottom-up planning giving overall information about technical options at a "glance".
SANIMAS (2005): Informed Choice Catalogue. pdf presentation. BORDA and USAID URL [Accessed: 29.05.2019]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., LUETHI, C., MOREL, A., ZURBRUEGG, C. and SCHERTENLEIB, R. (2008): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (EAWAG) and Water Supply and Sanitation Collaborative Council (WSSCC) URL [Accessed: 15.02.2010] PDFCompendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFA Guide to the Development of On-site Sanitation
The publication presents appropriate technologies for sanitation and highlights socio-economic aspects of planning and implementing. Emphasis is given to household-level sanitation improvements for urban areas, as well as rural areas and small communities. Background information on sanitation, in-depth technical information on the design, construction, operation and maintenance and project planning and development processes involved in projects and programmes complement the book.
WHO (1992): A Guide to the Development of On-site Sanitation. Geneva: World Health Organisation (WHO) URL [Accessed: 14.04.2010]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFGuidelines for Assessing the Risk to Groundwater from On-Site Sanitation
Many people in developing countries rely upon untreated groundwater supplies for their drinking water (e.g. from drilled boreholes, tube wells, dug wells or springs). The introduction of on-site sanitation systems might lead to groundwater contamination. The purpose of this manual is to provide guidance on how to assess and reduce the risk of contamination of groundwater supplies from on-site sanitation systems and is aimed at those responsible for planning low cost water supply and sanitation schemes.
ARGOSS (2001): Guidelines for Assessing the Risk to Groundwater from On-Site Sanitation. (= Commissioned Report , 142 ). Keyworth: British Geological Survey URL [Accessed: 11.05.2019]Latrine Building
Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Lecture Notes
Lecture notes on technical and non-technical aspects of sanitation systems in developing countries.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Lecture Notes . (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 4 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC)Faecal Sludge Management.
This issue presents studies from different regions (Bangladesh, Cameroon, Burkina Faso) that mainly show the non-existence of faecal sludge management. Additionally, the last paper describes a new technological solution (LaDePa) for producing hygienically safe organic fertiliser from sludge from ventilated improved pit toilets (VIPs).
ECOSAN CLUB (2012): Faecal Sludge Management.. (= Sustainable Sanitation Practice , 13 ). Vienna: Ecosan Club URL [Accessed: 16.10.2012]Pit Latrines and Their Impacts on Groundwater Quality: a systematic Review
This study reviews empirical studies on the impact of pit latrines on groundwater quality and identifies knowledge gaps regarding the potential and consequences of groundwater contamination by latrines.
Graham, J. ; Polizotto, M.L. (2013): Pit Latrines and Their Impacts on Groundwater Quality: a systematic Review. Advance Publication. المُدخلات: Environmental Health Perspectives: URL [Accessed: 09.04.2013]Emergency Sanitation: Assessment and Programme Design
This book has been written to help all those involved in planning and implementing emergency sanitation programmes. The main focus is a systematic and structured approach to assessment and programme design. There is a strong emphasis on socio-cultural issues and community participation throughout.Includes an extensive “guidelines” section with rapid assessment instructions and details on programme design, planning and implementation.
HARVEY, P. BAGHRI, S. REED, B. (2002): Emergency Sanitation: Assessment and Programme Design. Loughborough: Water, Engineering and Development Centre (WEDC) URL [Accessed: 31.05.2019]The design of Ventilated Improved Pit Latrines
The purpose of this paper is to discuss general design criteria for VIP latrines and to review recent developments in VIP latrine design.
MARA, D.D. (1984): The design of Ventilated Improved Pit Latrines. UNDP Interregional Project. (= United Nations Development Programme Interregional Project , 47 ). Washington: The World Bank URL [Accessed: 11.10.2013]Low-cost Urban Sanitation
This book covers the public health, technical, socioeconomic, sociocultural and institutional aspects of sanitation in towns and cities of developing countries. The text features excreta-related diseases and the use of sanitation to reduce their transmission. The sanitation technologies covered in detail are VIP latrines, pour-flush toilets, septic tanks, settled sewerage and simplified sewerage, with additional chapters on sullage disposal, pit emptying, and sewage treatment and reuse. Sociocultural constraints on sanitation systems and their socioeconomic costing are described, together with hygiene education, which is essential in order to achieve maximum benefits to health. The text also explains how to choose the most appropriate sanitation option for a given low-income community. Finally, institutional aspects are reviewed, including effective sanitation programme planning, monitoring and evaluation.
MARA, D. (1996): Low-cost Urban Sanitation. United Kingdom: WileyHow to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation
The purpose of this guide is to assist local contracting authorities and their partners in identifying those sanitation technologies best suited to the different contexts that exist within their town. The first part of the guide contains a planning process and a set of criteria to be completed; these assist you in characterizing each area of intervention so that you are then in a position to identify the most appropriate technical solutions. The second part of the guide consists of technical factsheets which give a practical overview of the technical and economic characteristics, the operating principle and the pros and cons of the 29 sanitation technology options most commonly used in sub-Saharan Africa.
