المُلخص التنفيذي
يعد الافتقار الي مياه الشرب الاَمنة بالاضافة الى عدم وجود المرافق الصحية والنظافة الكافية هم السبب الرئيسى لزيادة عدد الوفيات الناجمة عن أمراض الاسهال الى 1.8 مليون نسمة سنوياً. ويعد توفير المياه الصالحة للشرب من خلال المعالجة المركزية في البلدان النامية هي صعبة للغاية. أنظمة التوزيع تحتاج الى عمليات التشغيل والصيانة المستمرة وقد يحصل تلوث مياه الشرب أثناء التوزيع او التداول في المنزل فى كثير من الاحيان . ولذلك فان المعالجة لمياه الشرب على مستوى المنزل عن طريق استخدام طرق بسيطة و فعالة وتنقية المياه المنزلية والتخزين الآمن (HWTS) مع خيارات مثل الغليان، والترشيح، والمعالجة بالكلور وتعقيم المياه بالطاقة الشمسية SODIS يمكنه أن يقلل إلى حد كبير من حالات الأمراض التي تنقلها المياه.
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
المياة العذبة |
مياه الشرب |
حماية مصدر المياه
المخاطر التي قد تهدد نوعية مياه الشرب عند مصدرها أو نقطة جمعها تشمل: سوء اختيار الموقع أو ضعف الحماية؛ ضعف البناء والانشاءات وتدهور أو تهالك البنية التحتية . وانعدام المعرفة الخاصة بامور النظافة والصرف الصحي في المجتمع. الإجراءات التي يمكن اتخاذها على مستوى المجتمع المحلي للقضاء على هذه المخاطر تشمل ما يلي: تنظيف المنطقة حول مصدر المياه بشكل منتظم. نقل المراحيض بعيدا عن مجرى النهر ومصادر المياه؛ بناء الاسوار لمنع الحيوانات من الدخول في مصادر المياه المفتوحة. تبطين الآبار لمنع المياه السطحية من تلويث المياه الجوفية. بناء المجارى السليمة لمياه الصرف الصحي حول الصنابير والآبار.
الترسيب
الترسيب هو عملية المعالجة الفيزيائية المستخدمة للحد من عكارة الماء .المواد العالقة في الماء انظر الترسيب، مثل الجسيمات من الرمال والطين، ومواد أخرى يمكن إزالتها بشكل كبير ببساطة عن طريق ترسيب الماء. ويمكن القيام بذلك عن طريق استخدام مستودع أو خزان طبيعي، بركة ترسيب، أو خزان كبير.
يمكن تسريع عملية الترسيب من خلال استخدام مواد التخثير والتنديف. هذه المواد طبيعية (مثل المورينجا) واصطناعية (مثل منقي المياه، الشبة ) المواد الكيميائية التي تؤدي إلى تغيير الشحنات الكهربائية للمواد العالقة. وهذا يسمح للجزيئات للانضمام معا، وبالتالي زيادة كتلتها بحيث تترسب في قاع الإناء. و غالبا ما تلتصق البكتيريا والفيروسات على أسطح الجسيمات، ولذلك فإزالة الجسيمات من خلال الترسيب سوف يخفض بشكل ملحوظ تركيزات البكتيريا.
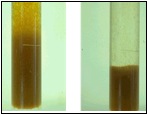
الترسيب وحده يمكنه إزالة كمية كبيرة من مسببات العكارة. المصدر: CAWST
الترشيح
يستخدم الترشيح عادة بعد الترسيب لازالة العكارة و مسببات الأمراض. الترشيح هو عملية فيزيائية تتضمن مرور المياه من خلال وسط ترشيح . تزيل المرشحات مسببات الأمراض بعدة طرق. وتشمل هذه التصفية، حيث الجسيمات أو مسببات الأمراض الكبيرة مثل الديدان تصبح محجوزة في الفراغات الصغيرة بين حبيبات وسط الترشيح ; الامتزاز، حيث تلتصق مسببات الأمراض في وسط المرشح. أو العمليات البيولوجية، حيث تموت مسببات الأمراض طبيعيا أو الكائنات الحية الدقيقة التي تعيش في المرشح تلتهم وتستهلك مسببات الأمراض.
