Executive Summary
Business growth and scaling go hand in hand. Different strategies are applicable to grow and develop your business by innovating in the areas of product/service and your market(s).
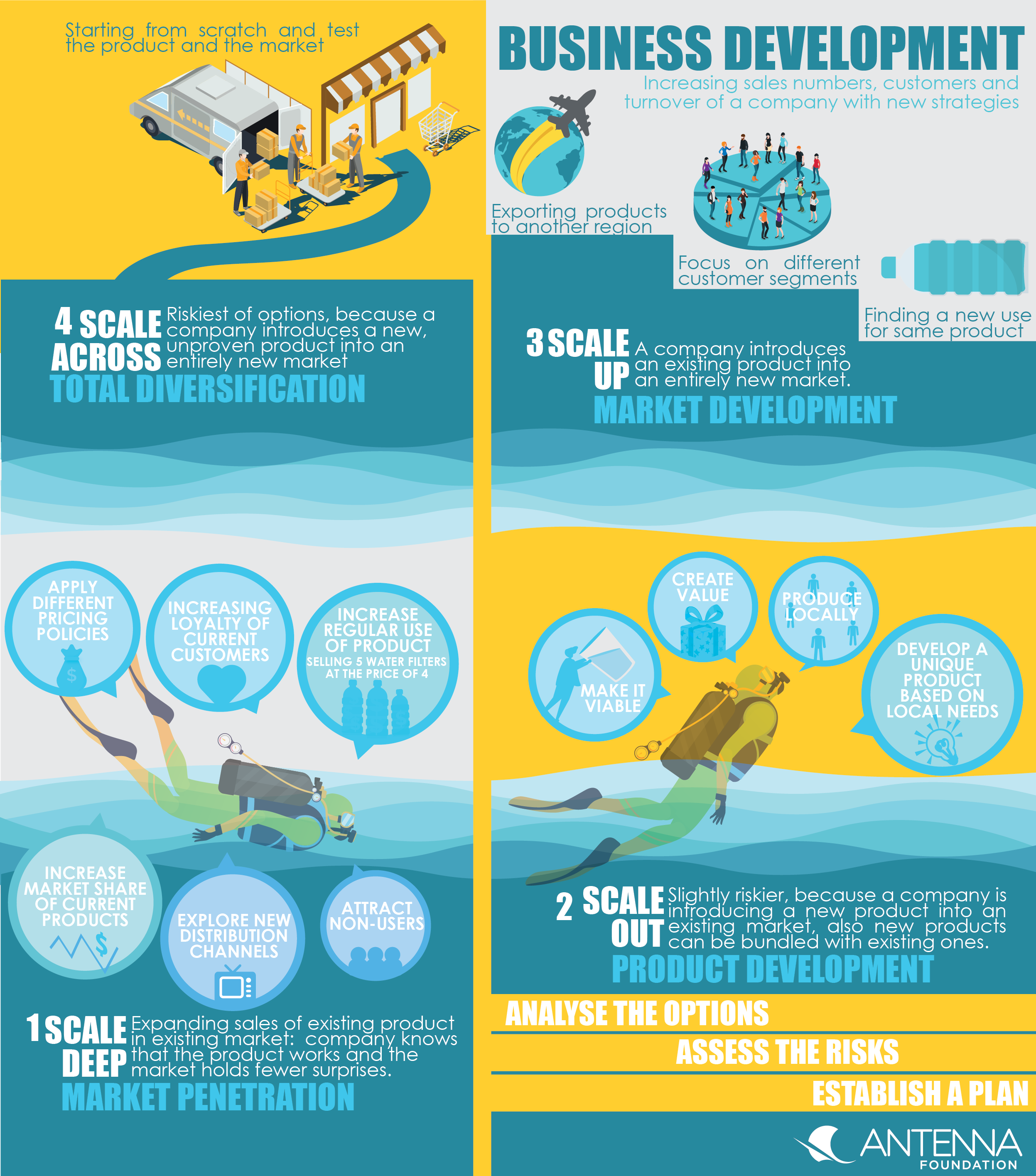
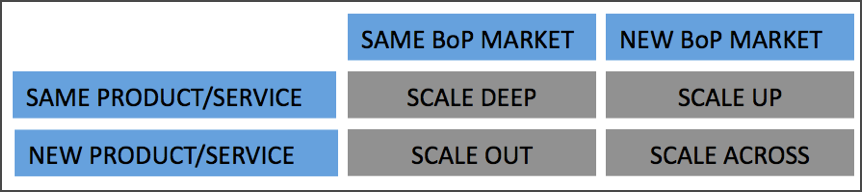
There are four different ways to grow: A company can grow with the old product in existing markets and increase the market penetration (scale deep) introduce a new product in existing markets (scale out), enter a new market with an existing product (scale up) or introduce a new product in a new market (scale across) (MIT PRACTICAL IMPACT ALLIANCE, 2017).