MONVOIS, J. GABERT, J. FRENOUX, C. GUILLAUME, M. (2010): How to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation. (= Six Methodological Guides for a Water and Sanitation Services' Development Strategy , 4 ). Cotonou and Paris: Partenariat pour le Développement Municipal (PDM) and Programme Solidarité Eau (pS-Eau) URL [Accessed: 19.10.2011]Ecological Toilets
This book describes how to construct Arborloo toilets and how it can be upgraded to VIPs at a later stage.
MORGAN, P. EcoSanRes (2009): Ecological Toilets. (pdf presentation). Stockholm: Stockholm Environment Institute URL [Accessed: 09.05.2019]The Upgradeable Blair VIP
This manual provides detailed design and construction information on the Blair VIP toilet.
MORGAN, P.P. (2011): The Upgradeable Blair VIP . Manual for upgradeable BVIP model with spiral superstructure and tubular vent. Stockholm: Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI) URL [Accessed: 31.01.2014]The Blair VIP
This simple document shows the development of the VIP toilet designed by the Blair Institute in Zimbabwe.
MORGAN, P. (2011): The Blair VIP. A Short History. Peter Morgan URL [Accessed: 19.06.2013]Ecodesign: The Bottom Line
There is no single design solution to sanitation. But there are universal principles for systematically and safely detoxifying human excreta, without contaminating, wasting or even using water. Ecological sanitation design — which is focused on sustainability through reuse and recycling — offers workable solutions that are gaining footholds around the world, as Nature explores on the following pages through the work of Peter Morgan in Zimbabwe, Ralf Otterpohl and his team in Germany, Shunmuga Paramasivan in India, and Ed Harrington and his colleagues in California.
NATURE (Editor) ; MORGAN, P. ; OTTERPOHL, R. ; PARAMASIVAN, S. ; HARRINGTON, E. (2012): Ecodesign: The Bottom Line. المُدخلات: Nature: International Weekly Journal of Science: Volume 486 , 186-189. URL [Accessed: 19.06.2012]Fact Sheets on Environmental Sanitation: Simple Pit Latrines
This factsheet contains practical information on the simple pit latrine.
ROBENS INSTITUTE (1996): Fact Sheets on Environmental Sanitation: Simple Pit Latrines. (= Fact Sheets on Environmental Sanitation ). Guildford / Geneva: University of Surrey, World Health Organization (WHO). Factsheet 3.4. URL [Accessed: 31.05.2019]Adventures in search of the ideal portable pit-emptying machine
This article explores the ideal portable pit-emptying machine for South Africa owing to site access constraints. The Water Research Commission of South Africa funded experimental development of a number of technologies designed to fill the gap between large vacuum tankers and manual emptying. This paper describes these attempts.
STILL, D. O RIORDAN, M. MC BRIDE, A. LOUTON, B. (2013): Adventures in search of the ideal portable pit-emptying machine. Rugby: Practical Action Publishing URL [Accessed: 07.08.2013]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFHow to Manage Public Toilets and Showers
The purpose of this decision-making aid is to provide practical advice and recommendations for managing toilet blocks situated in public places. It is primarily aimed at local decision-makers in developing countries and at their partners (project planners and managers).
TOUBKISS, J. (2010): How to Manage Public Toilets and Showers. (= Six Methodological Guides for a Water and Sanitation Services' Development Strategy , 5 ). Cotonou and Paris: Partenariat pour le Développement Municipal (PDM) and Programme Solidarité Eau (pS-Eau) URL [Accessed: 19.10.2011]Latrine and Sanitation Options Manual
This Manual aims to serve as a practical guide for the selection of sanitation technology options to satisfy local desires and meet national needs in Afghanistan. It is useful for the professionals and organisations working to address fecal contamination across Afghanistan.
USAID Afghanistan (2010): Latrine and Sanitation Options Manual. Sustainable Water Supply and Sanitation (SWSS) Project. Kabul: USAID Afghanistan URL [Accessed: 15.01.2013]Ventilated Improved Pit Latrines: Vent Pipe Design Guidelines
This technical note sets out preliminary guidelines for the design and construction of vent pipes for ventilated improved pit (VIP) latrines.
RYAN, B.A. MARA, D.D. (1983): Ventilated Improved Pit Latrines: Vent Pipe Design Guidelines. (= UNDP Interregional Project INT/81/047 ). Washington: The World Bank, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) URL [Accessed: 31.01.2014]A Guide to the Development of On-site Sanitation
The publication presents appropriate technologies for sanitation and highlights socio-economic aspects of planning and implementing. Emphasis is given to household-level sanitation improvements for urban areas, as well as rural areas and small communities. Background information on sanitation, in-depth technical information on the design, construction, operation and maintenance and project planning and development processes involved in projects and programmes complement the book.
WHO (1992): A Guide to the Development of On-site Sanitation. Geneva: World Health Organisation (WHO) URL [Accessed: 14.04.2010]Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume IV. Excreta and Greywater Use in Agriculture
Volume IV of the Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater recognizes the reuse potential of wastewater and excreta (including urine) in agriculture and describes the present state of knowledge as regards potential health risks associated with the reuse as well as measures to manage these health risks following a multi-barrier approach.