هناك أنواع مختلفة من المرشحات التي يتم استخدامها في المنزل جميع أنحاء العالم بما في ذلك المرشحات النسيجية ( مرشحات القماش) ; المرشحات الرمل الحيوية ; مرشحات الرمل الحيوية المحسنة لازالة الزرنيخ , مرشحات السيراميك-مرشحات الشمعة ; مرشحات الفضة الغروية , مرشحات الأغشية ( مثال مرشحات سيليلوز القش) . المرشحات الرملية والمرشحات سيراميك هي الاكثر شيوعا كاوسط للترشيح , وبالرغم من ذلك فان المرشحات النسيجية تستخدم أيضا في كثير من الأحيان.
التطهير والبسترة
يعرف التطهير بانه تدميرالجدار الخلوى لخلايا الكائنات الدقيقة بالأكسدة . والتطهير يشمل إضافة المواد الكيميائية مثل الكلور. كما يمكن عمل التطهيربالأشعة فوق البنفسجية، مثل ضوء الشمس الطبيعي أو الأشعة فوق البنفسجية الاصطناعية.
الطرق الأكثر شيوعا المستخدمة من قبل المنشأت المنزلية في جميع أنحاء العالم لتطهير مياه الشرب
• التطهير بالكلور .
• التطهير باستخدام الطاقة الشمسية (SODIS).
يمكن للحرارة أيضا قتل الكائنات الحية الدقيقة وتسمى هذه العملية البسترة. البسترة لها تقريبا نفس تأثير التطهير. الأساليب الأكثر شيوعا لتطهير المياه بالبسترة هى :
• الغليان
• التعقيم الشمسي أو البسترة الشمسية
العكارة المرتفعة تساعد الكائنات الحية الدقيقة لتختبيء من مواد التطهير الكيميائية وتختبيء من الاشعة فوق البنفسجية الطبيعية والاصطناعية ولذللك خفض العكارة بالترسيب والترشيح قبل المعالجة بالتطهير ضروري لتحسين فعالية طرق التطهير سابقة الذكر.
إذا كان الماء يحتوي على كميات عالية من المواد العضوية (على سبيل المثال المياه السطحية في المناطق الاستوائية)، هناك خطر من تكون منتجات التطهير السامة عندما يتفاعل الكلور مع هذه المواد العضوية.
التخزين الأمن
الاسر المنزلية تبذل الكثير من العمل لجمع ونقل ومعالجة مياه الشرب الخاصة بها.ليصبح الماء اَمن للشرب فانه يجب تخزينه وتداوله بصورة صحيحة للحفاظ عليه امناً.لو تم تخزين المياه بصورة غير امنة فان نوعية المياه المعالجة سوف تصبح اسوأ من مياه المصدر ويمكن أن يتسبب ذلك فى الاصابة بالامراض .
التخزين الآمن يعني الحفاظ على المياه المعالجة بعيدا عن مصادر التلوث، واستخدام وعاء نظيف ومغطي. وهذا يعني أيضا استعمال حاويات مياه الشرب بطريقة ما لا تنقل العدوى من شخص لاخر. يجب استخدام اوعية للماء لا تسمح للأيدي ، والكؤوس من لمس الماء، حتى لا يصير الماء ملوثا مرة اخري.
هناك العديد من التصاميم لخزانات المياه في جميع أنحاء العالم. وينبغي أن يشمل وعاء التخزين الآمنة الصفات التالية:
• غطاء قوي ومحكم أو وسيلة تغطية
• الصنبور أو فتحة ضيقة لخروج الماء
• قاعدة مستقرة حتى لا تنقلب
• دائمة وقوية
• لا ينبغي أن تكون شفافة (النظر من خلالها)
• سهلة التنظيف
وفيما يتعلق التخزين الآمن للمياه فان التطهير بالكلور لديه ميزة على غيرها من الطرق، كما الكلور المتبقى ( يبقي الاثر التطهيري فترة بعد التطهير لوجود الكلور المتبقي في الماء).