Developing new offerings and markets is a challenging process, and most start-ups fail when they are about to grow. This factsheet elaborates on the suggested strategies and shows how to prevent your safe water business from failing when developing and implementing growth strategies.
The two case studies of MinErgy and Pakoswiss show how a safe water product development strategy has been practically implemented in India and Pakistan.
What is business development?
Business development means increasing sales numbers, customers and turnover of a company with new strategies comprising of communication, marketing, product development etc. A variety of concepts and tools have been developed to facilitate business development. One of the new and most relevant publications is the document “Ready, Steady, Scale” by the MIT D-Lab, the BOP Innovation Centre and the Danone Communities. This study is based on the Ansoff Matrix (see the figure above), developed in 1957 by Igor Ansoff as a marketing planning tool that has been used for different applications over the entire globe. The matrix provides a useful framework for considering strategic moves for business development. It can be applied to look at opportunities to grow revenue for a business through developing new products and services or "tapping into" new markets. The approach distinguishes thereby whether the products and markets that a company is focusing on are existing or new and what strategy shall be applied in order to penetrate the respective markets. Hence the matrix offers four alternative marketing strategies: market penetration (scale deep), product development (scale out), market development (scale up) and market/product diversification (scale across).
Why is business development necessary?
Every business, also a safe water business, needs to continuously innovate in order to stay ahead of competition. Although some businesses may grow steadily with the same product and offering, many are struggling when continuing to offer the same unchanged product and service for years, implying a decrease in sales and reduced profits. Sometimes it is also not sufficient to have only one product generate enough returns to break-even. A key reason for such developments usually lies in consumers’ “needs and wants” that continuously change (MIT Practical Impact Alliance, 2017). Firms should respond to these changes through the products and services they offer. Otherwise, consumers will switch to products or services of competitors that satisfy their "needs and wants" in a better way. Considering new products and services can allow social enterprises to gain a new revenue stream, new customers and further growth. It can also help social enterprises to overcome seasonal business challenges or diversify the risk of competition joining one particular market. Keep in mind that any of these changes bring along costs and new risks (see risk management).
For whom is business development interesting?
The concept of business development is interesting for for-profit and socially oriented social enterprises aiming to grow. Interested initiatives may be considering one of the 4 options: a) entering new customer segments within the currently present market, thinking of b) entering new markets with existing products or c) new products and services in existing or d) in new markets and thus gain further financial stability or/or growth.
How can business development be applied?
First, a company should analyse their options and plot the approaches of promising options on the Matrix.
Second, the company should assess the risks (and chances) involved with each option. A systematic assessment – often supported with marketing intelligence and trials – should explore the four growth options together with a thorough risk analysis and establish a complementary contingency plan (see risk management). Additional research and discussions with partners can allow you to develop several choices to determine which option is right for the company and your organisation. Subsequently concrete examples and strategies are outlined for each of the four market development directions (WAIBEL, 2012; RILEY, 2016; OXFORD COLLEGE OF MARKETING, 2016):
1. Market penetration (scale deep) represents usually the safest of the four options. Here, a company can focus on expanding sales of an existing product in an existing market: the company knows that the product works and the market holds fewer surprises.
