المُلخص التنفيذي
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
التدفقات السائلة الخارجة , مياة الامطار |
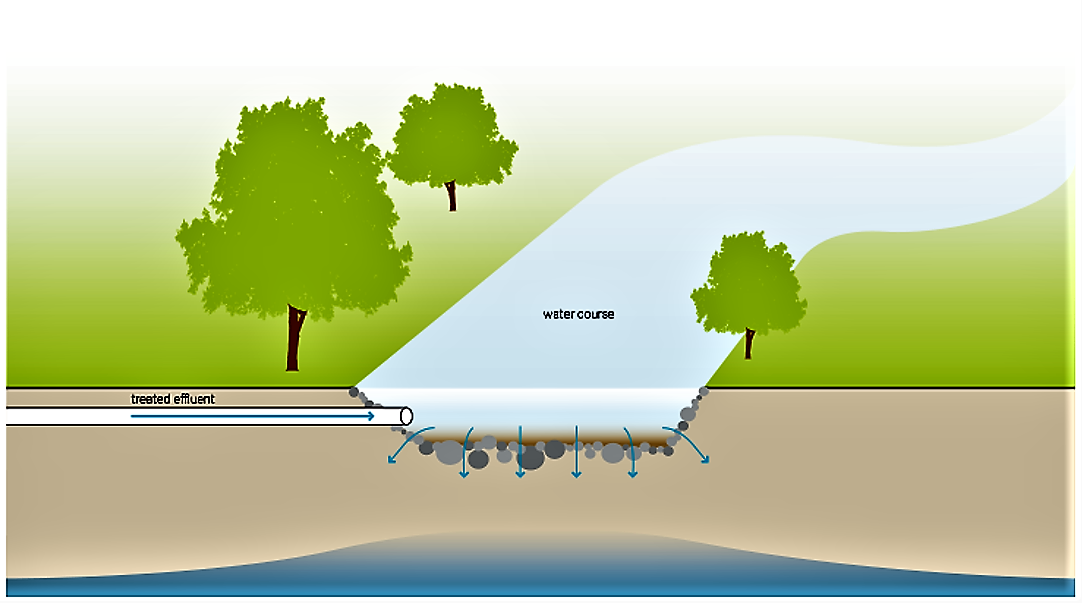
Introduction
The use of the surface water body, whether it is for industry, recreation, spawning habitat, etc., will influence the quality and quantity of treated wastewater that can be introduced without deleterious effects.
Alternatively, water can be discharged into aquifers. Groundwater recharge is increasing in popularity as groundwater resources deplete and as saltwater intrusion becomes a greater threat to coastal communities. Although the soil is known to act as a filter for a variety of contaminants, groundwater recharge should not be viewed as a treatment method. Once an aquifer is contaminated, it is next to impossible to reclaim it.
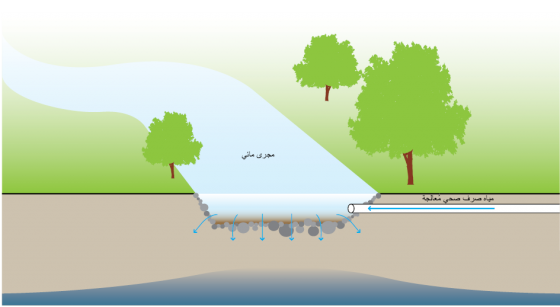
اعتبارات التصميم
يجب التأكد من عدم تجاوز القدرة الاستيعابية للمسطحات المائية المُستَقبِلة، بمعنى آخر يجب التأكد من أن المسطح المائي المُستَقبِل يمكنه استيعاب كمية المُغذّيات المضافة دونَ أن يمثل ذلك حِملًا زائدًا عليه. يجب أن تتم المتابعة والتحكم الدقيق في العوامل المتغيرة كالعكارة، ودرجة الحرارة، والعوالق، والاحتياج الحيوي للأكسجين BOD، والنيتروجين، والفوسفور )ومتغيرات أخرى(، قبل تصريف أي مياه في مورد طبيعي. ويجب الاستعانة بالسلطات المحلية من أجل تحديد معدلات الصرف المسموح بها حسب العوامل المرتبطة بالأمر، حيث يمكن أن تتفاوت على نطاق واسع. ويمكن أن تحتاج المناطق ذات الحساسية العالية لتقنية مُعالجة لاحقة مثل المُعالجة بالكلور،) للتوافق مع الحدود والمعايير الميكروبيولوجية Microbiological Limits (أو الميكروحيوية، أو المجهرية الحيوية.