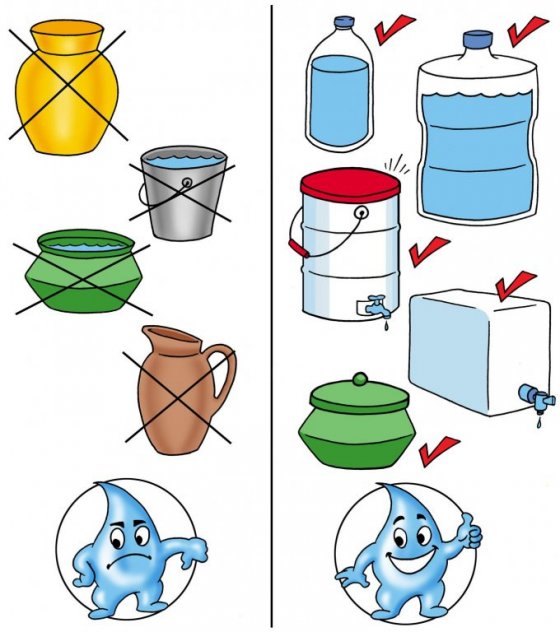
حاويات التخزين آمن للمياه المعالجة CAWST (2009)
الخلفية
اليوم أكثر من مليار شخص لا يزالون يفتقرون إلى مياه الشرب الاَمنة. وتشكل الأمراض التي تنقلها المياه الناجمة عن استهلاك مياه الشرب غير الاَمنة عبئا صحيا كبيرا في معظم البلدان النامية في العالم. ويودى نقص المياه الصالحة للشرب الى استمرار الفقر. وتعد المياه الصالحة للشرب والصرف الصحي الاَمن ضروية للصحة الجسدية والفكرية والانشطة الاجتماعية والاقتصادية والتنمية.
غالبا ما تُهمل جودة مياه الشرب التى يتم توريدها حتى لو تمت زيادة إمدادات المياه بشكل كبير. ومع ذلك، من المرجح ان تكون مياه الشرب التي توفرها نظم المعالجة المركزية ملوثة بسبب تهالك شبكات التوزيع وسواء ادارة الامداد بطريقة غير صحية قبل الاستهلاك.
لمعالجة المياه على مستوى المنزل لضمان الجودة الميكروبية (والكيميائية) جنبا إلى جنب مع التخزين الاَمن المياه والممارسات الصحية السليمة.ويمكن أن تسهم بشكل كبير في تحقيق الأهداف الإنمائية للألفية. فمن الممكن ان تققل تنقية المياه المنزلية والتخزين الآمن (HWTS) من أمراض الإسهال بنسبة 39٪. المنظمة الصحة العالمية (WHO 2007a).
وطبقا لمنظمة الصحة العالمية فان المعالجة المنزلية والتخزين الاَمن :
• يمكن ان تعمل بشكل كبير على تحسين نوعية المياه الميكروبية .
• يقلل بشكل ملحوظ الإسهال.
• هو من بين الأكثر فعالية لتدخلات المياه والصرف الصحي والصحة
• طريقة فعالة للغاية اقتصادياً
• ويمكن نشرها بسرعة وتناولها من قبل السكان المعرضين الخطر.
خطوات المعالجة المنزلية والتخزين الاَمن
هو منهج متعدد المراحل وهناك العديد الخطوات التي تسهم جميعها فى المعالجة والتخزين الاَمن (مقتبس من CAWST 2009):
_large.jpg)
الخطوات الخمس للنهج متعدد المراحل من HWTS
استخدام منهج متعدد المراحل هو أفضل وسيلة للحد من مخاطر شرب المياه غير اَمنة. نحن بحاجة لمتابعة العملية ( مراحل وخطوات المعالجة ) وليس فقط الاعتماد على تقنية واحدة لتحسين نوعية المياه. كلا من المجتمع وانظمة معالجة المياه المنزلية تتبع نفس مراحل المعالجة للمياه. والفرق الوحيد هو في حجم النظم التي تستخدم من قبل المجتمعات المحلية مقارنة بالمنازل.
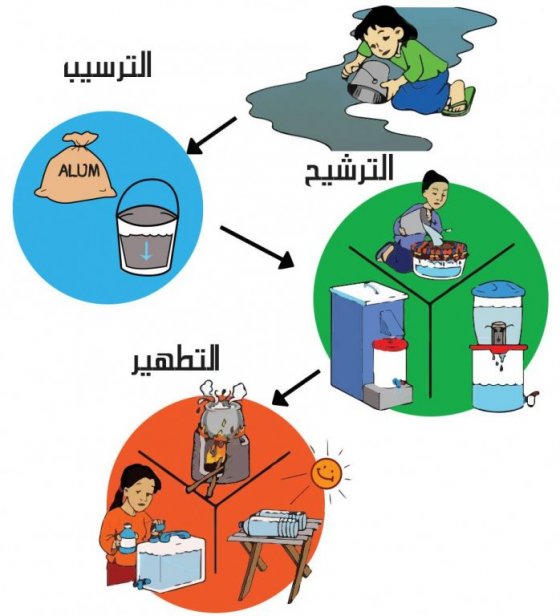
المنهج متعدد المراحل من HWTS يساهم في وقف التلوث الميكروبي، وبالتالي يقلل من المخاطر الصحية المرتبطة بالأمراض المنقولة عن طريق المياه. (CAWST 2008).
