Executive Summary
Surface disposal refers to the stockpiling of sludge, faeces , biosolids (e.g. humanure or compost) or other materials that cannot be used elsewhere. Once the material has been taken to a surface disposal site, it is not used later , thus nutrients are lost . Storage refers to temporary stockpiling. It can be done when there is no immediate need for the material and a future use is anticipated, or when further hygienization and drying is desired before application.
| In | Out |
|---|---|
Compost/Biosolids |
- |
Introduction
This technology is primarily used for treated sludge, although it is applicable for any type of dry, unusable material which is not harmful to the environment or human health when being exposude to air or humidity . One application of surface disposal is the disposal of dry cleansing materials, such as toilet paper, corn cobs, stones, newspaper and/or leaves. These materials cannot always be included along with other water-based products in some technologies and must be separated. A rubbish bin should be provided beside the user interface to collect the cleansing materials and menstrual hygiene materials. Dry materials can be burned (e.g., corn cobs) or disposed of along with the household waste. For simplicity, the remainder of this technology information sheet will be dedicated to sludge since standard solid waste practices are beyond the scope of the Compendium.
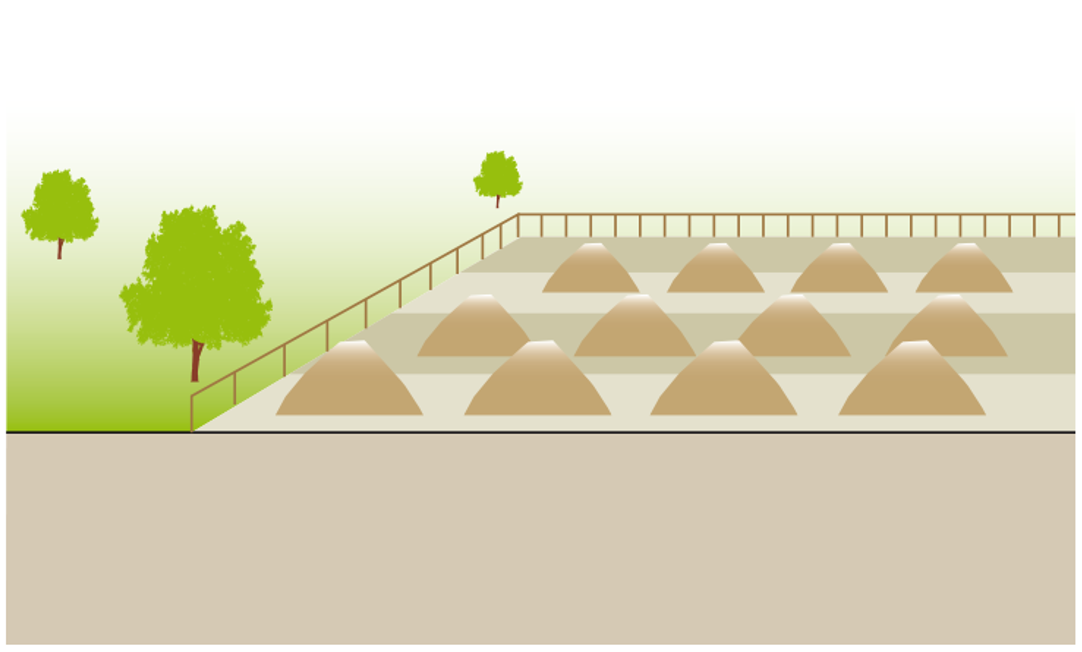
This technology should only be considered as an option when there is no local interest for reuse of waste material. When there is no demand for or acceptance of the beneficial use of sludge, it can be placed in monofills (sludge-only landfills) or heaped into permanent piles. Temporary storage contributes to further dehydration of the product and the die-off of pathogens before it is used.
