Executive Summary
The recipients of business plans want to understand how the entrepreneur is planning to achieve the set objectives. Therefore, an action plan is created to set the required short-term activities. A clear picture of the company’s starting position serves as the basis for setting business objectives in accordance with the SMART characteristics. Tasks have to be described, analysed and visualised in an adequate manner. Resources have to be planned for and possible risks have to be assessed. In the end, the tasks have to be executed and followed-up upon, possible adaptations to the original action plan might have to be made.
Introduction
The recipients of business plans want to understand how the entrepreneur is planning to achieve the set objectives. Therefore, an action plan, also called operational plan or tactical plan, is created to set short to long-term activities required in achieving the objectives of the strategic planning (SMALLBIZCONNECT NO YEAR). First of all, a company has to have a clear picture of where it stands. A SWOT analysis is a common tool to create such a picture and is described in more detail in Strategic Management. In a next step, the business objectives have to be set in order to describe where the company wants to be in the future. Then, at the heart of the action plan, the tasks are described and resources as well as risks are identified in order to show how the company is aiming to achieve these objectives (how to assess risks is described in more detail in Risk Management). In the end, the tasks have to be executed and followed-up upon, possible adaptations to the original action plan might have to be made.
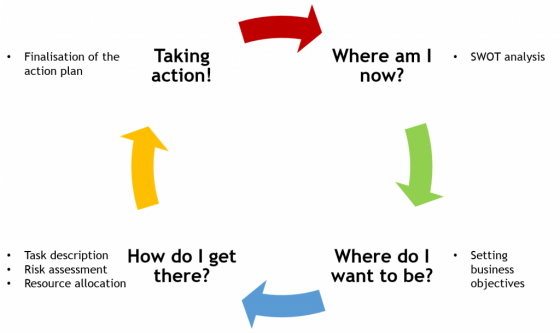
Steps of an Action Plan. Source: Own illustration
Setting Business Objectives
“Business Objectives are specific targets of performance that a business seeks to accomplish” (ZIMMERER & SCARBOROUGH 2011).
Business objectives are the link between the strategic plan and the action plan. Without business objectives it is not possible to know where a business is going or how well it is performing. They show what the entrepreneur wants to achieve and are maintain throughout the operation and growth of the business. Having a comprehensive list of business objectives gives you a foundation for your action plan.
Business objectives should be written in accordance to the SMART characteristics (ZIMMERER & SCARBOROUGH 2011):
- Specific: Business objectives should be quantifiable and precise, spelling out exactly what the management wants to achieve.
- Measurable: They should be well defined reference points from which to start and a scale for measuring progress.
- Assignable: Unless the responsibility of achieving an objective is assigned to an individual it will never be achieved.
- Realistic: Business objectives need to be challenging, but not demoralising. It should be just outside of your comfort zone.
- Timely: It should be specified when business objectives are to be accomplished.
Task Description
Tasks are the activities to be undertaken to achieve the business objectives. They are backed-up by a budget, assigned to individuals, designed in regard to the skills and expertise of the team and should be listed in chronological order under each objective.
In order to identify tasks, the business objectives are broken down in discreet steps that are necessary to achieve them (SILVERSTEIN 2009). After the tasks are identified in a brainstorming they should be prioritized. It is helpful to start with the task that can be executed immediately. Once an overview of all tasks is established, each task can be analysed in more detail. Unnecessary tasks can be dropped and bigger tasks can be broken down. End points of tasks should be identified and measurable milestones should be created. The list of tasks along the timeline should be visualised. Flowcharts, Gantt charts, spreadsheets, or some other type of business tool can be used to accomplish this.
Resource Allocation
Before putting an action plan into practice, it has to be ensured that all required resources are identified and available. For each task, costs for people, travel, internal transportation, consumables and supplies as well as subcontracted services have to be considered. It might be helpful to go back to the Gantt chart and calculate all costs in line with the action plan.
Finalisation of Action Plan
Once the action plan is formulated, shared among the team members and milestones are scheduled, it can be worked on. Daily action and follow-ups with the responsible parties ensure the compliance with action plan and its success. Occasionally, changing circumstances or unforeseen events might throw a wrench in the ability to meet the deadlines of the action plan. In order to absorb such shocks, the action plan might need a revision. Instead of getting discouraged, new deadlines shall be set to achieve the set objectives in the end (SILVERSTEIN 2009).
Create an Action Plan Now
Action Plan
Essentials of entrepreneurship and Small Business Management
http://www.tidyforms.com
This webpage provides downloadable templates for action plans.


