المُلخص التنفيذي
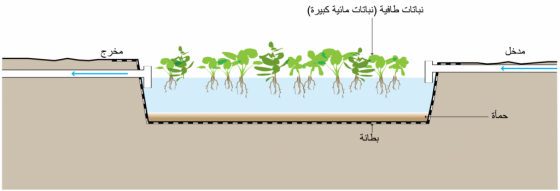
بِرَك النباتات العائمة (الطَّافِية) Floating Plant Ponds هي بِرَك إنضاج مُعدلة بها نباتات مائية عائمة، مثل: الخزامى المائي (أو اللافندر المائي Hyacinth) وعدس الماء (أو اللمناوات Duckweed)، حيث تطفو تلك النباتات على السطح وتتأصل جذورها في المياه من أجل امتصاص المُغذيات وتنقية المياه التي تمر خلالها.
يعتبر الخزامى المائي من نباتات المياه العذبة المُعمّرة (نباتات مائية كبيرة Macrophytes) والتي تنمو بصورة سريعة خصوصًا في مياه الصرف، وتتميز هذه النباتات بالنمو بصورة كبيرة؛ حيث يبلغ طولها عادة ما بين 0.5 متر و 1.2 متر من القمة للقاع. توفر الجذور الطويلة وسط ثابت للبكتيريا التي تعمل على تحلل المواد العضوية في المياه المارة بها. أما بالنسبة لعدس الماء فهو سريع النمو، كما أنه من النباتات عالية البروتين التي تستخدم طازجة أو جافة -كغذاء للأسماك والدواجن؛ فهي نباتات قادرة على تحمل الظروف المختلفة، كما يمكنها إزالة كميات كبيرة من المُغذيات الموجودة في مياه الصرف.
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
التدفقات السائلة الخارجة |
الكتلة الحيوية |
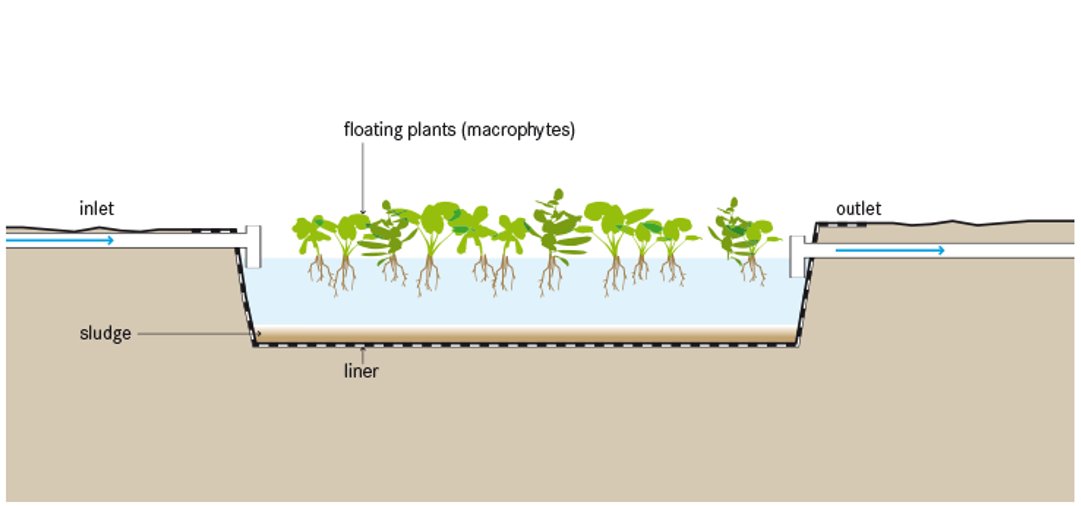
Introduction
Commonly used plants in floating plant ponds are water hyacinths and duckweed. Water hyacinths are perennial, freshwater, aquatic macrophytes that grow especially fast in wastewater. The plants can grow large: between 0.5 to 1.2 m from top to bottom. The long roots provide a fixed medium for bacteria which in turn degrade the organics in the water passing by.
