المُلخص التنفيذي
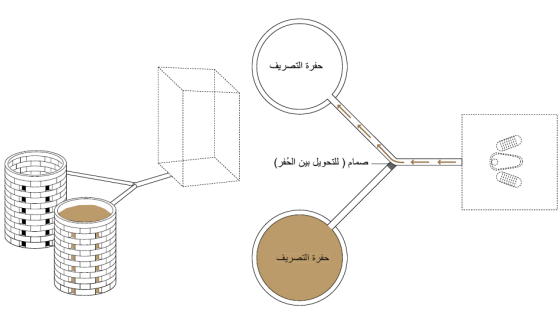
تتكون حُفر التصريف المزدوجة Twin Pits for Pour Flush من حُفرتين تبادليتين متصلتين بمِرحاض دفق بالصب حيث تُجمَع المياه السوداء (وأحيانًا المياه الرمادية) في الحُفر ويُسمح لها بالتسرب ببطء للتربة المحيطة، وبمرور الوقت تجف المواد الصلبة بشكلٍ كافٍ ويمكن إزالتها يدويًا بواسطة الجاروف.
يمكن تصميم حُفر التصريف المزدوجة بعدة طرق؛ إما بوضع المِرحاض فوق الحُفرة بشكلٍ مباشر، أو على مسافة منها، ويُمكن إنشاء البِنية الفوقية (الحمَّام) بشكل دائم فوق الحفرتين أو يتم تحريكها من جانبٍ لآخر وفقًا للحُفرة المستخدمة. ويتم استخدام حُفرة واحدة في كل مرة بغض النظر عن كيفية تصميم النظام؛ حيث تُترك الحُفرة الممتلئة لفترة توقف، ويتم ملء الحفرة الثانية.
بينما تتسرب السوائل من الحُفرة وتنتقل عبر التربة المسامية غير المُشبَّعة، فإن الجراثيم المسببة للأمراض تُمتص على سطح حبيبات التربة، وبهذه الطريقة يمكن إزالة مُسببات الأمراض قبل أن تصل إلى المياه الجوفية. وتختلف درجة الإزالة حسب نوع التربة، المسافة المقطوعة، الرطوبة وعوامل بيئية أخرى.
الاختلاف بين هذه التقنية وبين الحُفرة المزدوجة المُطورة المُهواة أو حُفرة ألترنا هو أنها تسمح باستخدام المياه، وليس من الضروري إضافة التربة أو أي مواد عضوية للحُفر. وحيث إن هذه التقنية قائمة على المياه (رطبة)، فإن الحُفر الممتلئة تتطلب فترة احتجاز أطول (يوصى بسنتين) حتى تتحلّل محتوياتها قبل أن يتم استخراجها بأمان.
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
المياة السوداء , المياة الرمادية |
دبال الحفرة |
المُلاءَمَة
حُفر التصريف المزدوجة هي تقنية ثابتة تلائم المناطق التي لا يمكن فيها بناء حُفر مراحيض جديدة باستمرار. وطالما توافرت المياه، فإن هذه التقنية تُعتبر ملائمة تقريبًا لكافة الكثافات الإسكانية. وبالرغم من ذلك لا يوصى بتواجد العديد من الحُفر الرطبة في مساحة صغيرة حيث إن مصفوفة التربة قد لا يكون لديها السعة الكافية لاستيعاب كافة السوائل وقد تُصبح الأرض مُشبعة جدًا بالمياه. ولكي يتم تصريف المياه بشكلٍ صحيح، يجب أن تكون التربة ذات سعة امتصاص جيدة؛ حيث تُعتبر التربة الطينية أو المدموكة أو الصخرية غير ملائمة. هذه التقنية لا تُلائم المناطق ذات منسوب المياه الجوفية المرتفع، أو ذات الفيضانات المتكررة.
يمكن إدارة المياه الرمادية في آن واحد مع المياه السوداء في الحُفر المزدوجة، خاصةً إذا كانت كميات المياه الرمادية قليلة نسبيًا ولا يوجد أي نظام إدارة آخر متاح لتخزينها أو نقلها للمعالجة. بينما قد تتسبب الكميات الكبيرة من مياه تنظيف المِرحاض و/أو المياه الرمادية في ارتشاح مفرط من الحُفرة و غالبًا ما يُسبّب تَلَوُّث المياه الجوفية.
