المُلخص التنفيذي
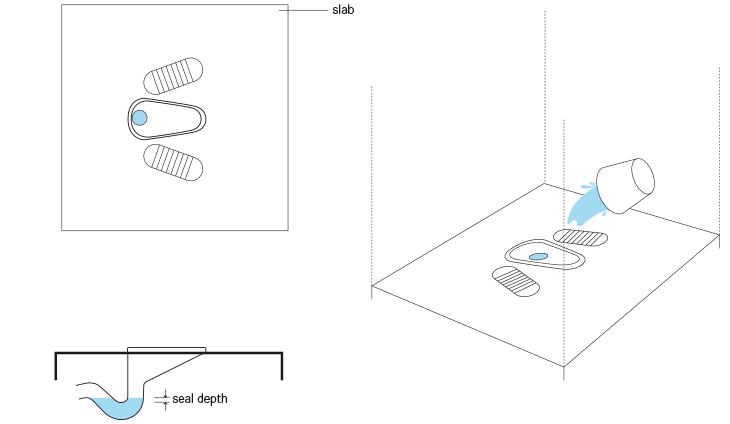
مِرحاض الدفْق بالصب Pour Flush Toilet مثل مِرحاض الدفْق بالسيفون المعتاد ، غير أن المياه يتم صبها من قِبَل المُستخدم بدلًا من أن تأتي من خزان المياه المخصص لذلك، فعندما لا يكون الإمداد بالمياه متواصل ومستمر فمن الممكن أن يتحول أي مِرحاض دفْق بالسيفون الى مِرحاض دفْق بالصب.
يحتوي مِرحاض الدفْق بالصب -مثل مِرحاض الدفْق بالسيفون- على حاجز المائي Water Seal (أو كوع الرائحة) يمنع الروائح والذباب من الارتداد والرجوع مرة أخرى من خلال الأنبوب. تُصَب المياه إلى داخل فتحة المرحاض لتنظيفه من فضلات الجسم، وعادةً ما يكفي 2 إلى 3 لترات من المياه تقريبًا لهذه العملية. ويجب أن تكون كمية المياه وقُوَّتِها كافية لتحريك فضلات الجسم (وصَبُّ الماء من أعلى يساعد على ذلك) فوق الحاجز المائي، الذي يكون على شكل مُنحني.
يُمكن استخدام كلٍّ من قواعد المراحيض Pedestals والبلاطات الأرضية المُستخدمة للجلوس فوقها بوضعية القُرفصاء Squatting pans في مراحيض الدفْق بالصب، وتسببت زيادة الطلب عليه في زيادة كفاءة المُصَنِّعين المحليين في إنتاج كميات كبيرة ذات أسعار معقولة من بلاطات ومراحيض الدفْق بالصب.
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
| مواد التنظيف الجافة , مياه تنظيف الشرج , البول , مياه الدفق , البراز |
المياه السوداء |

المُلاءَمَة
يُلائم مِرحاض الدفْق بالصب المُستخدمين الذين يُفضلون الجلوس المباشر على القاعدة، أو الجلوس بوضعية القُرفصاء دون ملامسة القاعدة )قواعد المراحيض أو البلاطة الأرضية(، وكذلك يُلائم المُستخدمين الذين يستخدمون المياه للاغتسال، إلا أنه يكون ملائمًا فقط في حال تَوَفُّر مصدر دائم للمياه. ويتطلب مِرحاض الدفْق بالصب مياه أقل -بكثير- من مِرحاض الدفْق بالسيفون التقليدي، غير أنه -نظرًا لقلة كمية المياه المُستخدمة- فإن مِرحاض الدفْق بالصب قد يتعرض للانسداد بسهولة أكبر، ومن ثَمَّ فإنه يتطلب المزيد من الصيانة.
إذا توفرت المياه؛ فإن هذا النوع من المراحيض يكون مُلائمًا للاستخدمات الخاصة والعامة على حد سواء.