Duckweed is a fast growing, high protein plant that can be used fresh or dried as a food for fish or poultry. It is tolerant of a variety of conditions and can significantly remove quantities of nutrients from wastewater.
اعتبارات التصميم
يمكن اختيار النباتات المناسبة محليًّا اعتمادًا على نسبة توافرها محليًّا وعلى خصائص مياه الصرف )مثل ورد النيل في مصر.(
ومن أجل زيادة الأكسجين الذائب للنباتات العائمة يمكن تهوية الماء ميكانيكيًّا، ولكن ذلك سيتم على حساب زيادة الطاقة والماكينات. ويمكن للبِرَك المُهواة استيعاب قدرٍ كبيرٍ من الأحمال العضوية كما يمكن أن يكون أثرها البيئي محدودٍ/ قليلًا. يجب ألا تكون البِرَك غير المُهواة عميقة أكثر من اللازم، وإلا سيكون هناك اتصال غير كافٍ بين الجذور الحاوية للبكتيريا ومياه الصرف.
الجوانب الصحية / القبول
يتميز نبات الخزامى المائي بزهوره الجذابة؛ لذلك فإن التصميم والصيانة الجيدة للبِركة يضيف إلى قيمة الأراضي القاحلة ويزيد الاهتمام بها.
يجب استخدام اللافتات المناسبة والأسوار من أجل منع دخول الإنسان والحيوان للبِرَكة وملامسة مياهها، كما يجب على العاملين ارتداء الملابس الواقية المناسبة. ينبغي الاستعانة بإرشادات منظمة الصحة العالمية بشأن استخدام مياه الصرف وفضلات الجسم في تربية الأحياء المائية؛ للحصول على معلومات مُفصَّلة وتوجيهات محددة.
التشغيل والصيانة
تتطلب النباتات العائمة حصادًا مستمرًّا، ويمكن استخدام الكتلة الحيوية التي يتم حصادها في المشروعات الحرفية الصغيرة، أو يمكن استخدامها في إعداد السماد. ويُحتمل زيادة مشاكل البعوض في حال عدم حصاد النباتات بانتظام. اعتمادًا على كمية المواد الصلبة التي تدخل إلى البِركة، فإنه يجب إزالة الحمأة بشكل دوري. ويجب أن تتم صيانتها وتشغيلها باستمرار من قِبَل فريق متدرب.
معالجة مياه الصرف الصحي لمنطقة تقرت بواسطة نباتات منتقية محلية
الاتجاھات الحديثة فى استخدام نبات ورد النيل
Integrated Systems of Agriculture and Aquaculture. Aquaculture in the Classroom
Small and Decentralized Wastewater Management Systems
Decentralised wastewater management presents a comprehensive approach to the design of both conventional and innovative systems for the treatment and disposal of wastewater or the reuse of treaded effluent. Smaller treatment plants, which are the concern of most new engineers, are the primary focus of this book.
CRITES, R. TCHOBANOGLOUS, G. (1998): Small and Decentralized Wastewater Management Systems. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies IncHydroponics
This document, rich in pictures, gives a good overview on the history of hydroponics and describes a variety of hydroponic methods and techniques.
DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE SRI LANKA (n.y): Hydroponics. Peradeniya: Sri Lanka: Department of Agriculture URL [Accessed: 21.04.2011]Aquaponics – Integration of Hydroponics with Aquaculture
Aquaponics is a bio-integrated system that links recirculating aquaculture with hydroponic vegetable, flower, and/or herb production. Recent advances by researchers and growers alike have turned aquaponics into a working model of sustainable food production. This publication provides an introduction to aquaponics with brief profiles of working units around the country. An extensive list of resources point the reader to print and Web-based educational materials for further technical assistance.
DIVER, S. (2006): Aquaponics – Integration of Hydroponics with Aquaculture. Arkansas, USA: ATTRA - National Sustainable Agriculture Information Service URL [Accessed: 22.05.2012]Duckweed Aquaculture
This literature review provides a first overview of the possibilities, potentials and limits of duckweed aquaculture and its combined use in wastewater treatment and animal feed production in low and middle-income countries. It is somewhat limited as critical literature on duckweed field use is scarce and difficult to obtain (e.g. unpublished internal documents).