يتم تفريغ المواد الصلبة الجافة -منزوعة المياه- من الحُفر يدويًا )بالحَفر وليس بالنزح(، لذلك ليس من الضروري مراعاة إمكانية دخول شاحنات الشفط إلى الحُفر.
اعتبارات التصميم
يجب أن يكون حجم الحُفر مناسب لاستيعاب حجم فضلات الجسم المُنتجة على مدار عام أو عامين، وهذا يسمح لمحتويات الحُفرة الممتلئة بالوقت الكافي لتصبح مادة شبه معقمة وشبيهة بالتربة ويمكن إزالتها يدويًا. ويوصى بأن تُبنى الحفرتان المزدوجتان على بُعد متر واحِد من بعضهما البعض لتقليل انتقال الملوثات من الحُفرة قيد التجفيف والتحلّل إلى الأخرى الجاري استخدامها، كما يوصى بأن تكون الحفرتان على بعد مترٍ واحد من أي بِنية تحتية حيث إن السوائل المرتشحة قد تؤثر سلبًا على الأساسات الهيكلية. قد تؤثر المياه داخل الحُفرة على بِنية الحُفرة نفسها، لذلك يجب أن تكون الجدران مُبطنة بالكامل لمنع انهيارها، وأن يكون الجزء العلوي )30 سم( مُمَلّط - مُمَحر- بالكامل لمنع التسريب المباشر وللحفاظ على البِنية الفوقية )الحمَّام(.
هناك أيضًا خطر تلوث المياه الجوفية عندما تتواجد الحُفر في مناطق ذات منسوب مياه مرتفع أو متغير، و/أو في حالة وجود تشققات أو تصدعات في البنية الأساسية للحُفرة. وحيث إن خواص التربة والمياه الجوفية عادةً ما تكون مجهولة، من الصعب تقدير المسافة اللازمة بين الحُفرة ومصدر المياه، وعادةً ما يوصى بأن تكون المسافة الأفقية بينهما لا تقل عن 30 مترًا للحد من تعرّض مصدر المياه للتلوث الميكروبي.
لضمان استخدام حُفرة واحدة في كل مرة، يجب إغلاق فتحة أنبوب التجميع الموصول بالحُفرة المتوقفة عن العمل )مثلًا: باستخدام الأسمنت أو الأحجار( وبدلًا عن ذلك، يمكن توصيل مِرحاض الدفق بالصب بالحُفرة مباشرة باستخدام أنبوب واحد مستقيم؛ على أن يكون مثبت في مكانه بالمحارة )الملاط الاسمنتي( ومُغطى بالتربة. وللحد من خطورة الإهمال أو سوء الاستخدام يجب ضمان أن تكون التوصيلات والأنابيب بعيدة عن متناول الأيدي.
الجوانب الصحية / القبول
تُعتبر هذه التقنية خيارًا مقبولًا بشكل عام للصرف الصحي؛ ومع ذلك، فتوجد بعض المخاوف الصحية:
• السوائل المرتشحة قد تُسبب تلوث المياه الجوفية.
• قد تعزّز المياه الراكدة في الحُفر من تكاثر الحشرات.
• قد تكون الحُفر عُرضة للهدم و/أو الطفح أثناء الفيضانات.
التشغيل والصيانة
يجب تفريغ الحُفر بانتظام )بعد فترة السنتين الموصى بها(، ويجب أخذ الحذر لضمان عدم فيض )طَفح( الحُفر أثناء المواسم الممطرة. يتم التفريغ يدويًا باستخدام جواريف طويلة الأذرع مع اتخاذ إجراءات الحماية الشخصية المناسبة.
حلول تقنيات وممارسات افضل للصرف الصحى دليل الاحياء الهاشمية فى نواكشوط -موريتانيا
Bogs, Baths and Basins: The Story of Domestic Sanitation
Sanitation & Cleanliness for a Healthy Environment
This booklet is a chapter from “A Community Guide to Environmental Health”. It offers basic information and learning activities to help communities understand and prevent sanitation-related health problems. The booklet includes instructions for building several kinds of latrines, as well as ecological sanitation solutions.