اعتبارات التصميم
يجب أن يكون ميل الحاجز المائي Water Seal )أو كوع الرائحة) الموجود في أسفل بلاطة أو مِرحاض الدفْق بالصب حوالي °25 على الأقل، ويجب أن تُصنَّع الحواجز المائية من البلاستيك أو السيراميك؛ لتمنع الانسدادات، ولتسهل من عملية التنظيف )فالخرسانة قد تسبب الانسدادات بسهولة إذا كانت خشنة الملمس(.
ويُحدِّد شكل S الذي يتخذه الحاجز المائي كمية المياه اللازمة للدفْق، ويكون الارتفاع الأمثل للحاجز المائي هو 2 سنتيمتر تقريبًا لتقليل كمية المياه اللازمة لتنظيف المِرحاض من فضلات الجسم، ويجب أن يكون قُطر مصيدة فضلات الجسم 7 سنتيمتر تقريبًا.
الجوانب الصحية / القبول
يَحول مِرحاض الدفْق بالصب دون رؤية المُستخدم لفضلات المُستخدمين السابقين وكذلك يقيه من التعرض لرائحتها. ومن ثَمَّ فإنه عادةً ما يتم قبوله بشكل جيد. وفي حال قيام الحاجز المائي بوظيفته بشكل جيد، فينبغي ألا تكون هناك أي رائحة تقريبًا وأن يكون المِرحاض نظيفًا ومُريحًا في استخدامه.
التشغيل والصيانة
نظرًا لعدم وجود أيَّة أجزاء ميكانيكية؛ فإن مِرحاض الدفْق بالصب مَتين جدًّا ونادرًا ما يحتاج لصيانة، وبغض النظر عن حقيقة أنه مِرحاض قائم على استخدام المياه، فإنه يجب أن يتم تنظيفه بانتظام؛ للحفاظ على النظافة الصحية، ومنع تراكم الأوساخ. ولتقليل احتياجات المياه اللازمة للدفْق ولمنع الانسداد يُوصَى بأن يتم تجميع مواد التنظيف الجافة، وكذلك المُنتجات التي تُستخدم للنظافة أثناء الطمث بشكل منفصل، وألا يتم رميها داخل المِرحاض.
المياه ،الصرف الصحي النظافة الصحية وظروف الإقامة في السجون
بناء الحمامات وطرق تحسينها وصيانتها
الصرف الصحي الموقعي والمركزي - للمدن والتجمعات السكانية الصغيرة
Bogs, Baths and Basins: The Story of Domestic Sanitation
Emergency Sanitation: Assessment and Programme Design
This book has been written to help all those involved in planning and implementing emergency sanitation programmes. The main focus is a systematic and structured approach to assessment and programme design. There is a strong emphasis on socio-cultural issues and community participation throughout.Includes an extensive “guidelines” section with rapid assessment instructions and details on programme design, planning and implementation.
HARVEY, P. BAGHRI, S. REED, B. (2002): Emergency Sanitation: Assessment and Programme Design. Loughborough: Water, Engineering and Development Centre (WEDC) URL [Accessed: 31.05.2019]The Design of Pour-Flush Latrines
The technical note was produced as a joint United Nations Development Programme and World Bank contribution to the International Drinking Water Supply and Sanitation Decade. It sets out guidelines for the design of pour-flush latrines, based upon TAG's (Technology Advisory Group) experience in India, Brazil and elsewhere. These guidelines have been written especially for use in developing countries. Consequently, emphasis has been placed on achieving simplicity of design consistent with reliability of operation.
MARA, D.D. (1985): The Design of Pour-Flush Latrines. (= TAG Technical Note No. 15 ). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and World Bank URL [Accessed: 02.08.2010]Low-cost Urban Sanitation
This book covers the public health, technical, socioeconomic, sociocultural and institutional aspects of sanitation in towns and cities of developing countries. The text features excreta-related diseases and the use of sanitation to reduce their transmission. The sanitation technologies covered in detail are VIP latrines, pour-flush toilets, septic tanks, settled sewerage and simplified sewerage, with additional chapters on sullage disposal, pit emptying, and sewage treatment and reuse. Sociocultural constraints on sanitation systems and their socioeconomic costing are described, together with hygiene education, which is essential in order to achieve maximum benefits to health. The text also explains how to choose the most appropriate sanitation option for a given low-income community. Finally, institutional aspects are reviewed, including effective sanitation programme planning, monitoring and evaluation.