معالجة المياه المنزلية والتخزين الآمن (HWTS) هو ملائم بصورة خاصة في الأماكن التي يستخدم فيها الناس مصادر ملوثة لمياه الشرب مع الثقة باحتمالية تلوث نظم امدادات المياه المركزية . HWTSهو ايضا ملائم للمجتمعات الحضرية الفقيرة مثل الاحياء الفقيرة حيث من المرجح جدا استخدامهم لمصادر مياه غير محمية.
Combating Waterborne Diseases at the Household Level
This document is divided into three main parts. The first part contains an introduction to the topic and depicts some possible, simple techniques for treating water at the household level. The second part describes the possibility of collaborating to fight against waterborne diseases and the last part presents again some low-cost solutions.
WHO (2007): Combating Waterborne Diseases at the Household Level. The International Network to Promote Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage. Geneva: World Health Organisation (WHO) URL [Accessed: 11.10.2010]An Introduction to Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage, A CAWST Training Manual
This training manual describes the need of safe drinking water and sanitation and provides relevant information on HWTS process, technologies. It is good reference material for trainers to conduct training on HWTS.
CAWST (2009): An Introduction to Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage, A CAWST Training Manual. Calgary: Centre for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST) URL [Accessed: 13.05.2019]Water Hygiene Sanitation Poster Presentation
Water, Hygiene and Sanitation Posters - The presentation includes 30 posters with key messages and questions on water, hygiene and sanitation. They are adapted for different regions including: Africa, Latin America, South Asia, Southeast Asia; and are available in multiple languages.
CAWST (2008): Water Hygiene Sanitation Poster Presentation. Alberta: Center for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST) URL [Accessed: 20.05.2019]حفظ الماء عبر التخزين الآمن في المباني.أكبر علي. بلدية دبي. حكومة دبي مجلة تصدر عن مركز البيئة للمدن العربية.العدد الثاني مايو 2012
Language: Arabic
ﺩﻻﺌل ﺠﻭﺩﺓ ﻤﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺸﺭﺏ.جينيف.سويسرا
ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﺧﻄﺔ ﺳﻼﻣﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﺎﻩ. ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﻣﻔﺼﻞ ﻹﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺎﻃﺮ ﻟﻤﻘﺪﻣﻲ ﻣﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺸﺮﺏ.جينف:منظمة الصحة العالمية.
يهدف هذا الدليل إلى تقديم الإرشاد العملي، لتسهيل تطوير خطة سلامة المياه، مع التركيز على إمدادات المياه المنظمة التي تديرها منشأة مياه أو ما شابه.
منظمة الصحة العالمية,الإتحاد الدولي للمياه (2009): ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﺧﻄﺔ ﺳﻼﻣﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﺎﻩ. ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﻣﻔﺼﻞ ﻹﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺎﻃﺮ ﻟﻤﻘﺪﻣﻲ ﻣﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺸﺮﺏ.جينف:منظمة الصحة العالمية.. URL [Accessed: 26.08.2017]Language: Arabic
لائحة الاشتراطات الصحية الواجب توافرها في خزانات مياه الشرب، المملكة العربية السعودية
Language: Arabic
محاكاة الأساليب القديمة في تخزين المياه السطحية في المناطق الجافة :أمثلة من سورية والسعودية، المؤتمر الدولي الثاني للموارد المائية والبيئة الجافة
Language: Arabic
دليل تطهير مياه الشرب في حالات الطوارئ.ﺍﻟﻤﻜﺘﺐ ﺍﻹﻗﻠﻴﻤﻲ ﻟﺸﺮﻕ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻮﺳﻂ
هو دليل يوضح تطهير مياه الشرب في حالات الطوارئ يتناول الأساليب والطرق.