Design Considerations
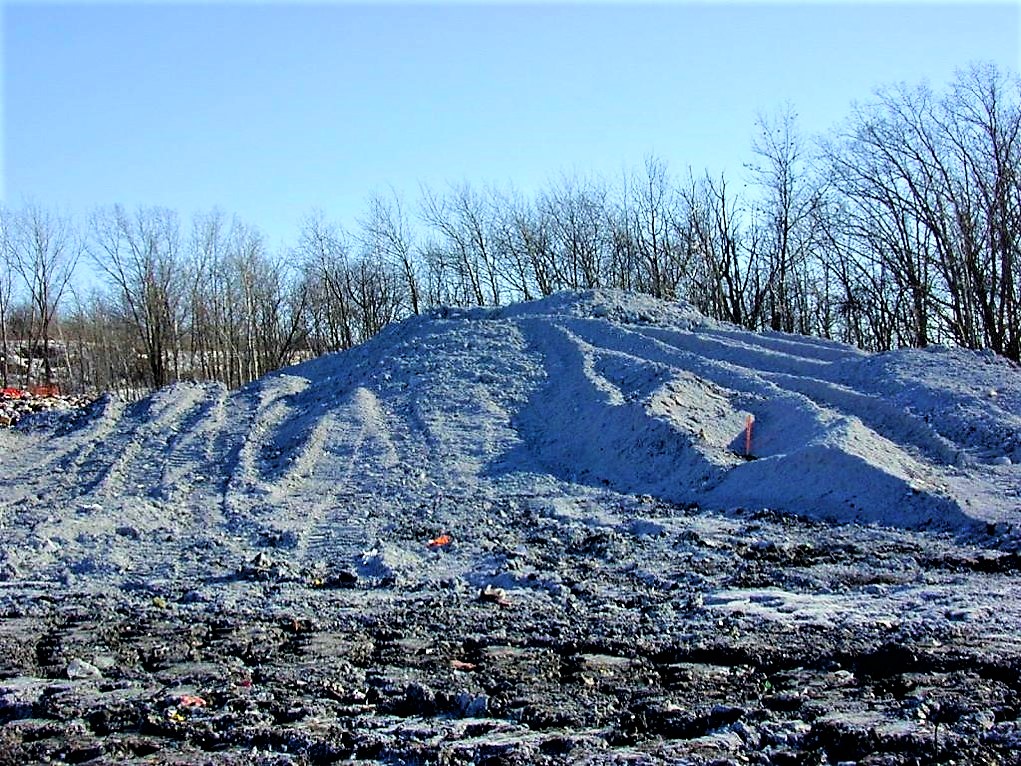

Landfilling sludge along with municipal solid waste (MSW) is not advisable since it reduces the life of a landfill (due to rapid fill up) , which has been specifically designed for the containment of more noxious materials. As opposed to more centralized MSW landfills, surface disposal sites can be situated close to where the faecal sludge is treated, limiting the need for long transport distances.
The main difference between surface disposal and land application is the application rate. There is no limit to the quantity of sludge that can be applied to the surface since nutrient loads or agronomic rates are not a concern. Attention must be paid, however, to groundwater contamination and leaching (see also water pollution) . More advanced surface disposal systems may incorporate a liner and leachate collection system in order to prevent nutrients and contaminants from infiltrating the groundwater (see also waste stabilisation ponds, leach fields,[ 681-soak pits] or evaporation beds) .
Sites for the temporary storage of a product should be covered to avoid rewetting by rainwater and the generation of leachate.
Health Aspects/Acceptance
If a surface disposal and storage site is protected (e.g., by a fence) and located far from the public, there should be no risk of contact or nuisance. The contamination of groundwater resources by leachate should be prevented by adequate siting and design or/and the sites should be located far away from water sources and at a sufficient distance from the maximum groundwater level (see also water pollution and water source protection). Care should be taken to protect the disposal or storage site from vermin and pooling water, both of which could exacerbate smell and vector problems.


Operation & Maintenance
Staff should ensure that only appropriate materials are disposed of at the site and must maintain control over the traffic and hours of operation. Workers should wear appropriate protective clothing.
