Executive Summary
Every business idea, no matter how good, will have its challenges and weak spots, even if these don’t seem evident at first. Having a solid grasp of your business idea and how it operates in its specific context and sector will allow you to foresee, understand and prepare for such challenges. This in turn will strengthen your business’ competitiveness in the market and help you manage your resources more efficiently. This factsheet aims to provide you with some guiding steps for identifying and mapping out the potential challenges that your business idea might face. This will allow you to be in a better position for picking an innovation strategy that will really work for your business model and your unique set of challenges. It is important not to underestimate just how important it is to conduct this preliminary step if you want to ensure the success and sustainability of your business.
What is an innovative business idea
Let’s start by looking at what a business idea is. In simple terms, a business idea seeks ways to make money by catering to a consumer need that has no solution yet – in other words, it is about filling a market gap with a novel product or service, for example an affordable water filter or a waste collection service. Of course, you can only fill this market gap if you can offer the solution in demand at a competitive price, and to do this you need to consider how you are going to access the raw material, set up efficient logistics and so on.
To establish whether your business idea really is innovative and will lead to a successful business, we will fire some questions at you. This will help you focus your innovation efforts on the challenges you have to overcome to move towards a successful business model. Defining your innovation challenge sounds simple, but it involves a significant amount of research and analysis if you want to do it properly. To ensure that you choose the right innovation strategy, you need to know which element of your business idea or which business model needs to be innovated in order to build a viable business that responds to customer needs while at the same time operating efficiently and achieving the highest quality.
Challenges of WASH businesses
Typical challenges in WASH businesses include low consumer prices that do not cover operational or capital expenditures, high sales costs due to potential customers that are still going for either alternative solutions that are free (open defecation, polluted surface water, littering, etc.) or for competing unsustainable products, and high investment and operational costs due to complex water and sanitation infrastructure. You might have identified similar challenges around your business idea, either challenges related to your operations and associated resources and costs or challenges related to solving your customers’ problems. You might be unaware of any challenges or might find it hard to pinpoint the exact challenges you will be facing in your business. Here are some questions to help you analyse your business idea and identify potential challenges (as well as missed opportunities!) that you should address before or at least during the launch of your business:
Step 1: Reflect on your business idea to map out potential challenges (Questions adapted from Osterwalder & Pigneur, 2010)
Market forces:
- What is the actual customer problem you solve and for whom?
- What would stick out to your customers / what is special about your business idea from a customer point of view?
- Are there any crucial issues affecting your customers and their needs (ex. climate change)?
- In what areas are customer segments and their associated needs growing? Where are they declining?
- Are there any other segments or unsatisfied customer needs that deserve your attention?
- Is it easy for your customers to find and purchase similar offers? How important is brand and quality to them?
- How much are your customers really willing and able to pay? Can your customers easily find and purchase cheaper products and services?
Industry forces:
- What do you need in order to realise your business idea and what is unique about how you will implement it? Why did nobody else do it successfully before you?
- Who are your competitors and what are their competitive advantages or disadvantages?
- Which barriers must you overcome to obtain market share?
- Who are the key partners in your value chain that you need to work with (i.e. suppliers etc.)? To what extent does your business idea depend on them?
- Which other stakeholders might influence your business idea (i.e. government, communities, etc.)? How influential are they?
- Could your business idea have any negative social or environmental impacts?
Key trends:
- What are the major technology trends both inside and outside your sector? Which emerging technologies are your customers adopting?
- Which regulatory trends and existent rules and regulations may affect your business idea? Which regulations and taxes affect your customers?
- Which societal or cultural values affect your business idea? Which societal or cultural trends might influence customer behaviour?
- Which key demographic trends affect your business idea? How would you characterise income and wealth distribution in your market? How high are disposable incomes? Describe spending patterns in your market (e.g. housing, healthcare, entertainment, etc.). What portion of the population lives in urban areas as opposed to rural settings and how are urbanisation trends impacting this ratio?