منظمة الصحة العالمية (2004): دليل تطهير مياه الشرب في حالات الطوارئ.ﺍﻟﻤﻜﺘﺐ ﺍﻹﻗﻠﻴﻤﻲ ﻟﺸﺮﻕ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻮﺳﻂ. URL [Accessed: 26.08.2017]Managing Water in the Home: Accelerated Health Gains from Improved Water Supply
This report has critically reviewed various HWT technologies on the basis of technical, social and economical factors and gives a good overview for an informed choice.
WHO (2002): Managing Water in the Home: Accelerated Health Gains from Improved Water Supply. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) URL [Accessed: 13.05.2019]Household water treatment 1
This Technical Brief is the first of two examining the treatment of water in the home. The subject is introduced, and treatment by straining, storage, settlement, solar disinfection, chemical disinfection, and boiling are covered.
SKINNER, B. SHAW, R. (1999): Household water treatment 1. London & Loughborough: Water And Environmental Health at London and Loughborough (Well). Technical Brief 58 URL [Accessed: 20.05.2019]Household water treatment 2
This Technical Brief is the second of two which examine the treatment of water at household level. It considers treatment by coagulation, flocculation, filtration and solar distillation and covers aspects of the reduction of some chemical concentrations.
SKINNER, B. SHAW, R. (1999): Household water treatment 2. London & Loughborough: Water And Environmental Health at London and Loughborough (Well). Technical brief 59 URL [Accessed: 20.05.2019]Combating Waterborne Diseases at the Household Level
This document is divided into three main parts. The first part contains an introduction to the topic and depicts some possible, simple techniques for treating water at the household level. The second part describes the possibility of collaborating to fight against waterborne diseases and the last part presents again some low-cost solutions.
WHO (2007): Combating Waterborne Diseases at the Household Level. The International Network to Promote Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage. Geneva: World Health Organisation (WHO) URL [Accessed: 11.10.2010]Scaling Up Household Water Treatment Among Low-Income Populations
This report examines the evidence to date regarding the scalability of HWTS. It seeks to consolidate existing knowledge and experience and distil the lessons learnt. Its primary aims are to 1) review the development and evolution of leading household water treatment technologies in their efforts to achieve scale, 2) identify the main constraints that they have encountered and 3) recommend ways forward.
CLASEN, T.D. (2009): Scaling Up Household Water Treatment Among Low-Income Populations. (PhD Thesis). Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) URL [Accessed: 09.04.2010]Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Options in Developing Countries. Review of Current Implementation Practices
Summary and brief evaluation of main household water treatment and safe storage (HWTS) options for developing countries. Options described are: chlorination, biosand filtration, ceramic filtration, solar disinfection, filtration and chlorination, flocculation and chlorination.
LANTAGNE, D. S. QUICK, R. MINTZ, E.D. (2006): Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Options in Developing Countries. Review of Current Implementation Practices. المُدخلات: ECSP (2006): Water Stories: Expanding Opportunities in small-scale Water and Sanitation Projects. Washington D.C.: 17-38. URL [Accessed: 20.05.2019]Implementation, Critical Factors and Challenges to Scale-Up of Household Drinking Water Treatment and Safe Storage Systems
This paper explores the current status of the adoption and sustained use of household drinking water treatment and safe storage systems, the critical factors that influence adoption and sustained use and the associated challenges to scale-up.
MURCOTT, S. (2006): Implementation, Critical Factors and Challenges to Scale-Up of Household Drinking Water Treatment and Safe Storage Systems. Background Paper on Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage (HWTS) for the Electronic Conference . USAID / Hygiene Improvement Project (HIP) URL [Accessed: 26.02.2010]Smart Disinfection Solutions
This booklet, part of the Smart Water Solutions series provides a wide range of methods and products for home water treatment in rural areas.
NWP (2010): Smart Disinfection Solutions. Examples of small-scale disinfection products for safe drinking water. (= Smart water solutions ). Amsterdam: KIT Publishers URL [Accessed: 17.05.2019]Small Community Water Supplies: Technology, People and Partnership: Desalination Technology - Chapter 18
This book provides a general introduction to a wide range of technologies. Among the topics covered are: planning and management of small water supplies, community water supplies in Central and Eastern European countries, water quality and quantity, integrated water resources management, artificial recharge, rainwater harvesting, spring water tapping, groundwater withdrawal, water lifting, surface water intake, water treatment, aeration, coagulation and flocculation, sedimentation, multi-stage filtration, desalination technology, disinfection, household level water treatment, technologies for arsenic and iron removal from ground water, and emergency and disaster water supply. Chapter 18: Desanilation Technology
SMET, J. ; WIJK, C. van (2002): Small Community Water Supplies: Technology, People and Partnership: Desalination Technology - Chapter 18. The Hague: International Water and Sanitation Centre (IRC) URL [Accessed: 20.05.2019]Drinking Water: Equity, Safety and Sustainability
The report investigates access to and use of drinking water in greater detail than is possible in the regular JMP progress reports, and includes increased disaggregation of water service levels and analyses of trends across countries and regions. It focuses on the three key challenges of equity, safety and sustainability.