تتوقف جودة المياه المستخرجة من خزان المياه الجوفي المعاد شحنه على جودة مياه الصرف التي صُرِّفت فيه وطريقة إعادة الشحن وخصائص الخزان الجوفي ومدة التخزين ونسب الخلط مع المياه الأخرى وتاريخ النظام. يجب أن يتم التحليل الدقيق لهذه العوامل قبل أن يتم بدء أي مشروع لإعادة الشحن.
الجوانب الصحية / القبول
بشكل عام، يتم احتجاز الكاتيونات Cations الماغنسيوم Mg2+، والبوتاسيوم , K+والأمونيوم NH4+ والمواد العضوية في تكتلات صلبة، في حين ستبقى الملوثات الاخرى )مثل النترات( في المياه. وهناك العديد من النماذج لإمكانية مُعالجة الملوثات والكائنات الحية الدقيقة، ولكن نادرًا ما يكون مُجديًا فحص مجموعة كبيرة من عوامل نوعية المياه المُستخرجة. وبالتالي يجب تحديد مصادر المياه الصالحة وغير الصالحة للشرب بوضوح، وأن يتم نمذجة أهم العوامل، وعمل تقييم للمخاطر.
التشغيل والصيانة
تُعتبر المتابعة وأخذ العينات بشكل منتظم من الأشياء المهمة لضمان الالتزام بالقوانين وضمان متطلبات الصحة العامة. وقد تكون هناك حاجة لبعض أعمال الصيانة الميكانيكية، وذلك اعتمادًا على طريقة إعادة الشحن.
حلقة العمل القومية حول حصاد المياه والتغذية الجوفية الاصطناعية في الوطن العربي
Language: Arabic
المياة العادمة المدنية كمصدر لتغذية المياه الجوفية وتقييم ادارة المخاطروالمنافع
Language: Arabic
حماية نوعية المياة الجوفية تعريف الاستراتيجية وتحديد الاولويات
Language: Arabic
Guidelines for Assessing the Risk to Groundwater from On-Site Sanitation
Many people in developing countries rely upon untreated groundwater supplies for their drinking water (e.g. from drilled boreholes, tube wells, dug wells or springs). The introduction of on-site sanitation systems might lead to groundwater contamination. The purpose of this manual is to provide guidance on how to assess and reduce the risk of contamination of groundwater supplies from on-site sanitation systems and is aimed at those responsible for planning low cost water supply and sanitation schemes.
ARGOSS (2001): Guidelines for Assessing the Risk to Groundwater from On-Site Sanitation. (= Commissioned Report , 142 ). Keyworth: British Geological Survey URL [Accessed: 11.05.2019]The Artificial Recharge of Groundwater
Drainage Ditches Flanking the Path into and out of Wholeo Dome
Typical spreading basin
Artificial Recharge: Methods, Hydraulics, and Monitoring
Groundwater Recharge from Run-off, Infiltration and Percolation
Wastewater Engineering, Treatment and Reuse
Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFSourcebook of Alternative Technologies for Freshwater Augmentation in Some Countries in Asia (Technical Publication)
Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume III. Wastewater and Excreta Use in Aquaculture
Volume III of the Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater deals with wastewater and excreta use in aquaculture and describes the present state of knowledge regarding the impact of wastewater-fed aquaculture on the health of producers, product consumers and local communities. It assesses the associated health risks and provides an integrated preventive management framework.
WHO (2006): Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume III. Wastewater and Excreta Use in Aquaculture. Geneva: World Health Organisation URL [Accessed: 08.05.2019]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFGroundwater recharge with recycled municipal wastewater: Criteria for health related guidelines
This article aims to highlight some principles related to aquifer recharge with recycled water, and to propose a simple approach to health related guidelines that take into account existing water regulations and guidelines.