Macroeconomic forces:
- How easy is it to obtain funding for your business idea? Is seed funding or investment readily available?
- How easy is it to obtain the resources you need for your business idea (raw material, petrol, human resources etc.)? How costly are they?
- How good is the (public) infrastructure in your market? How would you characterise transportation, access to suppliers and customers, etc.? How good are public services for small businesses?
Step 2: Uncover assumptions
If you are still confident that you have a good business idea after answering these questions, great! But remember that your business idea (and the answers to the questions above) are still a set of assumptions (unless you have already run a proof of concept/ prototyped your business idea). For example, you might assume that your potential customers will be willing to pay more if you deliver your product to their doorstep. Unless you have actually gone out and talked to a sufficient number of these potential customers, this remains an assumption. You assume that they will pay more, you do not know this for sure. And even if you have asked customers if they would pay more, that does not necessarily mean that they will actually pay more once your product is on the market and you offer home delivery service. So, in order to avoid any bad surprises, reflect on your assumptions now and decide which ones are vital to the success of your business and how difficult they are to test. Record your work in the worksheet “Assumption Mapper” to prioritise which assumptions need testing first.
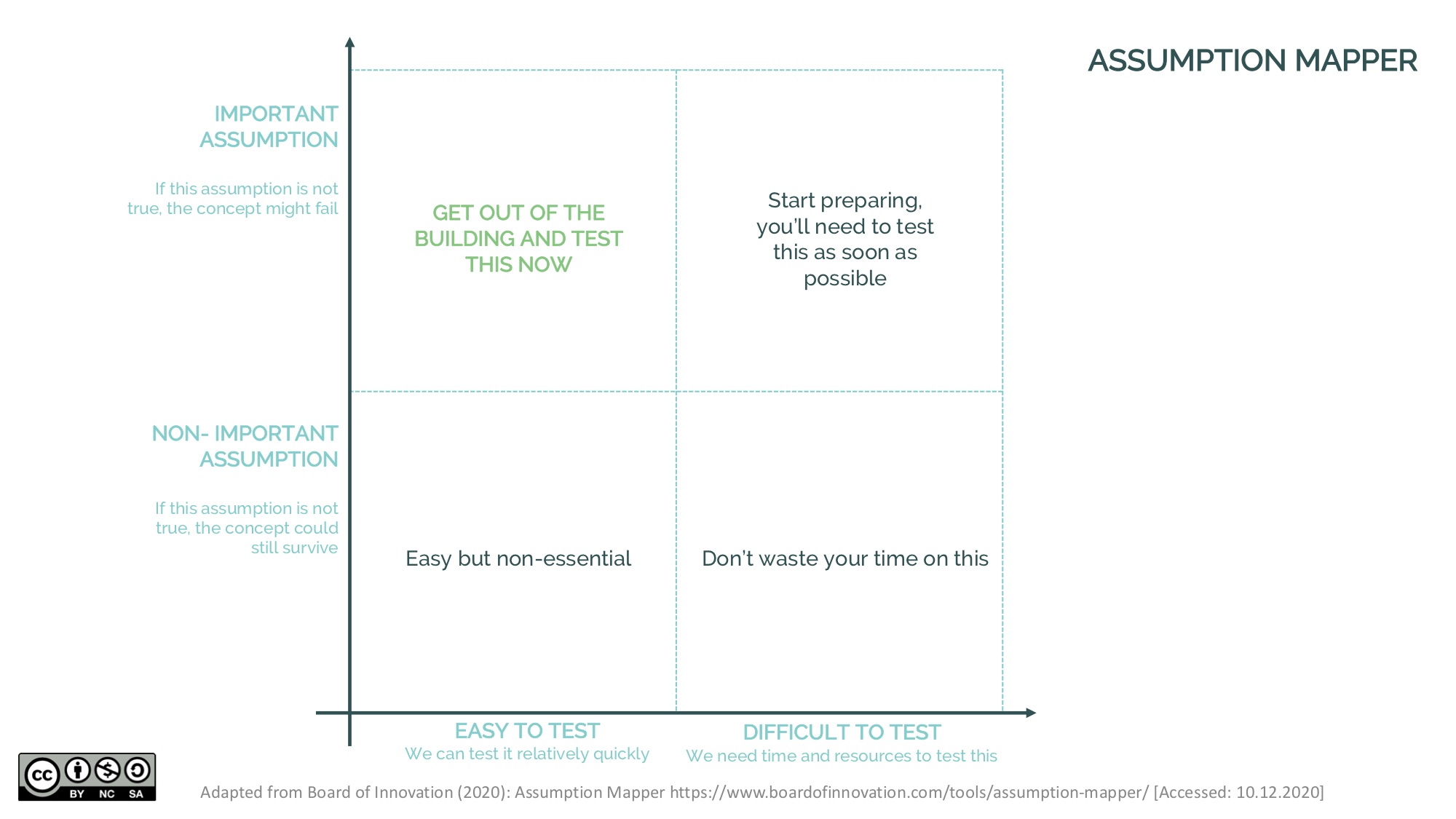
Step 3: Do your research to validate your challenges (or find additional ones)
- To understand your customers better and get a reality check of their needs, go out and talk to at least 10 potential customers that you have identified. Use this questionnaire or this guide to conduct user-centred research that will help you get a better understanding of who your customers are, what they do, what they need etc (THE CIRCULAR DESIGN GUIDE, 2016).
- Talk to at least 5 different sector experts about your business idea and ask them to give you honest feedback on the feasibility of your idea
- Look at similar businesses: What is the competition doing? Where are they struggling to ensure efficient operations or assuring quality? (i.e.: analyse current public toilets and why they are not being used)
- Are there any projects which recently explored similar business ideas/ faced similar challenges? How did they solve these challenges? (i.e.: are there any good/ bad examples of how businesses handle the logistics and costs around container-based on-site sanitation?)