UNICEF ; WHO (2011): Drinking Water: Equity, Safety and Sustainability. New York and Geneva: United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) and World Health Organization (WHO) URL [Accessed: 13.05.2019]A Bibliography on Point-of-Use Water Disinfection. Environmental Health
This is a compilation of various HWTS studies, research, case studies and technologies with useful links.
USAID and CDC/Safewater (2006): A Bibliography on Point-of-Use Water Disinfection. Environmental Health . Washington and Atlanta: United States Agency for International Development (USAID) and Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) URL [Accessed: 20.05.2019]A Bibliography of Selected Articles on Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage
This bibliography contains citations and abstracts to 24 journal articles on Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage (HWTS) compiled by USAID in 2009. The bibliography is continuously updated.
USAID (2009): A Bibliography of Selected Articles on Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage. Washington: United States Agency for International Development (USAID) URL [Accessed: 26.02.2010]Access and Behavioural Outcome Indicators for Water, Sanitation and Hygiene
This manual aims to help program planners, managers, and evaluators to design, implement, and evaluate WASH interventions. It is intended for use either in programmes and projects with a principal focus on WASH or with a broad child health agenda.
USAID (2010): Access and Behavioural Outcome Indicators for Water, Sanitation and Hygiene. New York: United States Agency for International Development (USAID), Hygiene Improvement Project URL [Accessed: 09.04.2010]Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, Fourth Edition
This volume of the Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality explains requirements to ensure drinking-water safety, including minimum procedures and specific guideline values, and how those requirements are intended to be used. The volume also describes the approaches used in deriving the guidelines, including guideline values. It includes fact sheets on significant microbial and chemical hazards.
WHO (EDITOR) (2011): Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, Fourth Edition. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) URL [Accessed: 11.07.2018]Evaluating Household Water Treatment Options
Household water treatment (HWT) interventions may play an important role in protecting public health where existing water sources, including those delivered via a piped network or other improved sources, are untreated, are not treated properly or become contaminated during distribution or storage. Properly formulated and locally relevant performance specifications are needed to protect users and inform decision-making regarding selection of technologies or approaches. This document provides a basis by which to evaluate the microbiological performance of HWT options.
WHO (2011): Evaluating Household Water Treatment Options. Health-based Targets and Microbiological Performance Specifications. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) URL [Accessed: 20.04.2018]Toolkit for monitoring and evaluating household water treatment and safe storage
In order to develop effective mechanisms to encourage and sustain correct use of household water treatment and safe storage (HWTS), there is a need to monitor and evaluate uptake. The Toolkit provides an overall framework for this. One of the key features is the presentation of 20 harmonized, global indicators to assess correct and consistent use of household water treatment and safe storage by those most at risk.
WHO ; UNICEF (2012): Toolkit for monitoring and evaluating household water treatment and safe storage. Geneva: World Health Organization URL [Accessed: 08.11.2012]Conservation et Traitement de l Eau a Domicile
This practical guide provides a review of different processing techniques and adequate water conservation at home and is structured around 10 key questions that should be posed before choosing a suitable solution.
DESILLE, D. (2013): Conservation et Traitement de l Eau a Domicile. Paris: Programme Solidarite Eau (PSeau) URL [Accessed: 06.06.2013]Combined Household Water Treatment and Indoor Air Pollution Projects in Urban Mambanda, Cameroon and Rural Nyanza, Kenya
Globally, the burden of ill‐health in Africa due to unsafe drinkingwater, inadequate sanitation and polluted indoor air stands out prominently. This report explores the possibilities, advantages and implications of integrating interventions on indoor pollution and household water treatment.