MARA, D. (1996): Low-cost Urban Sanitation. United Kingdom: WileyManual on the design, construction and maintenance of low-cost pour-flush water seal latrines in India
This manual has been prepared for agencies, contractors and individuals involved in various aspects of the low-cost pour-flush water seal latrine programme in India. The inherent principles are, however, of general application; with minor modifications, the technical details can be readily adapted to meet the needs of different areas, particularly where water is used for anal cleansing. The manual presents salient features in regards to design, construction and maintenance as well as the administration of low-cost pour-flush water seal latrines with offset twin pits. It contains extensive drawings, tables of quantities for construction materials used for different designs as well as standard forms for by-laws and for general information on project administration and supervision.
ROY, A.K. CHATTERJEE, P.K. GUPTA, K.N. KHARE, S.T. RAU, B.B. SINGH, R.S. (1984): Manual on the design, construction and maintenance of low-cost pour-flush water seal latrines in India. (= TAG technical note; no. 10 ). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and World Bank URL [Accessed: 01.06.2010]Shital Ceramic Works Company
Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFAssessment of Urine Diverting Ecosan Toilets in Nepal
This study assesses ecosan toilets and their implementation in different areas of Nepal from an n social, technical and financial point of view. It gives recommendations in the view of scaling-up ecosan in Nepal.
WATERAID (2008): Assessment of Urine Diverting Ecosan Toilets in Nepal. Kathmandu: WaterAid Nepal URL [Accessed: 31.05.2019]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFExcreta Disposal in Emergencies. A Field Manual
In this manual existing, innovative and new technologies and approaches for excreta disposal in emergency situations are investigated. It provides practical guidance on how to select, design, construct and maintain appropriate excreta disposal systems to reduce faecal transmission risks and protect public health in emergency situations.
HARVEY, P.A. (2007): Excreta Disposal in Emergencies. A Field Manual. Leicestershire: WEDC Loughborough University URL [Accessed: 29.07.2011]Low-cost Urban Sanitation
This book covers the public health, technical, socioeconomic, sociocultural and institutional aspects of sanitation in towns and cities of developing countries. The text features excreta-related diseases and the use of sanitation to reduce their transmission. The sanitation technologies covered in detail are VIP latrines, pour-flush toilets, septic tanks, settled sewerage and simplified sewerage, with additional chapters on sullage disposal, pit emptying, and sewage treatment and reuse. Sociocultural constraints on sanitation systems and their socioeconomic costing are described, together with hygiene education, which is essential in order to achieve maximum benefits to health. The text also explains how to choose the most appropriate sanitation option for a given low-income community. Finally, institutional aspects are reviewed, including effective sanitation programme planning, monitoring and evaluation.
MARA, D. (1996): Low-cost Urban Sanitation. United Kingdom: WileyHow to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation
The purpose of this guide is to assist local contracting authorities and their partners in identifying those sanitation technologies best suited to the different contexts that exist within their town. The first part of the guide contains a planning process and a set of criteria to be completed; these assist you in characterizing each area of intervention so that you are then in a position to identify the most appropriate technical solutions. The second part of the guide consists of technical factsheets which give a practical overview of the technical and economic characteristics, the operating principle and the pros and cons of the 29 sanitation technology options most commonly used in sub-Saharan Africa.
MONVOIS, J. GABERT, J. FRENOUX, C. GUILLAUME, M. (2010): How to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation. (= Six Methodological Guides for a Water and Sanitation Services' Development Strategy , 4 ). Cotonou and Paris: Partenariat pour le Développement Municipal (PDM) and Programme Solidarité Eau (pS-Eau) URL [Accessed: 19.10.2011]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFHow to Manage Public Toilets and Showers
The purpose of this decision-making aid is to provide practical advice and recommendations for managing toilet blocks situated in public places. It is primarily aimed at local decision-makers in developing countries and at their partners (project planners and managers).