IQBAL, S. (1999): Duckweed Aquaculture. Potentials, Possibilities and Limitations for Combined Wastewater Treatment and Animal Feed Production in Developing Countries. Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 08.05.2019]Comparative Study of Wastewater Lagoon with and without Water Hyacinth
Hydroponics is the growing of plants without soil
Community-Based Technologies for Domestic Wastewater Treatment and Reuse- options for urban agriculture
The report suggests that emerging trends in low-cost, decentralised naturally-based infrastructure and urban wastewater management which promote the recovery and reuse of wastewater resources are increasingly relevant. Technologies for these sanitation options are presented. The concept of managing urban wastewater flows at a decentralised or "intermediate" level, based on micro watersheds, is explored. Effluent treatment standards that are currently accepted in order to protect public health and safety are reviewed.
ROSE, D.G. (1999): Community-Based Technologies for Domestic Wastewater Treatment and Reuse- options for urban agriculture. (= Cities Feeding People (CFP) Report Series. , 27 ). Ottawa: International Development Research Center Canada (IDRC) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2018]Duckweed Aquaculture: A New Aquatic Farming System for Developing Countries
The purpose of this booklet is to present a group of tiny aquatic plants commonly known as "duckweeds" as a promising new commercial aquaculture crop.
SKILLICORN, P. SPIRA, W. JOURNEY, W. (1993): Duckweed Aquaculture: A New Aquatic Farming System for Developing Countries. Washington: The World Bank URL [Accessed: 15.04.2014]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFDesign Manual – Constructed Wetlands and Aquatic Plant Systems for Municipal Water Treatment
This document is a very complete design manual about constructed wetlands and aquatic plant systems for municipal water treatment. It describes different designs, application, performance and it includes several case studies.
U. S. EPA (1998): Design Manual – Constructed Wetlands and Aquatic Plant Systems for Municipal Water Treatment. Washington D.C.: United States : Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) URL [Accessed: 24.08.2011]Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume III. Wastewater and Excreta Use in Aquaculture
Volume III of the Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater deals with wastewater and excreta use in aquaculture and describes the present state of knowledge regarding the impact of wastewater-fed aquaculture on the health of producers, product consumers and local communities. It assesses the associated health risks and provides an integrated preventive management framework.
WHO (2006): Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume III. Wastewater and Excreta Use in Aquaculture. Geneva: World Health Organisation URL [Accessed: 08.05.2019]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFAquatic Plant Based Water Treatment Systems in Asia
Harvesting and Handling of Biomass
Chapter 4: Water Hyacinth Ponds
Small and Decentralized Wastewater Management Systems
Decentralised wastewater management presents a comprehensive approach to the design of both conventional and innovative systems for the treatment and disposal of wastewater or the reuse of treaded effluent. Smaller treatment plants, which are the concern of most new engineers, are the primary focus of this book.
CRITES, R. TCHOBANOGLOUS, G. (1998): Small and Decentralized Wastewater Management Systems. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies IncHydroponics
This document, rich in pictures, gives a good overview on the history of hydroponics and describes a variety of hydroponic methods and techniques.
DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE SRI LANKA (n.y): Hydroponics. Peradeniya: Sri Lanka: Department of Agriculture URL [Accessed: 21.04.2011]Aquaponics – Integration of Hydroponics with Aquaculture
Aquaponics is a bio-integrated system that links recirculating aquaculture with hydroponic vegetable, flower, and/or herb production. Recent advances by researchers and growers alike have turned aquaponics into a working model of sustainable food production. This publication provides an introduction to aquaponics with brief profiles of working units around the country. An extensive list of resources point the reader to print and Web-based educational materials for further technical assistance.
DIVER, S. (2006): Aquaponics – Integration of Hydroponics with Aquaculture. Arkansas, USA: ATTRA - National Sustainable Agriculture Information Service URL [Accessed: 22.05.2012]Water Quality Study of Graywater Treatment Systems
Duckweed Aquaculture
This literature review provides a first overview of the possibilities, potentials and limits of duckweed aquaculture and its combined use in wastewater treatment and animal feed production in low and middle-income countries. It is somewhat limited as critical literature on duckweed field use is scarce and difficult to obtain (e.g. unpublished internal documents).