SHAHEED, A. BRUCE, N. (2011): Combined Household Water Treatment and Indoor Air Pollution Projects in Urban Mambanda, Cameroon and Rural Nyanza, Kenya. (= Report of a Mission to Mambanda, Cameroon and Nyanza, Kenya, 2009 ). Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) URL [Accessed: 20.05.2019]Quality of Drinking Water at Source and Point of Consumption - Drinking Cup as a High Potential Recontamination Risk
This paper identifies the critical points of drinking water contamination and also determines the extent of recontamination after treating water by using HWTS. It also highlights the need of integrating messages on sanitation and hygiene practices during the promotion of HWTS at community.
RUFENER, S. ; MAUSEZAHL, D. ; MOSLER, H. J. ; WEINGARTNER, R. (2010): Quality of Drinking Water at Source and Point of Consumption - Drinking Cup as a High Potential Recontamination Risk. A Field Study in Bolivia. المُدخلات: The Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition: Volume 28 , 34-41. URL [Accessed: 20.05.2019]Not Just a Drop in the Bucket: Expanding Access to Point-of-Use Water Treatment Systems
This review paper summarizes the problem of household water treatment and discusses chlorination, solar disinfection, and safe storage as household water treatment options.
MINTZ, E. ; BARTRAM, J. ; LOCHERY, P. ; WEGELIN, M. (2001): Not Just a Drop in the Bucket: Expanding Access to Point-of-Use Water Treatment Systems. المُدخلات: American Journal of Public Health: Volume 91 , 1565-1570. URL [Accessed: 20.05.2019]Bringing the Consumer to the Table: Perceptions and Practice of Household Water Treatment Methods in Nepal
This factsheet provides information on point-of-use product trials conducted for four HWT options (boiling, chlorination, colloidal silver filter, and SODIS) in Nepal.
USAID (2006): Bringing the Consumer to the Table: Perceptions and Practice of Household Water Treatment Methods in Nepal . (= Research Brief ). Washington: United States Agency for International Development (USAID) URL [Accessed: 09.04.2010]Promotion of household water treatment and safe storage in UNICEF WASH programmes
Short introduction to household water treatment and the main treatment methods.
UNICEF (2008): Promotion of household water treatment and safe storage in UNICEF WASH programmes. pdf presentation. New York: United Nations Children's Fund URL [Accessed: 17.03.2010]Nudging to Use
This paper presents results from two complementary field experiments conducted in rural western Kenya and the urban slums of Dhaka, Bangladesh. In both settings, participating households received free trials with a variety of point of use products as well as repeated educational messages about the importance of safe drinking water and its link with diarrheal illness.
LUOTO, J. LEVINE, D. ALBERT, J. LUBY, S. (2013): Nudging to Use. Achieving Safe Water Behaviors in Kenya and Bangladesh. Berkeley: Center for Effective Global Action URL [Accessed: 07.08.2013]Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Fact Sheets - Academic
Factsheet compilation on the principles, construction, operation and maintenance of HWTS options.
CAWST (2009): Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Fact Sheets - Academic. Alberta: Center for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST) URL [Accessed: 20.05.2019]Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Fact Sheets - Simplified
Factsheet compilation on the principles, construction, operation and maintenance of HWTS options (simplified version).
CAWST (2009): Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Fact Sheets - Simplified. Alberta: Center for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST) URL [Accessed: 20.05.2019]UNICEF Handbook on Water Quality
This handbook is a comprehensive a new tool to help UNICEF WASH field professionals, but it will also be useful to other UNICEF staff and for partners in government, other external support agencies, NGOs and civil society. The handbook provides an introduction to all aspects of water quality, with a particular focus on the areas most relevant to professionals working in developing countries. It covers the effects of poor water quality, quality monitoring, the protection of water supplies, methods for improving water quality, and building awareness and capacity related to water quality.
UNICEF (2008): UNICEF Handbook on Water Quality. New York: United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) URL [Accessed: 19.05.2019]An Introduction to Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage, A CAWST Training Manual
This training manual describes the need of safe drinking water and sanitation and provides relevant information on HWTS process, technologies. It is good reference material for trainers to conduct training on HWTS.
CAWST (2009): An Introduction to Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage, A CAWST Training Manual. Calgary: Centre for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST) URL [Accessed: 13.05.2019]Course Outline for Introduction to HWTS workshop
This document provides the course outline to conduct two to three-days training for an introduction to HWTS.