In practice, such a strategy could entail following examples:
- Increasing the loyalty of current customers or attracting non-users to purchase the offered product or service.
- Increase the regular use of the product by existing customers, for example by introducing loyalty schemes. E.g. getting every 10th chlorine bottle for free, selling 5 water filters at the price of 4 etc.
- Maintain or increase the market share of current products – this can be achieved through a combination of pricing strategy, advertising, sales promotion and perhaps more resources dedicated to sales department. For more information see case study on Hydrologic’s sales process.
- Explore new distribution channels to reach different market segments.
- Apply different pricing policies to attract different customers or create new market segments.
2. With market development (scale up), a company introduces an existing product into an entirely new market.
Practical examples:
- Exporting a proven safe water product or service into another country or region (e.g. Hydrologic selling to Vietnam and Myanmar).
- This can also be achieved by finding a new use for the same product (e.g. using chlorine for disinfection in hospitals).
- Focus on different customer segments as well as developing new sales channels, or a combination of those.
3. Product development (scale out) is slightly riskier, because a company is introducing a new product or service into an existing market. This strategy implies the development of new products or the modification of existing ones and is usually a direct response to the needs of the market. Often products can also be bundled with existing products to offer a broader variety to accordingly reduce costs and increase profitability due to an increased product portfolio.
Practical examples:
- A safe water kiosk is developing a new water testing kit.
- A safe water company starts delivering another water filter.
- Micro-franchisees sell chlorine flasks and soaps, produced by the same company or as resellers from other companies.
- A safe water kiosk sells a totally different product (e.g. attractive food items or solar devices) and thus diversifies the range of products to generate higher revenues and possibility to break-even.
To keep in mind for product development for BoP customers:
- Produce locally
- Create value for customers
- Make it viable
For more information see human centred design.
4. Total Diversification (scale across) is the riskiest of the four options, because a company introduces a new, unproven product into an entirely new market that they may not know and might not understand yet. This procedure may require substantial resources and a long breath.
Practical examples:
- Develop and sell a new safe water product (in a new country or area).
- Starting from scratch and test the product and the market.
A concrete example of selling a new service in an existing market (scale out) provide the case studies of MinErgy and Pakoswiss.
Subscribe here to the new Sanitation and Water Entrepreneurship Pact (SWEP) newsletter. SWEP is a network of organizations joining hands to help entrepreneurs design and develop lasting water and sanitation businesses.
Strategies for Diversification
Ready, Steady, Scale – Is your social venture ready for scale?
Using the Ansoff Matrix to Develop Marketing Strategy
Putting the poor first : how base-of-the-pyramid ventures can learn from development approaches
Water and Sanitation Business Development Toolkit
10 things you need to know about how base of the pyramid businesses scale up
This article discusses major issues to reach scale when doing business at the bottom of the economic pyramid. The author advocates among others for local context, partnerships and clever use of technology in order to scaling up inclusive businesses in the developing world.
MOULDS, J. (2014): 10 things you need to know about how base of the pyramid businesses scale up. URL [Accessed: 16.04.2018]Rural Sanitation Market Expansion of Domestic Private Sector in Indonesia
This report is a synthesis of fieldwork findings and recommendations developed under the Technical Assistance programme carried out by the World Bank’s Water and Sanitation Program (WSP) in Indonesia. This report describes and assesses the performance of technical assistance rural sanitation market expansion of domestic private sector in Indonesia. The recommendations have been developed through on-going consultations and meetings with the Directorate of Environmental Sanitation and Directorate General of Human Settlements, Ministry of Health, and Government of Indonesia.
WORLD BANK (2015): Rural Sanitation Market Expansion of Domestic Private Sector in Indonesia. Washington, DC: URL [Accessed: 16.04.2018]BoP Innovation Center
BoP Innovation Center is a Dutch non-profit foundation that accelerates the impact of market-driven innovative welfare strategies in low-wage markets, the ‘Base of the Pyramid’