TOUBKISS, J. (2010): How to Manage Public Toilets and Showers. (= Six Methodological Guides for a Water and Sanitation Services' Development Strategy , 5 ). Cotonou and Paris: Partenariat pour le Développement Municipal (PDM) and Programme Solidarité Eau (pS-Eau) URL [Accessed: 19.10.2011]Available Sanitation Technologies for Rural and Peri-Urban Africa
The presentation allows for a good overview on existing types of pit latrines in Africa, but also on other types of sanitation technologies such as the conventional flush toilet, the pour flush toilet, and the urine diversion dehydration toilet (UDDT).
MORGAN, P. (2007): Available Sanitation Technologies for Rural and Peri-Urban Africa. Stockholm : Ecological Sanitation Research (EcoSanRes), Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI) URL [Accessed: 20.06.2013]Pour-flush toilets with biogas plant at DSK Training Institute. Gujarat, India - Draft
The project described aimed at avoiding manual scavenging of faecal products and at improving the sanitation situation at the Navsarjan Vocational Training Institute. Now greywater is separately treated and reused in the garden while the urine and faeces (blackwater) are directly introduced into a biogas plant. Digested sludge is dried on basic drying beds and used as compost for the garden. UDDTs were also installed. The concept was implemented and evaluated for its social and cultural acceptability, sustainable and hygienic safety.
WAFLER, M. HEEB, J. STAUB, A. OLT, C. (2009): Pour-flush toilets with biogas plant at DSK Training Institute. Gujarat, India - Draft. (= SuSanA - Case Studies ). Eschborn: Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) URL [Accessed: 25.04.2010]Assessment of Urine Diverting Ecosan Toilets in Nepal
This study assesses ecosan toilets and their implementation in different areas of Nepal from an n social, technical and financial point of view. It gives recommendations in the view of scaling-up ecosan in Nepal.
WATERAID (2008): Assessment of Urine Diverting Ecosan Toilets in Nepal. Kathmandu: WaterAid Nepal URL [Accessed: 31.05.2019]Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Lecture Notes
Lecture notes on technical and non-technical aspects of sanitation systems in developing countries.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Lecture Notes . (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 4 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC)Latrine Slabs
This poster is part of the series of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene posters designed by the Water, Engineering and Development Center of Loughborough University.
REED, B. SHAW, R. (2013): Latrine Slabs. (= WEDC Posters , 1 ). London: Water, Engineering and Development Center (WEDC) URL [Accessed: 07.08.2013]Simple Pit Latrines
This poster is part of the series of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene posters designed by the Water, Engineering and Development Center of Loughborough University.
REED, B. SHAW, R. (2013): Simple Pit Latrines. Poster. (= WEDC Posters , 10 ). London: Water, Engineering and Development Center (WEDC) URL [Accessed: 28.08.2013]Smart Sanitation Solutions
Smart Sanitation Solutions presents examples of low-cost household and community-based sanitation solutions that have proven effective and affordable. A wide range of innovative technologies for toilets, collection, transportation, treatment and use of sanitation products that have already helped thousands of poor families to improve their lives is illustrated.
NWP (2006): Smart Sanitation Solutions. Examples of innovative, low-cost technologies for toilets, collection, transportation, treatment and use of sanitation products. (= Smart water solutions ). Amsterdam: Netherlands Water Partnership (NWP) URL [Accessed: 09.05.2019]http://www.youtube.com
This is a lecture By Duncan Mara on Pour Flush Toilets for use in developing countries.
A Better Toilet For A Cleaner World
The sanitation technology paradigm is under review, as past approaches are not sufficient or affordable to close the sanitation coverage gap. In 2011, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) launched the bold Reinvent the Toilet Challenge (RTTC) program to promote the development of radically new innovations to address the sanitation challenge on a large-scale. The RTTC is premised on the fact that ground-breaking improvements are required in toilet design and fecal sludge management to close the urban sanitation gap. The RTTC is focused on reinventing the flush toilet, a break-through public health invention that has not changed substantially since the first flush toilet patent was issued in 1775.