HESPERIAN FOUNDATION (2004): Sanitation & Cleanliness for a Healthy Environment. The Hesperian Foundation in Collaboration with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) URL [Accessed: 01.08.2010]The Design of Pour-Flush Latrines
The technical note was produced as a joint United Nations Development Programme and World Bank contribution to the International Drinking Water Supply and Sanitation Decade. It sets out guidelines for the design of pour-flush latrines, based upon TAG's (Technology Advisory Group) experience in India, Brazil and elsewhere. These guidelines have been written especially for use in developing countries. Consequently, emphasis has been placed on achieving simplicity of design consistent with reliability of operation.
MARA, D.D. (1985): The Design of Pour-Flush Latrines. (= TAG Technical Note No. 15 ). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and World Bank URL [Accessed: 02.08.2010]Low-cost Urban Sanitation
This book covers the public health, technical, socioeconomic, sociocultural and institutional aspects of sanitation in towns and cities of developing countries. The text features excreta-related diseases and the use of sanitation to reduce their transmission. The sanitation technologies covered in detail are VIP latrines, pour-flush toilets, septic tanks, settled sewerage and simplified sewerage, with additional chapters on sullage disposal, pit emptying, and sewage treatment and reuse. Sociocultural constraints on sanitation systems and their socioeconomic costing are described, together with hygiene education, which is essential in order to achieve maximum benefits to health. The text also explains how to choose the most appropriate sanitation option for a given low-income community. Finally, institutional aspects are reviewed, including effective sanitation programme planning, monitoring and evaluation.
MARA, D. (1996): Low-cost Urban Sanitation. United Kingdom: WileyManual on the design, construction and maintenance of low-cost pour-flush water seal latrines in India
This manual has been prepared for agencies, contractors and individuals involved in various aspects of the low-cost pour-flush water seal latrine programme in India. The inherent principles are, however, of general application; with minor modifications, the technical details can be readily adapted to meet the needs of different areas, particularly where water is used for anal cleansing. The manual presents salient features in regards to design, construction and maintenance as well as the administration of low-cost pour-flush water seal latrines with offset twin pits. It contains extensive drawings, tables of quantities for construction materials used for different designs as well as standard forms for by-laws and for general information on project administration and supervision.
ROY, A.K. CHATTERJEE, P.K. GUPTA, K.N. KHARE, S.T. RAU, B.B. SINGH, R.S. (1984): Manual on the design, construction and maintenance of low-cost pour-flush water seal latrines in India. (= TAG technical note; no. 10 ). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and World Bank URL [Accessed: 01.06.2010]Appropriate Approaches to Hygiene and Environmental Sanitation in Remote Communities of Mugu and Humla Districts, Western Nepal
Mugu and Humla are among the least developed of the 75 districts of Nepal and have a sanitation coverage of 10 % only. This study assessed the sanitation situation of the area gives recommendations to for software and hardware approaches in order to reach an overall sanitation coverage.
TILLET, W. (2008): Appropriate Approaches to Hygiene and Environmental Sanitation in Remote Communities of Mugu and Humla Districts, Western Nepal. Action Contre la Faim (ACF) URL [Accessed: 02.08.2010]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., LUETHI, C., MOREL, A., ZURBRUEGG, C. and SCHERTENLEIB, R. (2008): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (EAWAG) and Water Supply and Sanitation Collaborative Council (WSSCC) URL [Accessed: 15.02.2010] PDFCompendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFEnvironmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment for the implementation of the UNEP/GPA "Guidelines on Municipal Wastewater Management"
Technical information on environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment.
UNEP ; MURDOCH UNIVERSITY (2004): Environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment for the implementation of the UNEP/GPA "Guidelines on Municipal Wastewater Management". The Hague: United Nations Environment Programme Global Programme of Action (UNEP/GPA), Coordination OfficeA Guide to the Development of On-site Sanitation
The publication presents appropriate technologies for sanitation and highlights socio-economic aspects of planning and implementing. Emphasis is given to household-level sanitation improvements for urban areas, as well as rural areas and small communities. Background information on sanitation, in-depth technical information on the design, construction, operation and maintenance and project planning and development processes involved in projects and programmes complement the book.