Since there are no benefits gained from surface disposal, it should not be considered as a primary option , only when there is no possibility or no acceptance for reusing the biosolids . However, where sludge use is not easily accepted, the contained and controlled stockpiling of solids is far preferable to uncontrolled dumping. It could also be an intermittent step, e.g. when a reuse system is not yet in place.
Storage may in some cases be a good option to further dry and hygienize a material and to generate a safe, acceptable product. Storage may also be required to bridge the gap between supply and demand in the case reuse is practiced . Surface disposal and storage can be practiced in almost every climate and environment, although they may not be feasible where there is frequent flooding or where the groundwater table is high.
Florida Commission Considers Sewage Sludge Rule Changes
Faecal Sludge Management
This is the first book to compile the current state of knowledge on faecal sludge management. It addresses the organization of the entire faecal sludge management service chain, from the collection and transport of sludge, to the current state of knowledge of treatment options, and the final end use or disposal of treated sludge. It presents an integrated approach that brings together technology, management, and planning, based on Sandec’s 20 years of experience in the field. It also discusses important factors to consider when evaluating and upscaling new treatment technology options. The book is designed for undergraduate and graduate students, engineers, and practitioners in the field who have some basic knowledge of environmental and/or wastewater engineering.
STRANDE, L. ; RONTELTAP, M. ; BRDJANOVIC, D. (2014): Faecal Sludge Management. Systems Approach for Implementation and Operation. London: IWA Publishing URL [Accessed: 16.07.2014]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFBiosolids Generation, Use, and Disposal in the United States
This report gives an overview on the use and disposal of biosolids/sewage sludge in the US between 1998 and 2010.
U.S. EPA (1999): Biosolids Generation, Use, and Disposal in the United States. Washington: United States Environmental Protection Agency URL [Accessed: 26.05.2019]A Plain English Guide to the EPA Part 503 Biosolids Rule
Environmental Impacts Associated with Disposal of Saline Water Produced During Petroleum Production
Organic Wastes
Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFTechnology Review of Composting Toilets
This GIZ publication explains the design, use and operational requirements of composting toilets. Ample examples for composting toilets from around the world are included in the publication to show that these types of toilets have a wide range of applications under a variety of circumstances (for wealthy or poor people; for cold, hot, wet or dry climates; for urban or rural settings). The appendix contains a listing of suppliers.
BERGER, W. (2011): Technology Review of Composting Toilets. Eschborn: Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) URL [Accessed: 12.05.2019]Decentralised Composting for Cities of Low- and Middle-Income Countries – A User’s Manual
This book describes approaches and methods of composting on neighbourhood level in small-and middle-scale plants. It considers issues of waste collection, composting technologies, management systems, occupational health concerns, product quality, marketing and end-user demands.
DRESCHER, S. ZURBRUEGG, C. ENAYETULLAH, I. SINGHA, M.A.D. (2006): Decentralised Composting for Cities of Low- and Middle-Income Countries – A User’s Manual. Dhaka: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) and Waste Concern URL [Accessed: 16.08.2010]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFBiosolids Generation, Use, and Disposal in the United States
This report gives an overview on the use and disposal of biosolids/sewage sludge in the US between 1998 and 2010.
U.S. EPA (1999): Biosolids Generation, Use, and Disposal in the United States. Washington: United States Environmental Protection Agency URL [Accessed: 26.05.2019]Chapter 15. Case Studies
These three case studies illustrate a range of surface disposal activities being conducted throughout the United States. Activities covered include surface disposal of sewage sludge in a monofill, at a dedicated disposal site, and at a dedicated beneficial use site, in addition to sludge storage in lagoons prior to final disposal.
U.S. EPA (1995): Chapter 15. Case Studies. In: U.S. EPA (1995): Surface Disposal of Sewage Sludge and Domestic septage. Process Design Manual. Washington: 251-265. URL [Accessed: 24.08.2010]