WHO (2006): Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume IV. Excreta and Greywater Use in Agriculture. Geneva: World Health Organisation (WHO) URL [Accessed: 09.05.2019] PDFPit Latrines and Their Impacts on Groundwater Quality: a systematic Review
This study reviews empirical studies on the impact of pit latrines on groundwater quality and identifies knowledge gaps regarding the potential and consequences of groundwater contamination by latrines.
Graham, J. ; Polizotto, M.L. (2013): Pit Latrines and Their Impacts on Groundwater Quality: a systematic Review. Advance Publication. المُدخلات: Environmental Health Perspectives: URL [Accessed: 09.04.2013]Available Sanitation Technologies for Rural and Peri-Urban Africa
The presentation allows for a good overview on existing types of pit latrines in Africa, but also on other types of sanitation technologies such as the conventional flush toilet, the pour flush toilet, and the urine diversion dehydration toilet (UDDT).
MORGAN, P. (2007): Available Sanitation Technologies for Rural and Peri-Urban Africa. Stockholm : Ecological Sanitation Research (EcoSanRes), Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI) URL [Accessed: 20.06.2013]How We Made an Arborloo Which Can be Upgraded to VIP
The Arborloo is the simplest ecological toilet and is an effective way of starting low cost sanitation programmes. It also demonstrates how valuable the nutrients in human excreta can be. This presentation gives an insight into the following aspects: - What is anArborloo? - What is an Arborloo? - Stages in life of the Arborloo - Planting trees on or near Arborloo pits - Stages in the construction of the Arborloo - Vent pipes - Construction of the Blair VIP
SHANGWA, A. MORGAN, P. (2008): How We Made an Arborloo Which Can be Upgraded to VIP. The Chisungu Primary School Water and Sanitation project. Stockholm : Ecological Sanitation Research (EcoSanRes), Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI) URL [Accessed: 19.06.2013]A Directory of Environmentally Sound Technologies for the Integrated Management of Solid, Liquid and Hazardous Waste for Small Island Developing States (SIDS) in the Pacific Region
This directory is part of UNEP collaboration with SIDS on the implementation of the Waste Management chapter of the Barbados Programme of Action. It focuses primarily on proven sound environmental technologies for solid, liquid and hazardous waste management plus those currently successfully being used in SIDS within the Pacific Region.
UNEP (2002): A Directory of Environmentally Sound Technologies for the Integrated Management of Solid, Liquid and Hazardous Waste for Small Island Developing States (SIDS) in the Pacific Region. The Hague: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) URL [Accessed: 28.03.2012]The ventilated improved pit (VIP) latrine
This poster shows a nice drawing how a VIP works and what needs to be considered.
WATERAID (n.y): The ventilated improved pit (VIP) latrine. London: WaterAid URL [Accessed: 08.12.2010]Ventilated Improved Pit Latrines
Short brief on the construction of ventilated improved pit latrines
PRACTICAL ACTION (n.y): Ventilated Improved Pit Latrines . (= Technical Briefs ). Bourton on Dunsmore: Practical Action, Schumacher Centre for Technology & Development URL [Accessed: 05.01.2011]Latrine Slabs
This poster is part of the series of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene posters designed by the Water, Engineering and Development Center of Loughborough University.
REED, B. SHAW, R. (2013): Latrine Slabs. (= WEDC Posters , 1 ). London: Water, Engineering and Development Center (WEDC) URL [Accessed: 07.08.2013]Simple Pit Latrines
This poster is part of the series of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene posters designed by the Water, Engineering and Development Center of Loughborough University.
REED, B. SHAW, R. (2013): Simple Pit Latrines. Poster. (= WEDC Posters , 10 ). London: Water, Engineering and Development Center (WEDC) URL [Accessed: 28.08.2013]Emptying Pit Latrines
This technical brief describes several possibilities of emptying pit latrines and helps to find the most suitable method.
PICKFORD, J. SHAW, R. (1997): Emptying Pit Latrines. (= Technical Briefs, No. 54 ). Loughborough: Water and Environmental health at London and Loughborough (WELL) URL [Accessed: 28.05.2019]Latrine Slabs and Seats
This technical brief describes pit latrines and possible slabs and seats to cover them.
WELL (n.y): Latrine Slabs and Seats. (= WELL Technical Briefs , 45 ). Loughborough: Water and Environmental health at London and Loughborough (WELL) URL [Accessed: 26.04.2010]The Microbial Contamination of Water Supplies from Pit Latrines
This factsheet describes the microbiological contamination of water supplies. It gives an overview on pathogens and its characteristics as well as methods to reduce the risk of contamination.
WELL (2006): The Microbial Contamination of Water Supplies from Pit Latrines. (= WELL Fact-sheets ). Loughborough: Water and Environmental health at London and Loughborough (WELL) URL [Accessed: 07.12.2010]WASHCost Mozambique: How much does it cost to build a traditional latrine?
This video by IRC’s WASHCost project examines the full costs of building traditional latrines in Mozambique. There, cost data for planning are collected by local authorities. They gather the information around households in the area. Households are visited and their sanitation situation is assessed. This gives a clear picture of what is actually achieved.