WHO (1992): A Guide to the Development of On-site Sanitation. Geneva: World Health Organisation (WHO) URL [Accessed: 14.04.2010]Strengthening Budget Mechanisms for Sanitation in Uganda
Technology Options for Urban Sanitation in India. A Guide to Decision-Making
These guidance notes are designed to provide state governments and urban local bodies with additional information on available technologies on sanitation. The notes also aid in making an informed choice and explain the suitability of approaches.
WSP (2008): Technology Options for Urban Sanitation in India. A Guide to Decision-Making. pdf presentation. New Delhi: Water and Sanitation Program (WSP) URL [Accessed: 03.06.2019]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFSanitation Systems and Technologies. Lecture Notes
Lecture notes on technical and non-technical aspects of sanitation systems in developing countries.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Lecture Notes . (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 4 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC)Manual on the design, construction and maintenance of low-cost pour-flush water seal latrines in India
This manual has been prepared for agencies, contractors and individuals involved in various aspects of the low-cost pour-flush water seal latrine programme in India. The inherent principles are, however, of general application; with minor modifications, the technical details can be readily adapted to meet the needs of different areas, particularly where water is used for anal cleansing. The manual presents salient features in regards to design, construction and maintenance as well as the administration of low-cost pour-flush water seal latrines with offset twin pits. It contains extensive drawings, tables of quantities for construction materials used for different designs as well as standard forms for by-laws and for general information on project administration and supervision.
ROY, A.K. CHATTERJEE, P.K. GUPTA, K.N. KHARE, S.T. RAU, B.B. SINGH, R.S. (1984): Manual on the design, construction and maintenance of low-cost pour-flush water seal latrines in India. (= TAG technical note; no. 10 ). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and World Bank URL [Accessed: 01.06.2010]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E., ULRICH L., LÜTHI, C., REYMOND P. and ZURBRÜGG C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 03.05.2023] PDFConstruction of Ecological Sanitation Latrine
This document sets out the principles for adopting an ecological sanitation approach, as well as providing guidance on the construction ecological sanitation latrines and their operation. It is intended to support sanitation field practitioners and WaterAid in Nepal ’s partners in the delivery of appropriate services and technologies to fit the needs of different users. .It is also equally hoped that this document will be of value to other organisations and sector stakeholders involved in sanitation promotion and ecological sanitation.
WATER AID (2011): Construction of Ecological Sanitation Latrine. Kathmandu: Water Aid URL [Accessed: 19.10.2011]A Guide to the Development of On-site Sanitation
The publication presents appropriate technologies for sanitation and highlights socio-economic aspects of planning and implementing. Emphasis is given to household-level sanitation improvements for urban areas, as well as rural areas and small communities. Background information on sanitation, in-depth technical information on the design, construction, operation and maintenance and project planning and development processes involved in projects and programmes complement the book.
WHO (1992): A Guide to the Development of On-site Sanitation. Geneva: World Health Organisation (WHO) URL [Accessed: 14.04.2010]Philippines Sanitation Source Book and Decision Aid
This Sanitation Sourcebook distils some of the core concepts of sanitation in a user-friendly format so that the book can serve as a practical reference to sanitation professionals and investment decision-makers, particularly the local governments. The annexe contains a practical collection of factsheets on selected sanitation system options.
WSP (2007): Philippines Sanitation Source Book and Decision Aid. pdf presentation. Washington: Water and Sanitation Program (WSP). URL [Accessed: 01.06.2019]Technology Options for Urban Sanitation in India. A Guide to Decision-Making
These guidance notes are designed to provide state governments and urban local bodies with additional information on available technologies on sanitation. The notes also aid in making an informed choice and explain the suitability of approaches.