IQBAL, S. (1999): Duckweed Aquaculture. Potentials, Possibilities and Limitations for Combined Wastewater Treatment and Animal Feed Production in Developing Countries. Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 08.05.2019]A Prototype Recirculating Aquaculture-Hydroponic System
This document introduces a recirculating aquaculture-hydroponic system. The system provides an artificial, controlled environment that optimises the growth of aquatic species and soil-less plants, while conserving water resources. In this system, fish and plants are grown in a mutually beneficial, symbiotic relationship.
JOHNSON, M. D. WARDLOW, G. W. (1997): A Prototype Recirculating Aquaculture-Hydroponic System. Arkansas, USA: University of Arkansas, Department of Agricultural & Extension Education URL [Accessed: 21.04.2011]Possibilities and Limits of Wastewater-fed Aquaculture
At the University of Applied Sciences Waedenswil, Switzerland, wastewater-fed aquaculture is a research focus since 1993. This paper summarises some of the results and insights gained since then.
JUNGE-BERBEROVIC, R. University of Applied Sciences Waedenswil. (2001): Possibilities and Limits of Wastewater-fed Aquaculture. Waedenswil: University of Applied Sciences Waedenswil URL [Accessed: 19.02.2010]Aquatic plants for domestic wastewater treatment: Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) and Hydrilla (Hydrilla verticillata) systems
The study focussed on the overall performances of lotus and hydrilla systems for post treatment of domestic wastewater. Removal of water quality parameters such as pH, biochemical oxygen demand, suspended substances, nitrogen, phosphorus and total coliform bacteria showed the differences between various plants and control unitas.
KANABKAEW, T. ; PUETPAIBOON, U. (2004): Aquatic plants for domestic wastewater treatment: Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) and Hydrilla (Hydrilla verticillata) systems. المُدخلات: Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technology: Volume 26 , 749-756. URL [Accessed: 21.04.2011]Comparative Study of Wastewater Lagoon with and without Water Hyacinth
Wastewater Treatment and Use in Agriculture
This Irrigation and Drainage Paper is intended to provide guidance to national planners and decision-makers, agricultural and municipal managers, field engineers and scientists, health and agricultural field workers, wastewater treatment plant operators and farmers. Consequently, it covers a broad range of relevant material, some in considerable depth but some more superficially. It is meant to encourage the collection, treatment and use of wastewater in agriculture in a safe manner, with maximum advantage taken of this resource. Informal, unplanned and unorganized wastewater use is not recommended, nor is it considered adviseable from the health or agricultural points of view.
PESCOD, M.B. (1992): Wastewater Treatment and Use in Agriculture. (= FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper , 47 ). Rome: Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO) URL [Accessed: 25.10.2011]Aquatic plants in Aquaculture
The article informs the reader about the biological role of aquatic plants in the waters with specific information on the anatomy of aquatic plants and descriptions of different types of plants.
PONGCHAWEE, K. (n.y): Aquatic plants in Aquaculture. India: Aquatic Plants and Ornamental Fish Research Institute URL [Accessed: 21.04.2011]Community-Based Technologies for Domestic Wastewater Treatment and Reuse- options for urban agriculture
The report suggests that emerging trends in low-cost, decentralised naturally-based infrastructure and urban wastewater management which promote the recovery and reuse of wastewater resources are increasingly relevant. Technologies for these sanitation options are presented. The concept of managing urban wastewater flows at a decentralised or "intermediate" level, based on micro watersheds, is explored. Effluent treatment standards that are currently accepted in order to protect public health and safety are reviewed.
ROSE, D.G. (1999): Community-Based Technologies for Domestic Wastewater Treatment and Reuse- options for urban agriculture. (= Cities Feeding People (CFP) Report Series. , 27 ). Ottawa: International Development Research Center Canada (IDRC) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2018]Water plants
This factsheet informs the reader about the most common water plants used for floating plant ponds. There are further information on growing and harvesting the plants. It is illustrated with many pictures.