CAWST (2009): Course Outline for Introduction to HWTS workshop. Alberta: Center for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST). [Accessed: 27.03.2010] PDFHousehold Water Treatment and Safe Storage (HWTS). Lecture Notes
Lecture notes on the technical and non-technical aspects of sanitation household-level drinking water treatment and safe storage (HWTS) in developing countries.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage (HWTS). Lecture Notes. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 3 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 08.04.2010]Amoeba and Water
This children’s book provides information on safe drinking water, ways of water contamination, simple HWTS options presented in attractive illustrations and simple languages so that school children can easily understand them.
ENPHO (2007): Amoeba and Water. Kathmandu and New York: Environment and Public Health Organization (ENPHO) and United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) URL [Accessed: 19.05.2019]Household water treatment and safe storage in emergencies
This document is intended as a general manual on household water treatment and storage in emergencies. Methods of treatment but also promotion are presented, including factsheets, a decision tree and very comprehensive illustrations.
IFRC (2008): Household water treatment and safe storage in emergencies. pdf presentation. Geneva: International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) URL [Accessed: 23.04.2012]Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Following Emergencies and Disasters
A six-pages compilation about what to do in emergency situations. Designated to the South Asia earthquake and tsunami.
WHO (n.y): Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Following Emergencies and Disasters. pdf presentation. Geneva: World Health Organisation (WHO) URL [Accessed: 17.05.2019]Flip Chart on HWTS
HWTS training guideline
This training manual provides information on various household drinking water treatment options. Each description contains an introduction to the technology, its working mechanism, costs, advantages and limitations (Nepali).
DWSS (2008): HWTS training guideline. Nepal: Department of Water Supply and Sewerage (DWSS)Water Hygiene Sanitation Poster Presentation
Water, Hygiene and Sanitation Posters - The presentation includes 30 posters with key messages and questions on water, hygiene and sanitation. They are adapted for different regions including: Africa, Latin America, South Asia, Southeast Asia; and are available in multiple languages.
CAWST (2008): Water Hygiene Sanitation Poster Presentation. Alberta: Center for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST) URL [Accessed: 20.05.2019]Combating Waterborne Diseases at the Household Level
This document is divided into three main parts. The first part contains an introduction to the topic and depicts some possible, simple techniques for treating water at the household level. The second part describes the possibility of collaborating to fight against waterborne diseases and the last part presents again some low-cost solutions.
WHO (2007): Combating Waterborne Diseases at the Household Level. The International Network to Promote Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage. Geneva: World Health Organisation (WHO) URL [Accessed: 11.10.2010]Preventing Diarrhoeal Disease in Developing Countries: Proven Household Water Treatment Options
One-page introduction to main household water treatments methods, and further reading links.
CDC/USAID (2008): Preventing Diarrhoeal Disease in Developing Countries: Proven Household Water Treatment Options. Atlanta and New York: Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and United States Agency for International Development (USAID) URL [Accessed: 15.03.2010]HWTS factsheets
Compilation of factsheets on water quality in general and description of different HWTS options such as chlorination, colloidal silver filters, biosand filter, chlorination and SODIS.
DWSS (2007): HWTS factsheets. Department of Water Supply and Sewerage (DWSS) Nepal, United States Agency for International Development (USAID), United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-HABITAT), United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF)HWTS Brochure (Nepali)
HWTS Posters (Nepali)
HWTS Comic Posters (Nepali)
HWTS Materials Users Guide
Household water treatment and safe storage
This link provides information on HWTS (background information, technical information, further weblinks etc.) and the WHO network to promote HWTS worldwide.
CAWST and the HWTS Knowledge Base
The homepage of the centre for affordable water and sanitation technology (CAWST) provides general description of sustainable drinking water treatment technologies and water, sanitation and hygiene issues. The publications section can provide you with important information. The profound HWTS knowledge base (https://www.hwts.info/) on Point-of-use water treatment solutions includes technology options to the implementation of best practices.
The Hygiene Improvement Project (HIP)
This website contains publications and resources developed under USAID-funded Hygiene Improvement Project (HIP). Various case studies, publications and training material are available.
Household Water Treatment & Safe Water Storage
This website provides useful information and factsheets on HWTS.
A glass full of water: Point-of-use solutions
A glass full of water: Point-of-use solutions. This video shows the four proven HWTS versus chlorination, biosand filters, ceramic filters and SODIS.
Household Water Treatment & Safe Water Storage
This website provides useful information and factsheets on HWTS.