WSP (2008): Technology Options for Urban Sanitation in India. A Guide to Decision-Making. pdf presentation. New Delhi: Water and Sanitation Program (WSP) URL [Accessed: 03.06.2019]Assessment of Ecosan Toilets in Nepal
India's national sanitation and hygiene programme: From experience to policy West Bengal and Maharashtra models provide keys to success
The national rural sanitation programme of the Indian government has evolved into the Total Sanitation Campaign, which successfully encourages households to finance their own toilets while giving financial incentives to poorer people.
GANGULY, S.C. (2008): India's national sanitation and hygiene programme: From experience to policy West Bengal and Maharashtra models provide keys to success. المُدخلات: WATERAID: URL [Accessed: 02.08.2010]Appropriate Approaches to Hygiene and Environmental Sanitation in Remote Communities of Mugu and Humla Districts, Western Nepal
Mugu and Humla are among the least developed of the 75 districts of Nepal and have a sanitation coverage of 10 % only. This study assessed the sanitation situation of the area gives recommendations to for software and hardware approaches in order to reach an overall sanitation coverage.
TILLET, W. (2008): Appropriate Approaches to Hygiene and Environmental Sanitation in Remote Communities of Mugu and Humla Districts, Western Nepal. Action Contre la Faim (ACF) URL [Accessed: 02.08.2010]Sanitation & Cleanliness for a Healthy Environment
This booklet is a chapter from “A Community Guide to Environmental Health”. It offers basic information and learning activities to help communities understand and prevent sanitation-related health problems. The booklet includes instructions for building several kinds of latrines, as well as ecological sanitation solutions.
HESPERIAN FOUNDATION (2004): Sanitation & Cleanliness for a Healthy Environment. The Hesperian Foundation in Collaboration with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) URL [Accessed: 01.08.2010]The Design of Pour-Flush Latrines
The technical note was produced as a joint United Nations Development Programme and World Bank contribution to the International Drinking Water Supply and Sanitation Decade. It sets out guidelines for the design of pour-flush latrines, based upon TAG's (Technology Advisory Group) experience in India, Brazil and elsewhere. These guidelines have been written especially for use in developing countries. Consequently, emphasis has been placed on achieving simplicity of design consistent with reliability of operation.
MARA, D.D. (1985): The Design of Pour-Flush Latrines. (= TAG Technical Note No. 15 ). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and World Bank URL [Accessed: 02.08.2010]Manual on the design, construction and maintenance of low-cost pour-flush water seal latrines in India
This manual has been prepared for agencies, contractors and individuals involved in various aspects of the low-cost pour-flush water seal latrine programme in India. The inherent principles are, however, of general application; with minor modifications, the technical details can be readily adapted to meet the needs of different areas, particularly where water is used for anal cleansing. The manual presents salient features in regards to design, construction and maintenance as well as the administration of low-cost pour-flush water seal latrines with offset twin pits. It contains extensive drawings, tables of quantities for construction materials used for different designs as well as standard forms for by-laws and for general information on project administration and supervision.
ROY, A.K. CHATTERJEE, P.K. GUPTA, K.N. KHARE, S.T. RAU, B.B. SINGH, R.S. (1984): Manual on the design, construction and maintenance of low-cost pour-flush water seal latrines in India. (= TAG technical note; no. 10 ). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and World Bank URL [Accessed: 01.06.2010]Eco-Sanitation from waste to resource
A PDF presentation describing the sanitation approach (rainwater harvesting, twin-pit pour-flush toilets, ecosan toilets) in Karnataka, India.
UNKNOWN (n.y): Eco-Sanitation from waste to resource. URL [Accessed: 02.08.2010]Selected Ecosan Technology Components
This PowerPoint presentation (in pdf format) gives an overview on different ecosan hardware including urine-diversion twin-pit pour-flush toilets; double-vault urine-diversion dehydration toilets; single-vault urine-diversion dehydration toilets; composting toilets; toilet-linked biogas systems; decentralized wastewater treatment systems; constructed wetlands; vermin-composting; rainwater harvesting.
WAFLER (2006): Selected Ecosan Technology Components. (= Ecosan Expert Training Course “Capacity Building for Ecological Sanitation in Bhutan ). Vienna: seecon international gmbh