SHARP, D. (n.y): Water plants. South Africa: Water Affairs, Agriculture Forestry and Fisheries, Environmental Affairs URL [Accessed: 21.04.2011]Duckweed Aquaculture: A New Aquatic Farming System for Developing Countries
The purpose of this booklet is to present a group of tiny aquatic plants commonly known as "duckweeds" as a promising new commercial aquaculture crop.
SKILLICORN, P. SPIRA, W. JOURNEY, W. (1993): Duckweed Aquaculture: A New Aquatic Farming System for Developing Countries. Washington: The World Bank URL [Accessed: 15.04.2014]Hydroponics 101. Yo, Where’s the dirt?
This article provides general information on the topic of hydroponics. The reader gets to known what this technology is about. Several global key data are given and various examples for implementation are described.
SPIEGELMAN, A. (n.y): Hydroponics 101. Yo, Where’s the dirt?. New York, USA: Annie Spiegelman URL [Accessed: 21.04.2011]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFDesign Manual Onsite Wastewater Treatment and Disposal Systems
Rather old design manual for onsite wastewater treatment options. However, valuable information on established systems such as septic tanks, sand filters, aerobic treatment units (suspended growth and fixed film), disinfection, nutrient removal as well as wastewater segregation and recycling are given. Additional information is given on disposal methods and appurtenances.
U.S.EPA (1980): Design Manual Onsite Wastewater Treatment and Disposal Systems. (= EPA 625/1-80-012 ). United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water Office of Research and Development (U.S.EPA) URL [Accessed: 18.03.2010]Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume III. Wastewater and Excreta Use in Aquaculture
Volume III of the Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater deals with wastewater and excreta use in aquaculture and describes the present state of knowledge regarding the impact of wastewater-fed aquaculture on the health of producers, product consumers and local communities. It assesses the associated health risks and provides an integrated preventive management framework.
WHO (2006): Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume III. Wastewater and Excreta Use in Aquaculture. Geneva: World Health Organisation URL [Accessed: 08.05.2019]Volume III: Wastewater and excreta use in aquaculture.
This presentation gives a detailed overview on the 3. volume of the WHO guidelines on the safe use of wastewater and excreta in aquaculture including many pictures of existing wastewater-fed aquaculture and fish pond technologies all over the world. Apart from the health risk and appropriate health protection measures, a lot of information on socio-cultural, environmental and economic aspects is given as well as supporting information on planning and implementation of sewage-fed fish ponds.
EDWARDS, P. (2008): Volume III: Wastewater and excreta use in aquaculture.. (pdf presentation). Bangkok, Thailand: Asian Institute of TechnologyKey Issues in the Safe Use of Wastewater and Excreta in Aquaculture
This document is a guidance note for program managers and engineers that summarises the key issues of the 3. Volume of the WHO Guidelines that focuses on the safe use of wastewater and excreta in aquaculture.
EDWARDS, P. Asian Institute of Technology (2008): Key Issues in the Safe Use of Wastewater and Excreta in Aquaculture. (pdf presentation). (= Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater in Agriculture and Aquaculture , 3 ). Bangkok, Thailand: World Toilet Organisation URL [Accessed: 19.02.2010]http://www.fishfarming.com/
This webpage describes the sustainable technology of growing plants (duckweed) and fish (Tilapia) in a symbiotic way. The text is illustrated with various pictures (English).
http://ag.arizona.edu/
This webpage shows many pictures of integrated systems of aquaculture and agriculture. Furthermore, the most important facts and key figures are given.
http://aquaponicsworld.net/Aquaponics
This webpage provides information on large-scale aquaculture systems. It contains information on aquaculture for producing crops and gives information on farming in this very special field.
http://www.webofcreation.org/
This webpage is about aquaponics. Aquaponics is the combination of aquaculture and hydroponics. While algae, submerged plants, and floating plants do a good job of removing fish wastes from a recirculating aquaculture system, so can lettuce, basil, or many other common vegetables and herbs. Fish wastes can be treated with a biofilter and then allowed to pass through hydroponic troughs, where the roots of cultivated plants can remove the wastes as fertiliser.