BRISSAUD, F. (1999): Groundwater recharge with recycled municipal wastewater: Criteria for health related guidelines. France: Hydrosciences, MSE, Univ. Montpellier II, 34095 Montpellier Cedex 05Management of aquifer recharge and discharge processes and aquifer storage equilibrium
This paper draws attention to case studies from a range of hydro-geological, climatic and societal settings where innovative management has been successful in reversing groundwater storage declines (or increases). Informing and engaging stakeholders in governance has resulted in more resilient outcomes that take better account of local needs. Importantly, in many settings local action by motivated communities has run ahead of state and national policies and been highly effective in managing groundwater storage, increasing farm incomes and protecting the environment.
FAO GEF IAH IHP World Bank (2012): Management of aquifer recharge and discharge processes and aquifer storage equilibrium. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) URL [Accessed: 08.04.2013]Artificial Recharge and Rainwater Harvesting
Innovations in Groundwater Recharge. Water Policy Briefing. IWMI-TATA Water Policy Program
This brochure gives an overview on different low-cost aquifer recharge solutions based on the results from a 10-year pilot project in Uttar Pradesh. It indicates a practical and low-cost way to conserve and rejuvenate falling groundwater reserves.
IWMI (2002): Innovations in Groundwater Recharge. Water Policy Briefing. IWMI-TATA Water Policy Program. Vallabh Vidyanagar: International Water Management Institute URL [Accessed: 21.03.2019]Water Harvesting
Water harvesting has been practiced successfully for millennia in parts of the world – and some recent interventions have also had significant local impact. Yet water harvesting’s potential remains largely unknown, unacknowledged and unappreciated. These guidelines cover a wide span of technologies from large-scale floodwater spreading to practices that collect and store water from household compounds.
MEKDASCHI STUDER, R. LINIGER, H. (2013): Water Harvesting. Guidelines to Good Practice. Bern/Amsterdam/Wageningen/Rome: Centre for Development and Environment (CDE), Rainwater Harvesting Implementation Network (RAIN), MetaMeta, The International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) URL [Accessed: 12.03.2019] PDFGuide on Artificial Recharge to Groundwater
This document provides guidance on artificial recharge techniques and designs and the planning and monitoring of artificial recharge projects.
MINISTRY OF WATER RESOURCES (2000): Guide on Artificial Recharge to Groundwater. New Delhi: Central Ground Water Board URL [Accessed: 21.03.2019]Chapter 9: Artificial Groundwater Recharge
This is a chapter on a rainwater-harvesting manual from the Public Health Engineering Department in India. It gives an extensive overview on different groundwater recharge technologies and approaches.
PHEDM (n.y): Chapter 9: Artificial Groundwater Recharge. المُدخلات: PHEDM (n.y): Rain Water Harvesting ManuaI. Meghalaya State Centre, India: . URL [Accessed: 26.05.2019]Small Community Water Supplies: Technology, People and Partnership: Artificial Recharge - Chapter 6
This book provides a general introduction to a wide range of technologies. Among the topics covered are: planning and management of small water supplies, community water supplies in Central and Eastern European countries, water quality and quantity, integrated water resources management, artificial recharge, rainwater harvesting, spring water tapping, groundwater withdrawal, water lifting, surface water intake, water treatment, aeration, coagulation and flocculation, sedimentation, multi-stage filtration, desalination technology, disinfection, household level water treatment, technologies for arsenic and iron removal from ground water, and emergency and disaster water supply. Chapter 6: Artificial Recharge
SMET, J. ; WIJK, C. van (2002): Small Community Water Supplies: Technology, People and Partnership: Artificial Recharge - Chapter 6. The Hague: International Water and Sanitation Centre (IRC) URL [Accessed: 21.03.2019]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFGroundwater recharge with recycled municipal wastewater: health and regulatory considerations
This case study on groundwater recharge with recycled wastewater focuses on quantifying possible health implications.
ASANO, T. COTRUVO, J. (2004): Groundwater recharge with recycled municipal wastewater: health and regulatory considerations. Davis: Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California URL [Accessed: 15.04.2011]Water and Community Development. Rainwater harvesting and groundwater recharge. A sustainable approach to human development at the global level
Article on rainwater harvesting and groundwater recharge in India and other countries.
DAVIES, R. ROY, B. (2004): Water and Community Development. Rainwater harvesting and groundwater recharge. A sustainable approach to human development at the global level. London: International Business Leaders Forum URL [Accessed: 22.03.2019] PDFArtificial Recharge of Groundwater
This website provides the online-version of the Sourcebook of Alternative Technologies for Freshwater Augmentation of the United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP).