- Do you have any market research/reports which could provide you with some guidance regarding potential operational pitfalls that your business idea might face? (i.e.: what are the findings/ recommendations from major research/ implementing agencies regarding your particular challenge?)
Step 4: Structure your findings
You can use the following tools adapted from Board of Innovation to structure your findings:
- Assumption learning card: The assumption learning card will help you collect and refine your learnings following an experiment on critical assumptions, user tests, or solution validations. This tool will be most effective if you record your findings/feedback directly after conducting the interviews or tests. Use one card per assumption and highlight clear discoveries, findings, and pivots.
- Personas: The persona tool is designed to help you visualise and better understand your customer segment. Personas are fictional characters that you create in order to keep the target audience that you want to serve in mind.
- Customer journey map: The tool customer journey map allows you to reconsider the interaction with your products or services from the customer's perspective.
- Customer empathy map: The customer empathy map is a simple tool to deep dive into the mind of your customer. It provides a basis for identifying the needs of the customer and opportunities for the project through visualisation of what she/he says, does, thinks and feels
- Insights selector: The tool ‘insights selector‘ is a simple tool that facilitates a group discussion around the different gathered insights from customer stories and helps you identify the insights that could potentially lead to innovative ideas.
Step 5: Define your innovation challenges
Once you have done your research and gathered more insights and verified your assumptions, it is time to define your innovation challenges. These are the challenges you will solve by innovating your business model. Frame the challenges using the “how might we…” format, which frames the context clearly, while also leaving options for solutions open (BOARD OF INNOVATION, 2020).

This worksheet provides guidance on how to formulate your innovation challenge in the “how might we…” format.
Examples:

Board of Innovation
An online platform that transforms leading innovation management theory into hands-on, easy-to-use, actionable innovation tools which can be downloaded for free.
(2020): https://www.boardofinnovation.com/tools/ [Accessed: 23.12.2020]
